P.04 Practical: Colorimeter
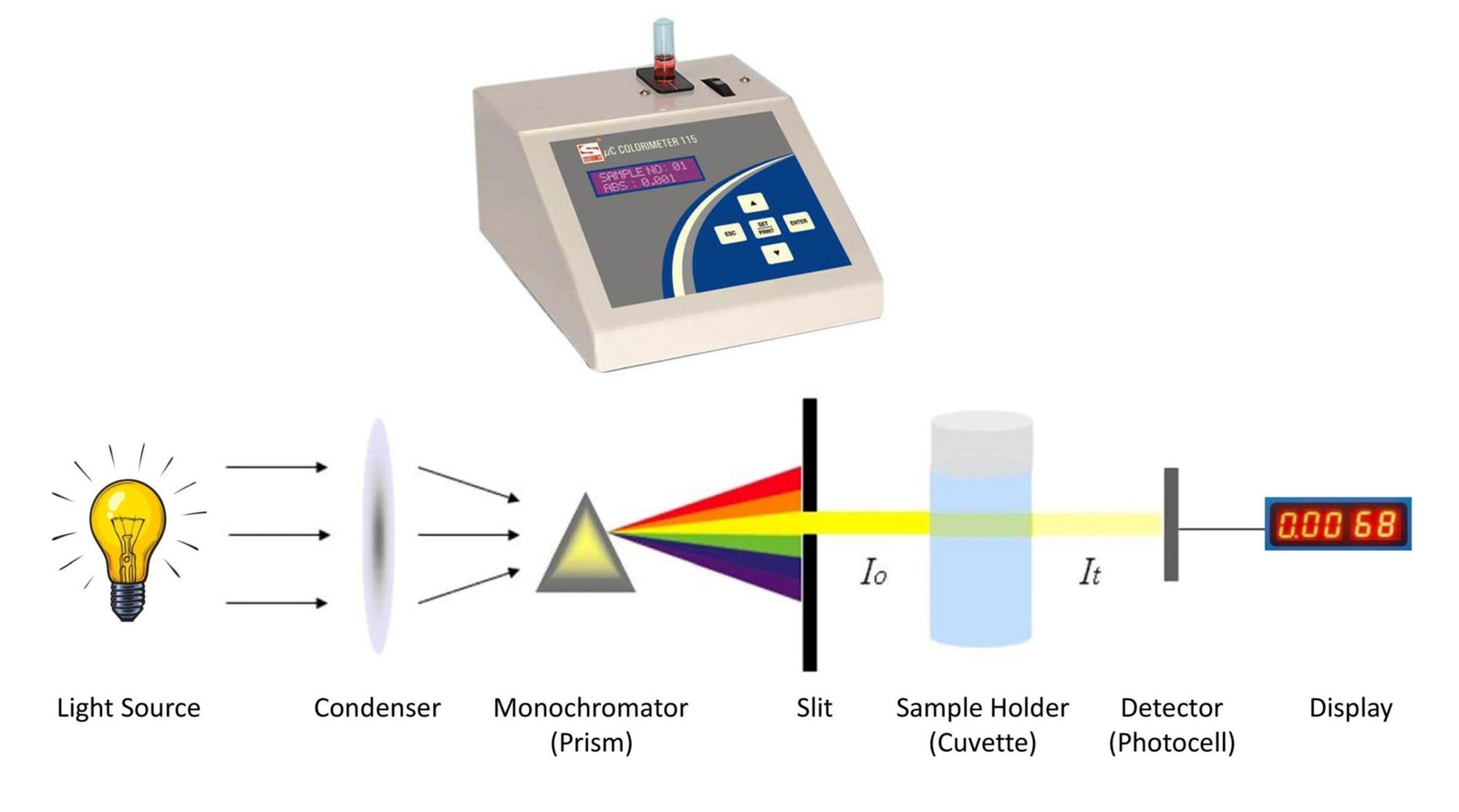
Comprehensive Guide to Using a Colorimeter
Colorimetry is a fundamental technique in analytical chemistry used to determine the concentration of a colored substance. By measuring the amount of light absorbed by a solution, you can infer how much of the substance is present. This guide covers the basic principles, instrument setup, calibration, and practical advice to ensure reliable and reproducible results.
