2021 Summer Paper 11
May/June Summer (11)
1. The diagram shows a mitochondrion drawn from an electron micrograph.
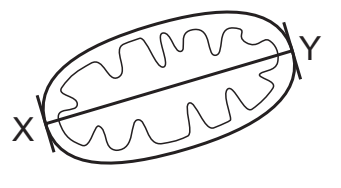
The actual length of the mitochondrion, using the line X–Y, is 3000 nm.
What is the magnification of the drawing of the mitochondrion?
(In the exam you have to use a ruler and measure the length of the figure. We measured it for you, and it is 3cm long).
A x100
B x1000
C x10 000
D x100 000
Steps:
1. Measure the length of XY with your ruler.
2. Always use the same units. So either convert nm to cm or cm to nm. In this case we converted nm to cm: 3000nm ÷ 10,000,000 = 0.0003cm.
(Note: nm to micrometers you divide by 1000. From micrometers mm we divide by 1000. To go from mm to cm, we divide by 10).
3. Use the formul I = AM.
Rearranged: M = I/A.
Substitute your values:
M = 3cm/0.0003cm.
M = x10 000
2. A specimen of plant tissue is observed twice with a microscope, firstly using red light with a
wavelength of 650 nm and then using green light with a wavelength of 510 nm.
What happens to the magnification and resolution when using green light compared to red light?
| magnification: | resolution: | |
| A B C D | decreases increases remains the same remains the same | decreases increases decreases increases |
D
To be able to have greater magnificaation, the type of lenses should have been changed.
A shorter wavelength allows waves to be refracted by areas that lay closer together. This mens we can see more details.
3 The electron micrograph shows a structure found in the cytoplasm of an animal cell.
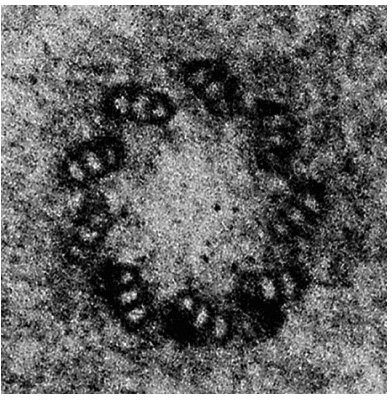
What is this cell structure?
A centriole
B lysosome
C ribosome
D vesicle
A
4. Which cell structures contain nucleic acid?
1 Golgi body
2 lysosome
3 mitochondria
4 ribosomes
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1, 2 and 4
C 1 and 4 only
D 3 and 4
D
Ribosomes are made of rRNA.
Mitochondria conains its own DNA and ribosomes.
5 Which statements about mitochondria, chloroplasts or prokaryotes are correct?
1 Mitochondria and chloroplasts have a fully permeable inner membrane and a partially permeable outer membrane.
2 Prokaryotes and chloroplasts have 70S ribosomes that are the sites for translation and polypeptide synthesis.
3 Prokaryotes and mitochondria have an outer membrane and an inner, folded membrane where ATP synthesis occurs.
4 Prokaryotes and mitochondria have circular DNA where genes coding for information are located.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1, 2 and 4
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 4 only
D
It can’t be 1: Mitochondria has a selectively permeable inner membrane. This allows it to build up a proton gradient across the membrane, which helps with ATP synthesis.
It can’t be 3: Mitochondria has prokaryotic features, but not all prokaryotes function or are structurally the same as mitochondria. Prokaryotes may lack the inner folds for example:
6 The very large (1000 nm) Pandora viruses found in Chile and Australia are considered to be
viruses because they cannot replicate their own genome and cannot make proteins.
They also share essential structural features with other viruses.
What are the essential structural features of viruses?
1 non-cellular
2 protein coat
3 both DNA and RNA
4 either DNA or RNA
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1, 2 and 4
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 4 only
B
Viruses usully contains either RNA or DNA, not both.
7 A sample of food was heated with Benedict’s solution which changed colour to green.
A second sample of the same food was boiled with dilute hydrochloric acid and neutralised using
sodium hydrogencarbonate. It was then heated with Benedict’s solution which changed colour to red.
What did these results show?
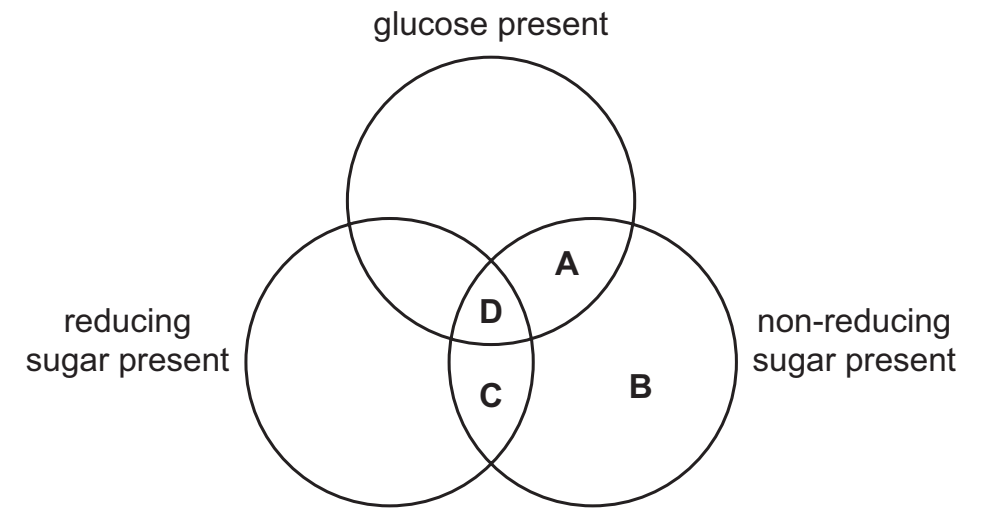
C
Glucose is not the only reducing sugar.
8 Which pair of molecules only includes macromolecules that can be found in animal cells?
A amylase and amylopectin
B collagen and glycogen
C deoxyribose and starch
D sucrose and haemoglobin
B
amylase and amylopectin (found in starch, which is produced by plants).
deoxyribose and starch (glycogen is the storage version of starch in animals)
sucrose and haemoglobin (sucrose is produced by plans, and when consumed is broken up into flucose and fructose before it enters the body).
collagen and glycogen

9 Homogalacturonan is a polysaccharide found in plant cell walls.
The diagram shows a molecule of the monomer used to form homogalacturonan.
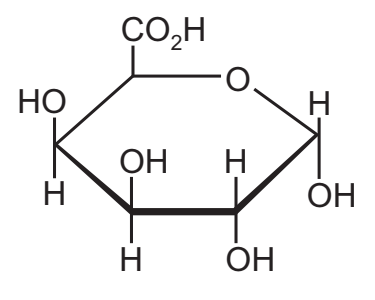
A student studied the structure of this monomer and compared it with the structure of the
monomer used to form cellulose. Which carbon atoms in the monomer in the diagram have hydroxyl groups arranged in different positions to those found in the cellulose monomer?
A carbon one and carbon four
B carbon one only
C carbon three and carbon four
D carbon three only
A

