Question 5b (ii)
Outline the sequence of events that follows the binding of glucagon
to its membrane receptor on a liver cell. [6]
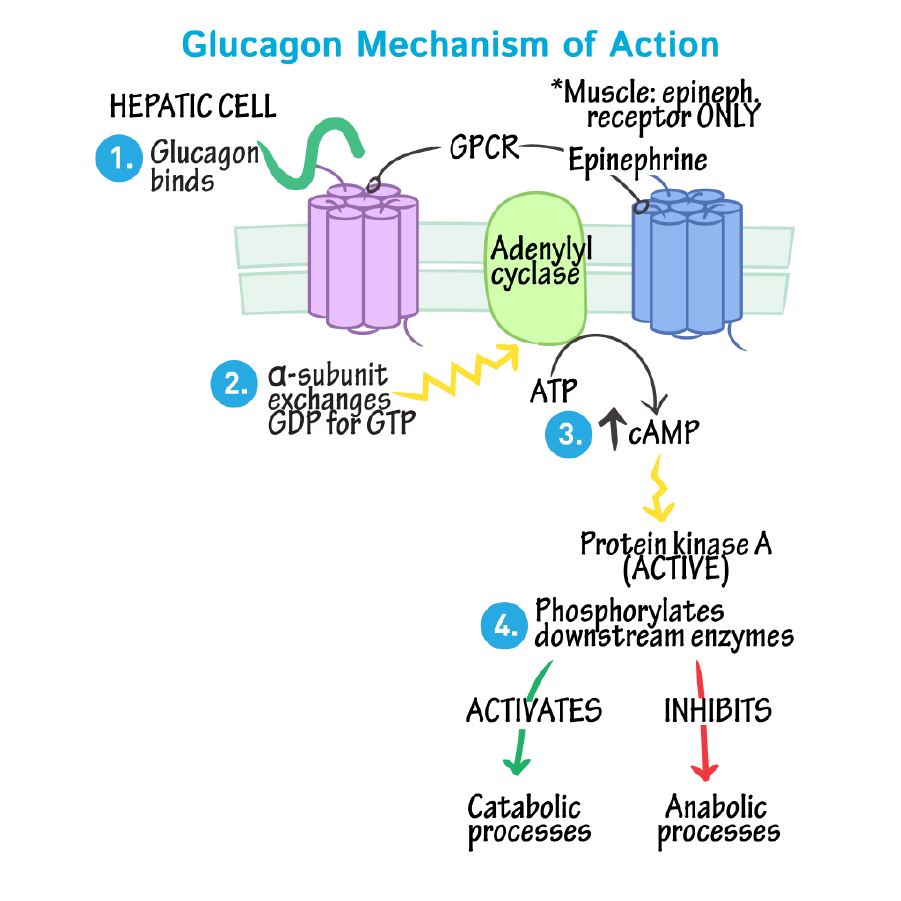
Binding of Glucagon to Receptor:
- Glucagon binds to a specific glucagon receptor on the cell membrane of liver cells.
- This receptor is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR).
- Activation of G-Protein:
- Binding of glucagon activates the G-protein associated with the receptor.
- The G-protein exchanges GDP for GTP, which activates it.
- Activation of Adenylate Cyclase:
- The activated G-protein stimulates adenylate cyclase, an enzyme embedded in the cell membrane.
- Production of Cyclic AMP (cAMP):
- Adenylate cyclase converts ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP).
- cAMP acts as a second messenger within the cell.
- Activation of Protein Kinase A (PKA):
- cAMP binds to and activates protein kinase A (PKA).
- PKA is an enzyme that triggers a cascade of reactions within the cell.
- Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis:
- PKA activates enzymes involved in glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen to glucose) and gluconeogenesis (synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources).
- This increases the release of glucose into the bloodstream, raising blood glucose levels.