03.08 Enzyme Affinities
Key Concepts
- Affinity:
- Definition: Measure of the strength of attraction between an enzyme and its substrate.
- High Affinity: Strong attraction; substrate binds easily and product forms quickly.
- Low Affinity: Weaker attraction; substrate may detach before reaction occurs, leading to a slower rate.
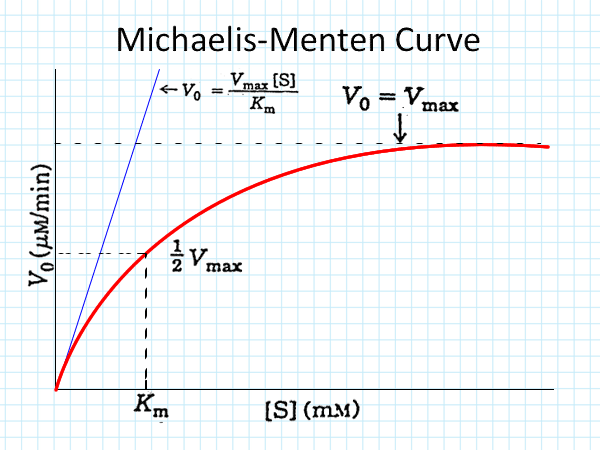
- Vmax (Maximum Velocity):
- Represents the maximum rate at which an enzyme can catalyze a reaction.
- Achieved when all active sites are occupied by substrate molecules, meaning the enzyme is fully saturated.
- Determining Vmax:
- Initial reaction rates at different substrate concentrations are plotted.
- The curve approaches but never completely flattens, reaching Vmax only theoretically.
- Km (Michaelis-Menten Constant):
- Definition: Substrate concentration at which the enzyme works at half of Vmax (½ Vmax).
- Indicator of Affinity:
- Lower Km: Higher affinity; enzyme reaches ½ Vmax at a lower substrate concentration.
- Higher Km: Lower affinity; more substrate is needed to reach ½ Vmax.
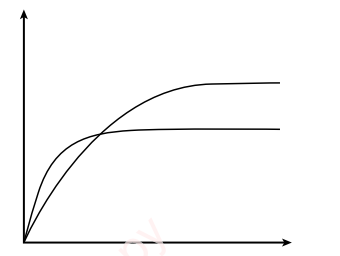
How to Determine Affinity
Plot Reaction Rate vs. Substrate Concentration:
- As substrate concentration increases, the reaction rate initially rises until reaching a plateau (Vmax).
Calculate ½ Vmax:
- Find the substrate concentration at ½ Vmax on the graph to determine Km.
Interpret Km Value:
- Lower Km values indicate higher enzyme-substrate affinity.
- Higher Km values indicate lower affinity.
Example Enzyme Affinities
| Enzyme | Substrate | Vmax (arbitrary units) | Km (µmol dm⁻³) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonic Anhydrase | Carbon dioxide | 600,000 | 8000 |
| Penicillinase | Penicillin | 2000 | 50 |
| Chymotrypsin | Protein | 100 | 5000 |
| Lysozyme | Acetylglucosamine | 0.5 | 6 |
Analysis of Table
- Fastest Enzyme:
- Carbonic Anhydrase with the highest Vmax (600,000) works the fastest, catalyzing CO₂ conversion efficiently to prevent toxic buildup.
- Highest Affinity:
- Lysozyme has the lowest Km (6 µmol dm⁻³), indicating the highest affinity for its substrate (acetylglucosamine) since it reaches ½ Vmax at a low substrate concentration.
Summary of Key Terms
- Vmax: Maximum rate when all enzyme active sites are occupied by substrate.
- Km (Michaelis-Menten Constant): Substrate concentration at ½ Vmax; a lower Km indicates higher enzyme affinity.
Example Graph Interpretation
Graph Features:
- Initial rate rises with increasing substrate concentration, eventually plateauing at Vmax.
- ½ Vmax point helps determine Km, reflecting enzyme-substrate affinity.