The hydroxyl groups (OH) is different/reversed in both the c1 and c4 positions.
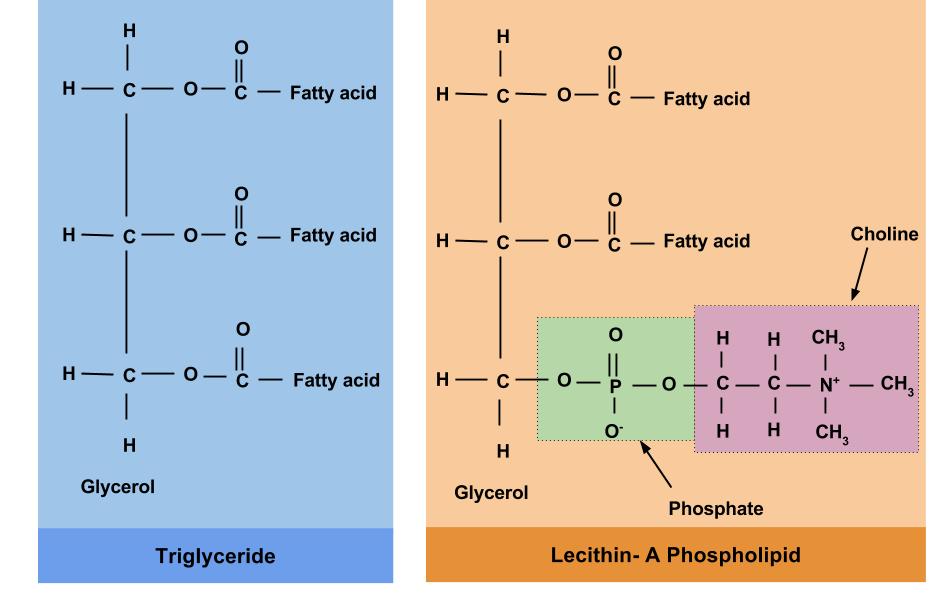
10 Which statement is correct for triglycerides and phospholipids?
A A phosphate group is joined to a glycerol molecule.
B Hydrocarbon chains may be saturated or unsaturated.
C They are polar molecules.
D They contain three ester bonds.
B
11 Which description of collagen is correct?
A A collagen molecule consists of three polypeptide chains, each in the shape of a helix. The
three chains are wound together into a triple helix called a fibre.
B A collagen molecule consists of three polypeptide chains, each of which is an α-helix. The
three chains are wound tightly together into a triple helix. Many of these triple helices bind
together as a fibre.
C A collagen molecule consists of three polypeptide chains wound tightly into a triple helix
called a fibre.
D A collagen molecule consists of three polypeptide chains in which every third amino acid is
glycine. The three polypeptides are wound tightly together into a triple helix. Many of these
helices form a fibre.
D

12 In a healthy human, the mean value for the number of haemoglobin molecules in one red blood
cell is 260 million.
How many α-globin chains does one red blood cell contain in a healthy human?
A 1.3 x 108
B 2.6 x 108
C 5.2 x 108
D 1.04 x 109
C

260,000,000 x 2 = 5.2 x 108
13 Which statements about a peptide bond are correct?
1 It joins two monomers which are always identical to each other.
2 It contains four different atoms.
3 It can be broken by the addition of water at room temperature.
4 It is important in the primary structure of proteins.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 3 only
C 2, 3 and 4
D 2 and 4 only
D

14 Which graph correctly shows the activation energy of a reaction when an enzyme is added?
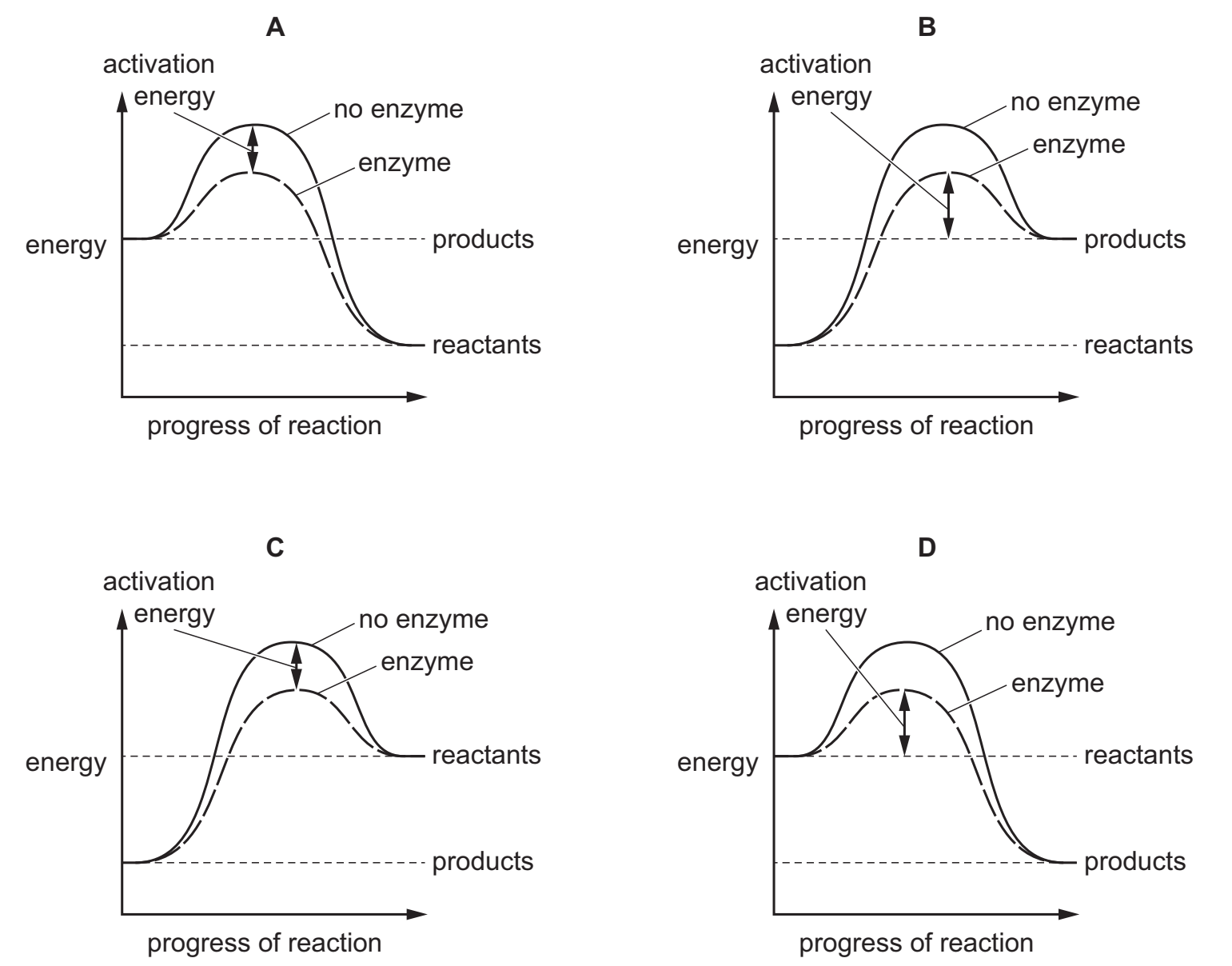
D
B or C are the only two good candidates. B is wrong, since the activation is measured from the reagents starting energy level. In B, it was measured from the products’ energy level.
15 The enzyme lactase is found in the membranes of epithelial cells lining the small intestine.
The enzyme is formed by a single polypeptide that folds to give three regions.
o an active site with the free amino group outside the cell
o a short section inside the membrane
o a short section inside the cell
What type of amino acid would be found in each of the three regions?
| outside the cell | inside the membrane | inside the cell | |
| A B C D | hydrophilic hydrophilic hydrophobic hydrophobic | hydrophobic hydrophobic hydrophilic hydrophobic | hydrophilic hydrophobic hydrophobic hydrophilic |
A

