Question 5a (i)
An investigation was carried out to determine the response of pancreatic cells to an increase in the glucose concentration of the blood. A person who had been told not to eat or drink anything other than water for 12 hours then took a drink of a glucose solution. Blood samples were taken from the person at one-hour intervals for five hours, and the concentrations of glucose, insulin and glucagon in the blood were determined. The results are shown in the graph.
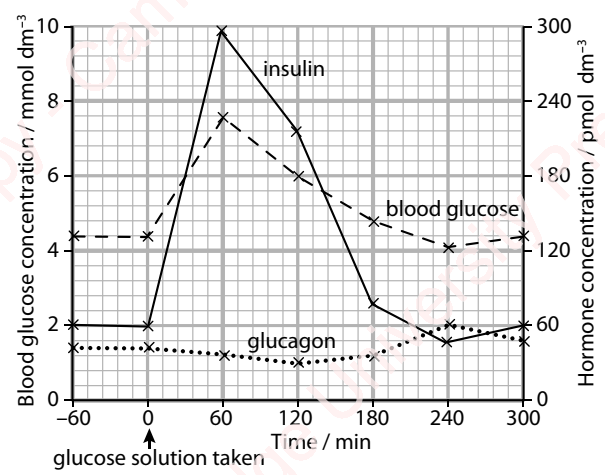
Explain why the person was told not to eat or drink anything other
than water for 12 hours before having the glucose drink. [3]
1. Establishing a Baseline
- Purpose: Fasting helps stabilize blood glucose, insulin, and glucagon levels at a consistent baseline.
- Benefit: Provides a reliable starting point to accurately measure changes caused by the glucose drink.
2. Avoiding Interference
- Reason: Food or drink (other than water) could raise blood glucose and hormone levels beforehand.
- Benefit: Ensures that the results are not affected by variables unrelated to the glucose drink.
3. Isolating the Effect of the Glucose Drink
- Outcome: Results reflect the body’s true response to an increase in blood glucose concentration without other factors involved.
- Purpose: Fasting means any changes observed are due directly to the glucose drink alone.