1. How a Colorimeter Works
Basic Function and Principle
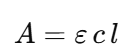
- Function:
A colorimeter measures the absorbance of light by a solution. It directs a beam of light through the sample and records how much of that light is absorbed. - Key Principle – Beer-Lambert Law:
According to the Beer-Lambert law, absorbance (A) is directly proportional to the concentration (c) of the colored compound in the solution and the path length (l) that the light travels through:
A = εcl
where ε is the molar absorptivity. Essentially, darker solutions (higher concentration) absorb more light than lighter ones. - Example:
When analyzing a red pigment solution, a colorimeter can help determine the pigment concentration by measuring how much light the sample absorbs.
2. Selecting the Appropriate Light
Choosing the Correct Wavelength
- Complementary Colour Principle:
To maximize sensitivity, select a light wavelength that is complementary to the color of the sample.- Example: For a red pigment, using green light is ideal because red solutions absorb green (and blue) wavelengths while reflecting red. This enhances the contrast and improves measurement accuracy.
- Why It Matters:
Using the appropriate light ensures that the absorbance readings are both sensitive and specific, leading to more reliable determinations of concentration.
3. The Role of Cuvettes
Using Cuvettes Effectively
- Definition:
Cuvettes are small, clear containers that hold the liquid sample during measurement. They provide a consistent path length for light, which is crucial for accurate readings. - Best Practices:
- Handling: Always handle cuvettes by the edges to avoid fingerprints and smudges that could scatter light.
- Cleaning: Ensure that cuvettes are clean and free of any residues before use.
- Consistency: Use cuvettes with identical optical properties to ensure uniformity in measurements.
- Example:
When measuring the absorbance of a pigment solution, a scratch-free, clean cuvette ensures that the light passes uniformly through the sample, yielding accurate absorbance data.
4. Calibration Process for a Colorimeter
Step-by-Step Calibration
Proper calibration is essential to obtain accurate measurements. The calibration process typically involves setting a baseline (blank) and creating a calibration curve using standards with known concentrations.
A. Preparing the Blank
- What is a Blank?
A blank is a cuvette filled with the solvent (without the pigment). It is used to zero the instrument. - Procedure:
- Fill a cuvette with the pure solvent.
- Insert the cuvette into the colorimeter.
- Set the absorbance reading to 0, which corrects for any absorbance due solely to the solvent.
B. Measuring Standard Solutions
- Standard Solutions:
Prepare several solutions with known concentrations of the pigment. - Procedure:
- Fill identical cuvettes with each standard solution.
- Record the absorbance values for each standard.
- Periodically re-check the blank to ensure the baseline remains at zero.
C. Creating a Calibration Curve
- Plotting the Curve:
Plot absorbance (y-axis) against concentration (x-axis) to create a calibration curve. - Usage:
The calibration curve serves as a reference for determining the concentration of unknown samples. By comparing the unknown sample’s absorbance to the curve, you can interpolate its concentration.
5. Measuring Unknown Sample Concentrations
Procedure for Analysis
- Preparation:
- Ensure the cuvette is clean and filled with the unknown sample.
- Verify that the cuvette’s volume matches that used in calibration.
- Measurement:
- Insert the cuvette into the colorimeter.
- Record the absorbance reading.
- Determination:
- Use the calibration curve to match the absorbance value with a corresponding concentration.
- Ensure that all measurements are made using consistent protocols to maintain accuracy.
6. Key Terms and Practical Tips
Key Terms
| Term | Definition | Example/Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Colorimeter | Instrument used to measure the light absorbance of a colored solution. | Determining the concentration of a pigment. |
| Cuvette | A small, clear container that holds the sample during analysis. | Provides a consistent light path for accurate measurements. |
| Blank | A cuvette filled with only the solvent, used to zero the instrument. | Corrects for background absorbance due to the solvent. |
| Calibration Curve | A graph plotting absorbance against known concentrations to determine unknown values. | Used to interpolate the concentration of unknown samples. |
| Beer-Lambert Law | The relationship that defines how absorbance relates to concentration and path length. | A=ε c lA = \varepsilon \, c \, lA=εcl |
Practical Tips
- Ensure Cleanliness:
Clean cuvettes thoroughly to avoid smudges that could alter light transmission. - Maintain Consistent Volumes:
Use the same sample volume in each cuvette for consistency. - Frequent Calibration:
Regularly check the blank during experiments to ensure accuracy. - Detailed Record Keeping:
Document every measurement and calibration step. This is essential for troubleshooting and verifying results.