16 A student wrote three statements about cell signalling.
1 A signal chemical always has the same shape as a protein receptor on a target cell.
2 An increase in temperature may decrease the effect of cell to cell signalling.
3 A mutation may decrease production of active protein receptors for the cell surface membrane.
Which statements are correct?
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 3 only
C 1 only
D 2 and 3 only
D
Hormones mediate changes in target cells by binding to specific hormone receptors. In this way, even though hormones circulate throughout the body and come into contact with many different cell types, they only affect cells that possess the necessary receptors. Receptors for a specific hormone may be found on many different cells or may be limited to a small number of specialized cells. For example, thyroid hormones act on many different tissue types, stimulating metabolic activity throughout the body. Cells can have many receptors for the same hormone but often also possess receptors for different types of hormones. The number of receptors that respond to a hormone determines the cell’s sensitivity to that hormone, and the resulting cellular response. Additionally, the number of receptors that respond to a hormone can change over time, resulting in increased or decreased cell sensitivity. In up-regulation, the number of receptors increases in response to rising hormone levels, making the cell more sensitive to the hormone and allowing for more cellular activity. When the number of receptors decreases in response to rising hormone levels, called down-regulation, cellular activity is reduced.
17 At which stages of mitosis are chromosomes composed of two chromatids that are held together by a centromere?
A anaphase and telophase
B anaphase and prophase
C metaphase and prophase
D metaphase and telophase
C

18 The jellyfish, Turritopsis dohrnii, is described as being immortal. If T. dohrnii is not eaten by
predators or diseased, it seems to be able to live forever. There is no way to determine the
biological age of a T. dohrnii individual.
Which feature of the cells in T. dohrnii could explain these observations?
A very long G phases in the cell cycle
B a very short S phase in the cell cycle
C an ability to restore telomeres to their original length
D fewer chromosomes than other eukaryotic organisms
C
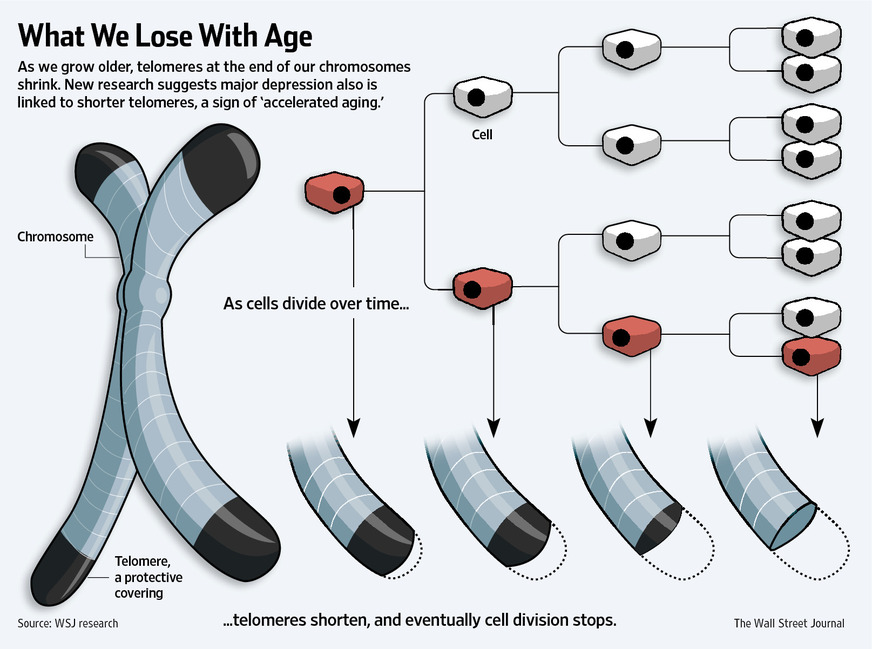
19 Some chemicals, used to stop tumour growth, work by preventing the DNA double helix from
uncoiling and separating.
During which stage of the cell cycle would they act?
A anaphase
B interphase
C metaphase
D prophase
B
20 Four nucleotides, A, B, C and D, each consist of three phosphate groups, a nitrogenous base
and a pentose sugar. Characteristics of the base and sugar components before they are joined to
form each nucleotide are shown in the table.
Which nucleotide could pair with an adenine base during DNA replication?
| ring structure of nitrogenous base | ratio of carbon to oxygen atoms in pentose sugar | |
| A B C D | double double single single | 1 : 1 5 : 4 1 : 1 5 : 4 |
D
Thymine would bind to adenine.


Deoxyribose is a sugar, although not the kind we usually think of when we’re sweetening our coffee. Deoxyribose is a monosaccharide. Monosaccharides are the building blocks for more complicated sugars. Here, ‘mono’ means ‘one,’ and ‘saccharide’ means ‘sugar.’
Deoxyribose is also known more precisely as 2-deoxyribose and is a component of DNA. Any molecule that ends in ‘ose’ is considered a sugar. The chemical formula for deoxyribose is C5 H10 O4. This might look complicated, but the letters represent the names of elements from the periodic table, and the numbers (presented in subscript) tell us how many of each of these elements make up a particular compound. So, this formula means that deoxyribose is made of 5 carbon atoms, 10 hydrogen atoms, and 4 oxygen atoms. Atoms can be found everywhere and are the basic chemical elements of life.
21 The statements describe the process of translation.
1 A peptide bond forms between adjacent amino acids.
2 Hydrogen bonds form between the anticodon and the codon.
3 mRNA binds to the ribosome.
4 tRNA enters the ribosome carrying a specific amino acid.
In which order does this process take place?
A 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
B 3 → 4 → 2 → 1
C 4 → 2 → 1 → 3
D 4 → 2 → 3 → 1
B

22 The sequence of amino acids in a section of a polypeptide is:
… histidine–proline–aspartic acid–leucine…
| amino acid | possible DNA triplet codes |
| aspartic acid histidine leucine proline | CTA CTG GTA GTG GAT GAC GGA GGG |
What is a correct sequence of mRNA codons for this polypeptide section?
A …CAC CCC GAA CUG…
B …CAU CCU GAC CUA…
C …GTA CCA CTG GAT…
D …GUA GGA CUG GAU…
B
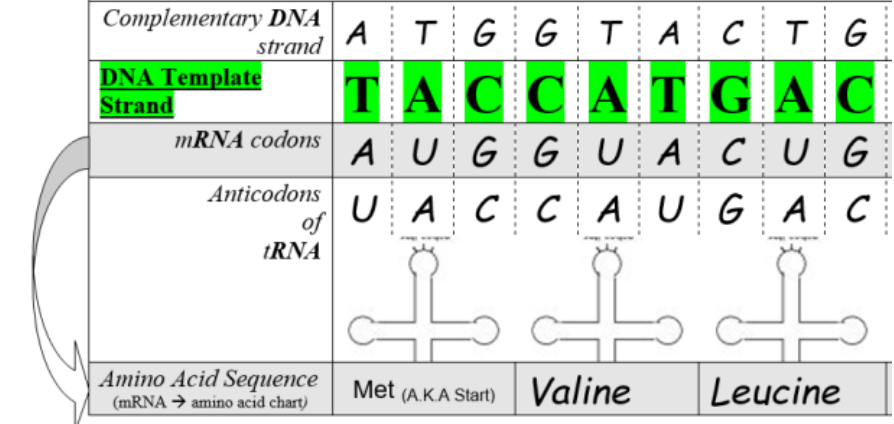