Question Practise
Question 1
Define the terms Vmax and Km in enzyme kinetics and explain their significance. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Vmax is the maximum rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction when all active sites are saturated with substrate. (1 mark)
- It represents the enzyme’s maximum catalytic efficiency under given conditions. (1 mark)
- Km (Michaelis-Menten Constant) is the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is ½ Vmax. (1 mark)
- A lower Km indicates a higher affinity between the enzyme and substrate, meaning the enzyme binds the substrate efficiently even at low concentrations. (1 mark)
- These values are critical for understanding enzyme efficiency and substrate affinity in biochemical processes. (1 mark)
Question 2
How does the Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) reflect enzyme affinity? Use examples from the provided table. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Km indicates the substrate concentration at which the enzyme works at ½ Vmax. (1 mark)
- A lower Km value reflects a higher affinity between enzyme and substrate. (1 mark)
- Example: Lysozyme has the lowest Km (6 µmol dm⁻³), meaning it has the highest affinity for acetylglucosamine. (1 mark)
- A higher Km indicates a lower affinity, as more substrate is needed to reach ½ Vmax. (1 mark)
- Example: Carbonic anhydrase has a higher Km (8000 µmol dm⁻³), indicating lower affinity for CO₂ compared to lysozyme’s substrate. (1 mark)
Question 3
Explain how Vmax and Km are determined from a graph of reaction rate vs. substrate concentration. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Vmax is the maximum reaction rate, represented by the plateau on the graph. (1 mark)
- It reflects the rate when all enzyme active sites are saturated with substrate. (1 mark)
- ½ Vmax is calculated by dividing the maximum rate by two. (1 mark)
- Km is the substrate concentration corresponding to ½ Vmax on the X-axis. (1 mark)
- A lower Km value indicates higher enzyme-substrate affinity. (1 mark)
- A higher Km value suggests that more substrate is needed to achieve the same rate, reflecting lower affinity. (1 mark)
Question 4
Compare the affinities of the enzymes penicillinase and chymotrypsin based on their Km values. (4 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Penicillinase has a Km of 50 µmol dm⁻³, indicating a higher affinity for penicillin. (1 mark)
- Chymotrypsin has a Km of 5000 µmol dm⁻³, showing a lower affinity for its substrate (protein). (1 mark)
- Penicillinase reaches ½ Vmax at a much lower substrate concentration than chymotrypsin. (1 mark)
- This suggests penicillinase is more efficient at binding its substrate compared to chymotrypsin. (1 mark)
Question 5
What is the relationship between Vmax and enzyme saturation? (4 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Vmax is achieved when all enzyme active sites are fully saturated with substrate. (1 mark)
- At this point, the reaction rate is limited by the enzyme’s turnover rate and not by substrate concentration. (1 mark)
- Increasing substrate concentration beyond saturation does not increase the reaction rate. (1 mark)
- Vmax reflects the enzyme’s maximum catalytic efficiency under given conditions. (1 mark)
Question 6
Describe how affinity impacts enzyme efficiency using examples of high and low Km values. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Enzymes with high affinity (low Km) bind substrates more efficiently, achieving ½ Vmax at low substrate concentrations. (1 mark)
- Example: Lysozyme (Km = 6 µmol dm⁻³) has high affinity for acetylglucosamine, making it highly efficient even with low substrate availability. (1 mark)
- Enzymes with low affinity (high Km) require higher substrate concentrations to reach ½ Vmax. (1 mark)
- Example: Carbonic anhydrase (Km = 8000 µmol dm⁻³) has low affinity for CO₂ but compensates with a very high Vmax (600,000 units). (1 mark)
- High-affinity enzymes are better suited for environments with low substrate availability. (1 mark)
Question 7
Why does the reaction rate plateau at high substrate concentrations, and how does this relate to Vmax? (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- At high substrate concentrations, all enzyme active sites are occupied, leading to enzyme saturation. (1 mark)
- The reaction rate cannot increase further because the enzyme is working at full capacity (Vmax). (1 mark)
- Additional substrate molecules must wait for active sites to become available, so they do not affect the rate. (1 mark)
- Vmax reflects this maximum reaction rate under saturating substrate conditions. (1 mark)
- The plateau illustrates that the reaction rate is now limited by enzyme concentration or turnover rate, not substrate availability. (1 mark)
Question 8
| Enzyme | Substrate | Vmax (arbitrary units) | Km (µmol dm⁻³) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonic Anhydrase | Carbon dioxide | 600,000 | 8000 |
| Penicillinase | Penicillin | 2000 | 50 |
| Chymotrypsin | Protein | 100 | 5000 |
| Lysozyme | Acetylglucosamine | 0.5 | 6 |
Using the provided table, identify the enzyme with the highest reaction rate and explain why. (3 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Carbonic anhydrase has the highest reaction rate, with a Vmax of 600,000 units. (1 mark)
- This high Vmax indicates it can catalyze reactions at an exceptionally fast rate, efficiently converting CO₂ into a less toxic form. (1 mark)
- Its high turnover rate allows rapid processing, compensating for its lower affinity (Km = 8000 µmol dm⁻³). (1 mark)
Question 9
What conclusions can be drawn about enzyme efficiency by comparing Vmax and Km values? (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Vmax indicates the maximum rate at which an enzyme can catalyze a reaction when saturated with substrate. (1 mark)
- Km reflects the substrate concentration needed to achieve ½ Vmax, indicating affinity. (1 mark)
- Enzymes with high Vmax are capable of processing large amounts of substrate quickly. (1 mark)
- Enzymes with low Km have high affinity, functioning efficiently even at low substrate concentrations. (1 mark)
- Example: Carbonic anhydrase (high Vmax) processes CO₂ quickly but has low affinity (high Km). (1 mark)
- Lysozyme (low Km) is highly efficient at binding acetylglucosamine but has a low Vmax, reflecting slower overall processing. (1 mark)
Question 10
Describe the relationship between substrate concentration, Vmax, and Km using a reaction rate graph. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- At low substrate concentrations, the reaction rate increases linearly as substrate concentration rises. (1 mark)
- As substrate concentration approaches Km, the reaction rate begins to slow, reflecting increasing enzyme saturation. (1 mark)
- At Km, the rate is ½ Vmax, showing the substrate concentration required for moderate enzyme activity. (1 mark)
- Beyond Km, the graph levels off, reaching a plateau at Vmax, where all active sites are occupied. (1 mark)
- The graph illustrates that enzyme activity depends on both substrate availability and the enzyme’s catalytic capacity. (1 mark)