23 What contributes to the upward movement of water in a xylem vessel of a plant?
1 cohesion of water molecules by hydrogen bonding
2 adhesion of water molecules to the cellulose walls of xylem vessels by hydrogen bonding
3 removal of water from xylem vessels in a leaf reduces the hydrostatic pressure in the xylem
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
A
24 The diameter of a tree trunk usually decreases slightly during the day.
Which changes in environmental factors during the day could cause the diameter to decrease even more?
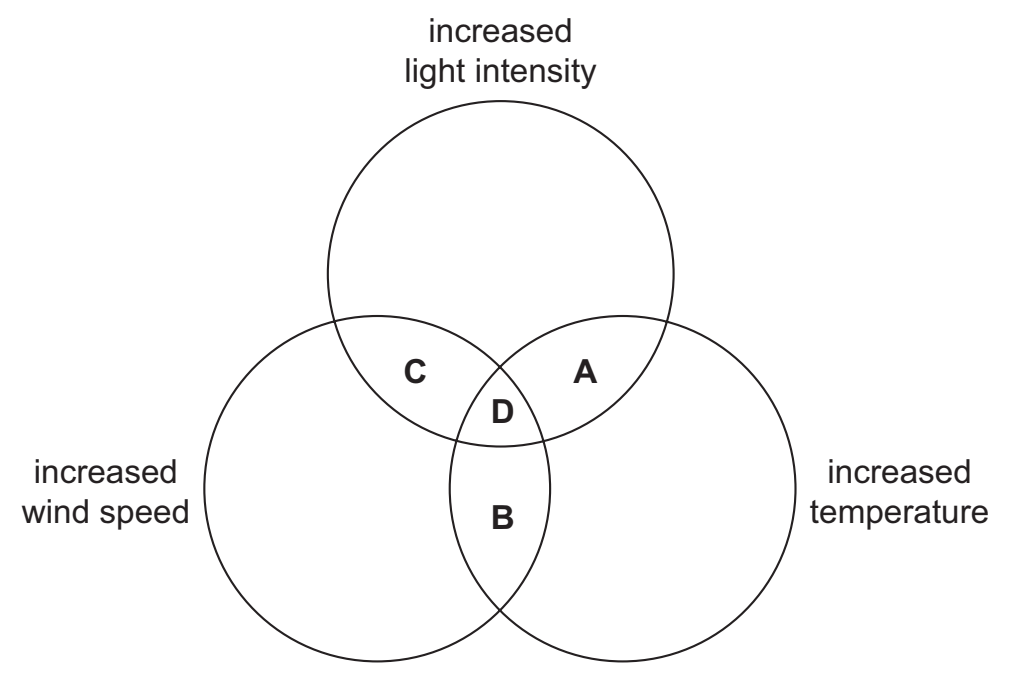
D
25 The diagram shows a transverse section of a stem.
Which area is the phloem?
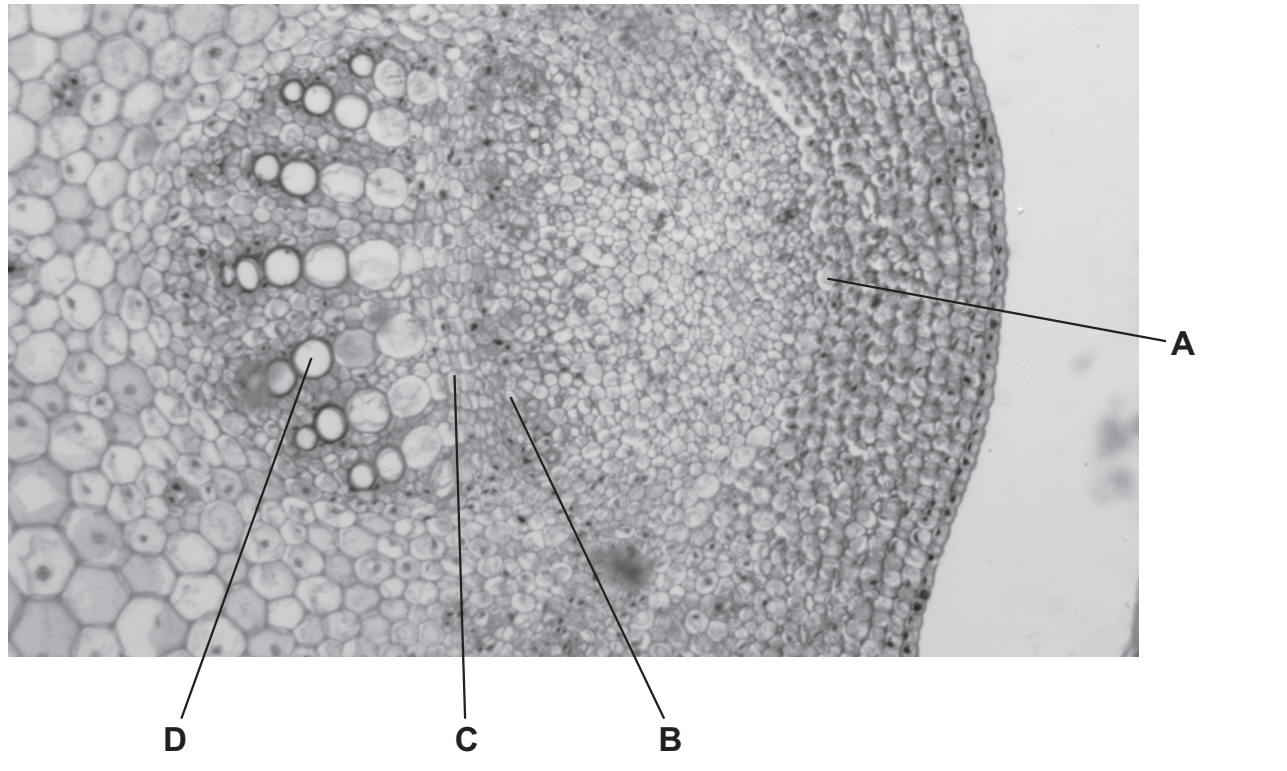
B
26 The diagram shows a xerophytic leaf in different conditions, P and Q.

Which statements describe the difference between the cells in layer Y in conditions P and Q?
1 more negative water potential in P than Q
2 more cells plasmolysed in P
3 cells less turgid in Q
4 water potential becomes zero in Q
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 2 and 4
D 3 and 4
B
27 Different substances, such as sucrose and amino acids, can move in different directions in the
phloem sieve tube elements.
Which statement explains this?
A Active transport occurs in some phloem sieve tube elements and mass flow occurs in other
sieve tube elements.
B Both active transport and mass flow occur in each individual phloem sieve tube element.
C Mass flow occurs in both directions at the same time in each individual phloem sieve tube
element.
D Mass flow occurs in different directions in different phloem sieve tube elements at the same
time.
D
28 The statements list some of the events in a cardiac cycle. The statements are not in the correct
order.
Which statement describes the fourth of these events to occur in the cardiac cycle?
1 The impulse travels through Purkyne tissue.
2 A wave of excitation sweeps across the atria.
3 The atrioventricular node delays the impulse for a fraction of a second.
4 The sinoatrial node contracts.
5 The wave of excitation sweeps upwards from the base of the ventricles.
6 The ventricles contract.
7 The atria contract.
A 1
B 3
C 4
D 7
B

29 Which row correctly identifies components of both lymph and tissue fluid?
| antibodies | red blood cells | sodium ions | white blood cells | |
| A B C D | ✓ ✓ x x | ✓ x ✓ x | ✓ ✓ x ✓ | ✓ ✓ x ✓ |
key
✓= component present
x = component not present
B
30 Which row is correct for the mean blood pressure in different parts of the human circulatory
system?
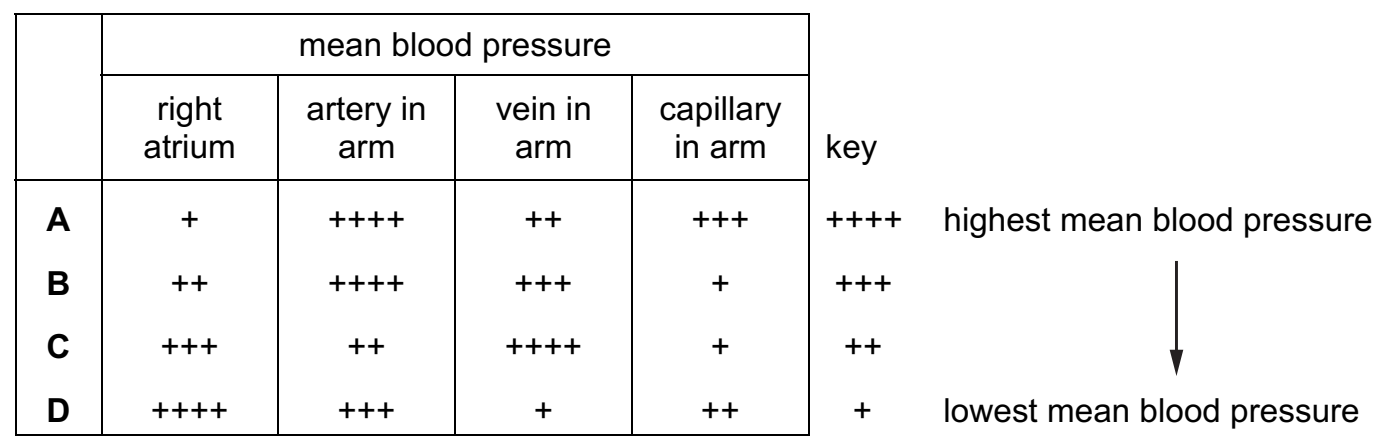
A
31 Which mechanism accounts for the way most of the carbon dioxide is transported in blood?
A Carbon dioxide dissolves in plasma and is carried in solution.
B Carbon dioxide is converted to carbaminohaemoglobin inside red blood cells.
C Carbon dioxide is converted to carboxyhaemoglobin inside red blood cells.
D Carbon dioxide is converted to hydrogencarbonate ions inside red blood cells.
D

32 The graph shows the dissociation curves for haemoglobin at two different partial pressures of
carbon dioxide. At which position on the graph, A, B, C, or D, is the concentration of haemoglobinic acid lowest in red blood cells?
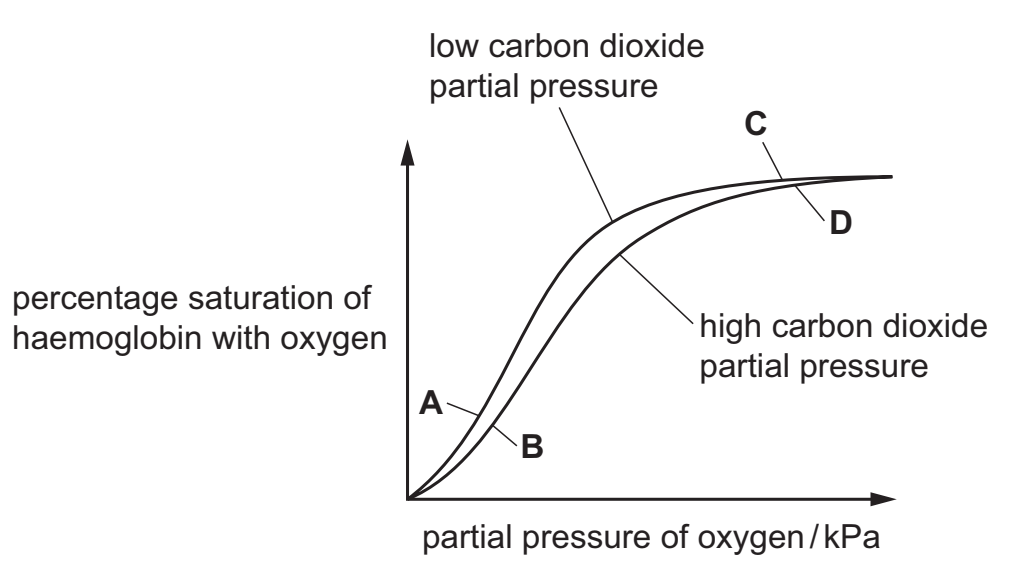
C
C not D, because if more oxygen is bound to Hb (which is the case in C), then less CO2 is bound to it.

33 The table shows the partial pressure of carbon dioxide and oxygen in two blood vessels.
| partial pressure of gas in pulmonary artery / kPa | partial pressure of gas in pulmonary vein / kPa | |
| carbon dioxide oxygen | 6 5 | 5 15 |
What explains the difference in the partial pressures of oxygen in the pulmonary artery and
pulmonary vein?
A Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood in the capillaries.
B Carbon dioxide diffuses into the alveoli from the blood in the capillaries.
C Oxygen diffuses from the body cells into the blood in the capillaries.
D Carbon dioxide diffuses into the body cells from the blood in the capillaries.
A

34 Which graph shows the effect of carbon monoxide on the percentage saturation of haemoglobin
with oxygen?
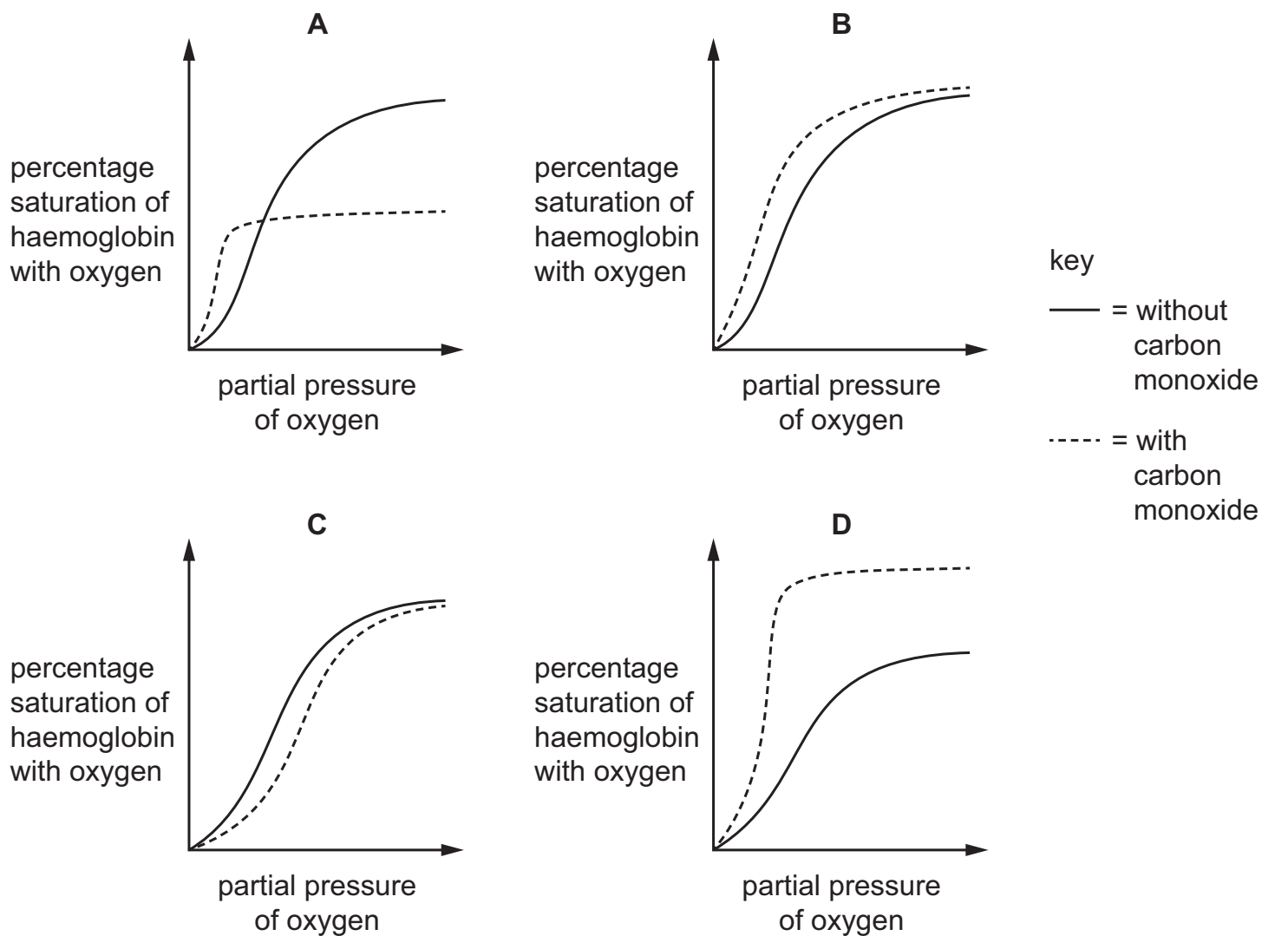
A
Carbonmonoxide effectively reduces the number of Hb availble, since they permantly binds to them, which prevents oxygen from binding.
35 Which row shows the correct methods of transmission of the named pathogens?
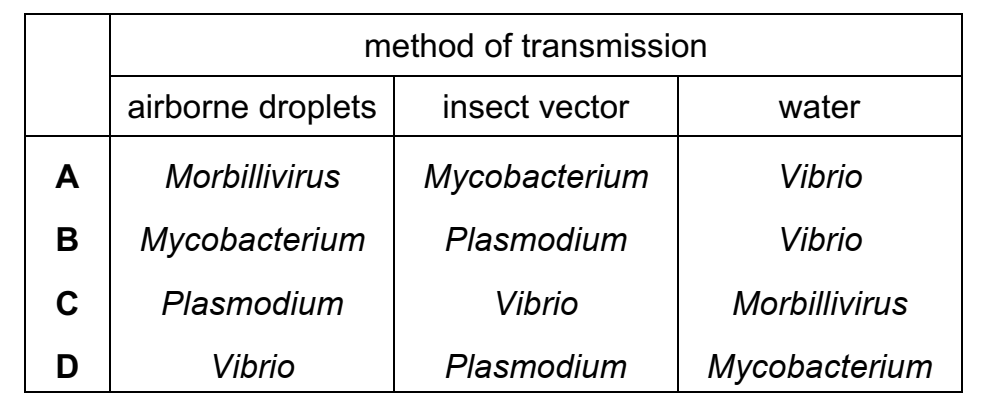
B
Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Plasmodium causes malaria in humans.
Vibrio cholerae.
36 Which disease is caused by a eukaryote?
A cholera
B malaria
C measles
D smallpox
B
Cholera is an acute diarrheal illness caused by infection of the intestine with Vibrio cholerae bacteria.
Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a eukaryotic protozoan parasite of the genus Plasmodia.
Measles is an acute viral respiratory illness.
Smallpox is an acute contagious disease caused by the variola virus.
37 What is the initial mechanism by which bacteria become resistant to antibiotics?
A genetic mutation
B overuse of antibiotics
C natural selection
D patients not finishing a course of antibiotics
A
38 What are functions of T-lymphocytes?
1 production of cytokines
2 production of toxins
3 recognition of an antigen bound to an antigen-presenting cell
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
A

39 What is correct about the role of memory cells in long-term immunity?
1 They divide to form plasma cells and memory cells when the pathogen enters the body a second time.
2 They produce a fast response so that the person infected with the pathogen does not become ill again.
3 They produce more antibodies than were produced during the primary immune response.
4 They remain in the blood and lymphatic system after the pathogen has been destroyed.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1, 2 and 4
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 4 only
B

40 Which events result in a person developing actively acquired immunity?
1 becoming infected by TB bacteria
2 drinking breast milk
3 receiving an injection of antigens
4 receiving an injection of antibodies
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1, 3 and 4
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 4
C
May/June Summer (12)
Q1
1 Which row describes the membranes surrounding each cell structure?
| chloroplast | mitochondrion | nucleus | |
| A B C D | single double single double | single single double double | double single single double |
D

Q2
The mean width of mitochondria in an electron micrograph is 6 mm.
The magnification of the electron micrograph is x9600.
What is the actual mean width of the mitochondria?
A 6 x 10–3 mm
B 6 x 10–4 mm
C 6 x 10–2 μm
D 6 x 103 μm
B
I = AM
A = I/M
A = 6mm/9600
A = 0.000625mm
A = 6 x 10–4 mm
Q3
Which sequence shows the correct order of some of the stages in the production and secretion of an enzyme?
A Golgi body → ribosome → rough endoplasmic reticulum → mRNA.
B mRNA → smooth endoplasmic reticulum → Golgi body → vesicle.
C ribosome → rough endoplasmic reticulum → vesicle → Golgi body.
D smooth endoplasmic reticulum → mRNA → vesicle → ribosome.
C
Q4
Different antibiotics function in different ways. Ideally, the antibiotic kills the bacteria, but does not harm the infected human. One type of antibiotic, tetracycline, can affect the way in which human mitochondria function.
What explains the effect of tetracycline on human mitochondria?
1 The antibiotic prevents the synthesis of peptidoglycan cell walls.
2 The antibiotic prevents synthesis of linear DNA.
3 The antibiotic prevents translation by binding to 70S ribosomes.
A 1 and 2
B 2 and 3
C 2 only
D 3 only
D
Tetracyclines inhibit protein synthesis by binding at the A site of the small ribosomal subunit and blocking the accommodation of an incoming aminoacyl-transfer RNA (aa-tRNA) into the A site of the bacterial 70S ribosome.

Q5
A prokaryotic cell is 5.0 μm in length.
A virus particle is 300 nm in length.
How many times larger is the prokaryotic cell compared to the virus particle?
A 2
B 17
C 60
D 167
B
5,000 : 300 (divide both sides by 300).
= x16.66
Q6
A student carries out a semi-quantitative test with Benedict’s solution.
Which statement about this procedure is correct?
A It detects only the presence or absence of glucose.
B It provides an indication of relative reducing sugar concentrations.
C The precipitate needs to be filtered, dried and weighed to give the reducing sugar concentration.
D A colorimeter needs to be used to determine the glucose concentration.
B
Q7
Which row is correct for carbohydrates?
| macromolecule | monomer | polymer | |
| A B C D | sucrose glycogen α-glucose starch | starch sucrose glycogen α-glucose | α-glucose starch sucrose glycogen |
D
| Macromolecule | Basic Formula, key features | Monomer | Examples | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteins | CHON−NH2 + −COOH +R group | Amino acids | Enzymes, some hormones | Storage; Signals; Structural; Contractile; Defensive; Enzyme; Transport; Receptors |
| Lipids | C:H:O Greater than 2:1 H:O (carboxyl group) | Fatty acid and glycerol | Butter, oil, cholesterol, beeswax | Energy storage; Protection; Chemical messengers; Repel water |
| Carbohydrates | C:H:O1:2:1 | Monosaccharides | Glucose, Fructose, Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose | Energy storage; Structure |
| Nucleic Acids | CHONP pentose, nitrogenous base, phosphate | Nucleotides | DNA, RNA | Genetic information |
Q8
Which shows the correct general formula for glycogen?
A (C5H10O5)n
B (C5H10O6)n
C (C6H10O5)n
D (C6H12O6)n
C
The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. Shouldnt the formula be (C6H12O6)? The reason it is not, is because when two glucose molecules combine to form a glycosidic bond, water (H20) is removed. This leaves us with: C6H10O5
Q9
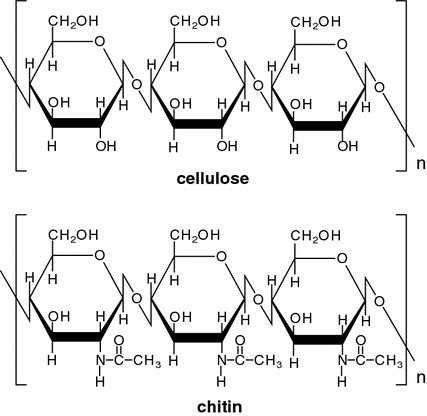
Chitin is a structural polysaccharide found in the hard, outer shells of animals such as crabs.
Chitin is made of chains of amino sugars that contain NH groups.
The diagram shows two sugars in the chain of a chitin molecule.
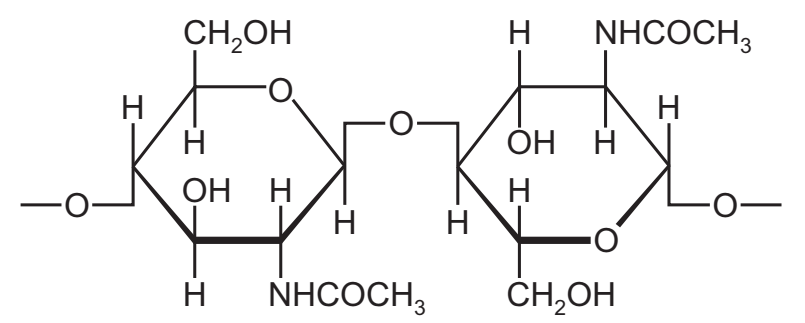
Which polysaccharide is most like chitin?
A amylopectin
B amylose
C cellulose
D glycogen
C
Q10
Four fatty acids and their formulae are listed.
| caprylic acid lauric acid oleic acid palmitoleic acid | CH3(CH2)6COOH CH3(CH2)10COOH CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
Which fatty acids are saturated?
A caprylic acid and lauric acid
B caprylic acid and oleic acid
C lauric acid and palmitoleic acid
D oleic acid and palmitoleic acid
A
Q11
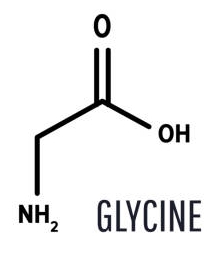
Which molecule contains the smallest number of hydrogen atoms?
A α-glucose
B glycine, an amino acid in which the R group is H
C glycerol
D a saturated fatty acid containing eight carbon atoms
B

Q12
The diagram shows sucrose and sucralose.
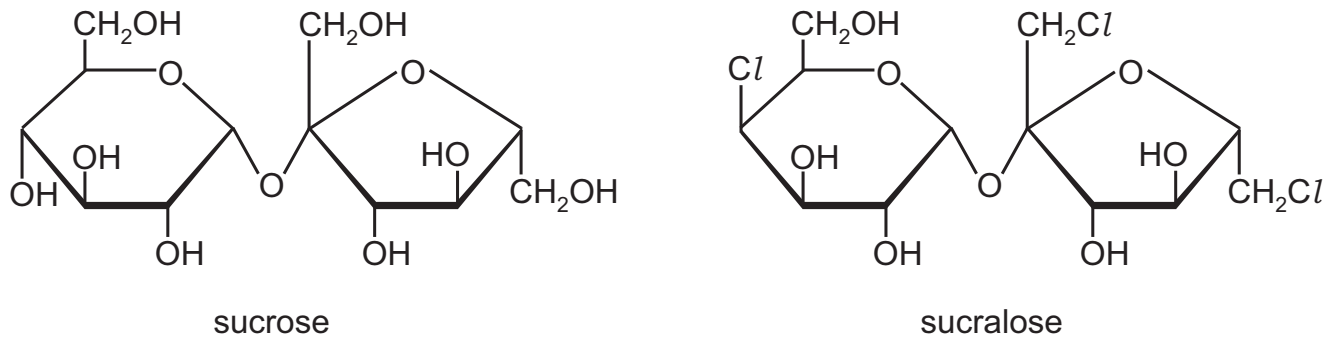
The enzyme sucrase breaks down sucrose but cannot break down sucralose. Four students were asked to suggest why sucrase can break down sucrose but not sucralose.
Three of the students gave correct suggestions.
Which suggestion cannot be correct?
A The Cl atoms change the shape of the sucralose molecule so it is not the same shape as the active site of sucrase.
B The Cl atoms of the modified fructose cannot bind to the active site of sucrase.
C The Cl atoms cannot cause an induced fit, so sucralose does not enter the active site of
sucrase.
D The Cl atoms cause fewer temporary hydrogen bonds between sucralose and the active site of sucrase.
A
Q13
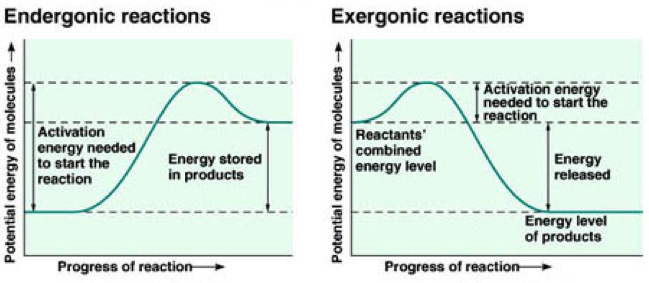
The graph shows the energy levels involved in an enzyme-catalysed reaction. Substrate molecules X and Y combine to give product Z.
Which arrow shows the reduction in activation energy due to the enzyme?
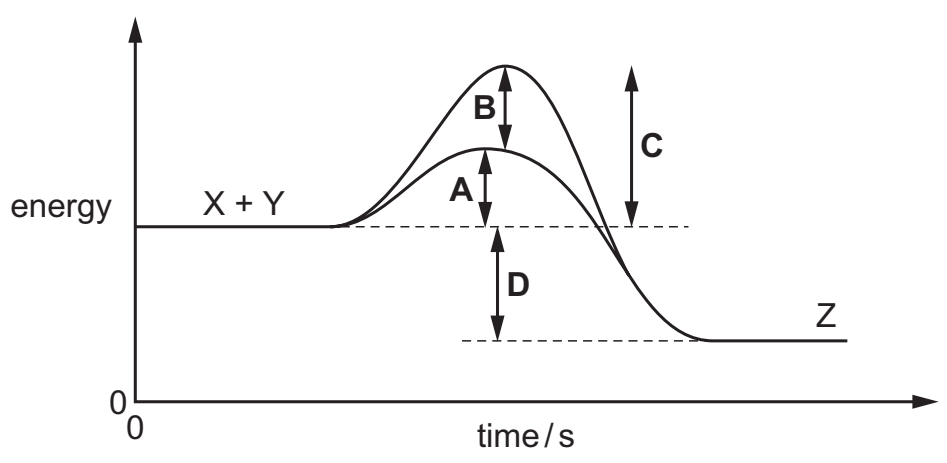
B
Q14
Which roles of the cell surface membrane result from the properties of the phospholipids?
1 to allow cytokinesis to occur in mitotic cell division
2 to allow entry and exit of oxygen and carbon dioxide
3 to allow the phagocytosis of a bacterium into a cell
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
A
Q15
Which factors can be changed to affect the rate of facilitated diffusion across a cell surface membrane?
1 the surface area of the membrane
2 the concentration gradient
3 the number of specific protein channels
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 3 only
A
Q16
The diagram shows an experiment using a model cell to investigate the movement of substances.
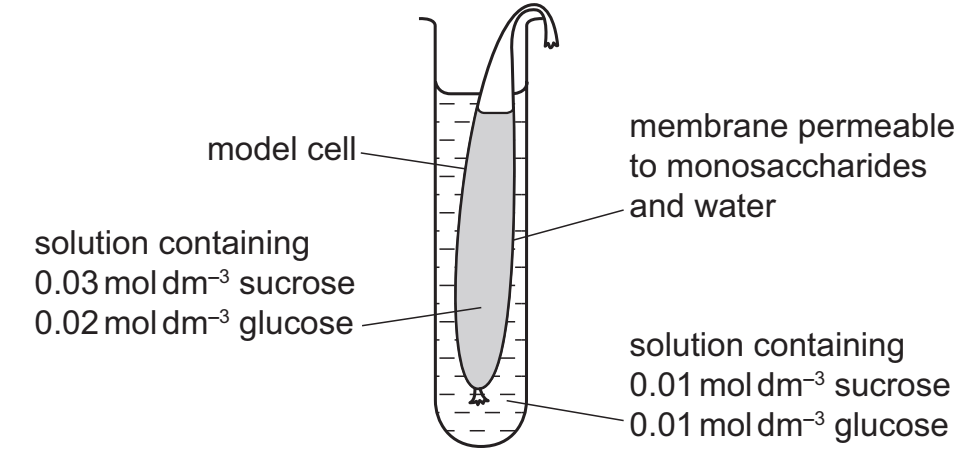
Which statements are correct?
1 There is net movement of sucrose out of the model cell.
2 There is net movement of glucose out of the model cell.
3 There is net movement of water into the model cell.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
D
Q17
Human chromosomes have different parts. Some parts are more numerous than others.
Which parts are listed in order from most numerous to least numerous in a human white blood cell?
A centromere → nucleotide → histone protein
B DNA molecule → telomere → centromere
C histone protein → telomere → DNA molecule
D telomere → centromere → nucleotide
C
Q18
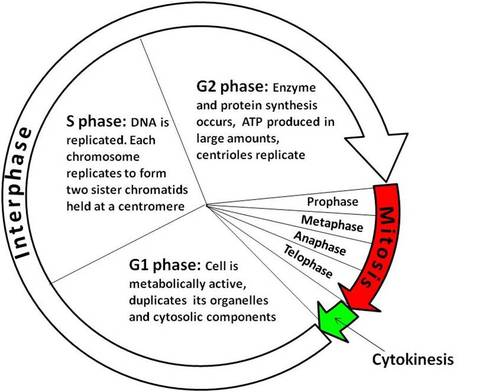
The diagram represents the cell cycle of a human cell. During the cell cycle the number of chromatids changes.
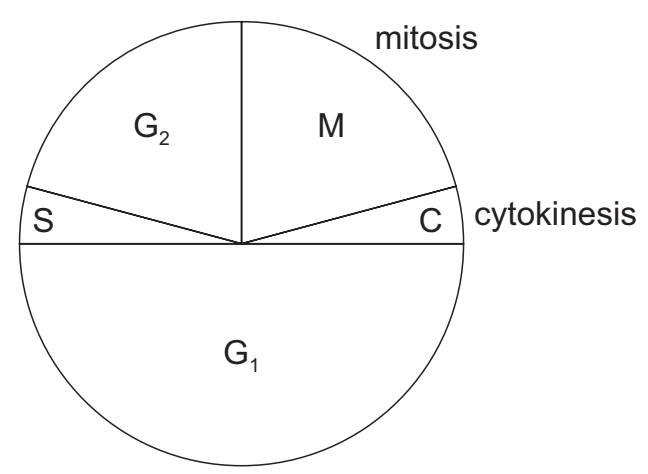
Which row is correct for the number of chromatids in M, G1, and G2?
| M | G1 | G2 | |
| A B C D | 46 46 92 92 | 46 92 46 92 | 92 92 92 92 |
C
Q19
A single skin cell was isolated and transferred to growth medium in a sterile Petri dish. The Petri dish was incubated for 16 days. During this time, the number of skin cells multiplied as a result of repeated mitotic divisions.
One of the chromosomes in the nucleus of each skin cell has a telomere that contains many repeats of the base sequence TTAGGG. On each of days 4, 8, 12 and 16 of the incubation period, a single cell was removed from the Petri dish. The total number of bases in the telomere of this chromosome was determined for each cell. Each of the four cells had a different total number of telomere bases for this chromosome: 5548, 5580, 5645 and 5700.
What was the total number of telomere bases in the chromosome from the cell that had undergone the most mitotic divisions?
A 5548
B 5580
C 5645
D 5700
A
Q20
A short piece of DNA, 18 base pairs long, was analysed to find the number of nucleotide bases in each of the polynucleotide strands.
Some of the results are shown in the table.
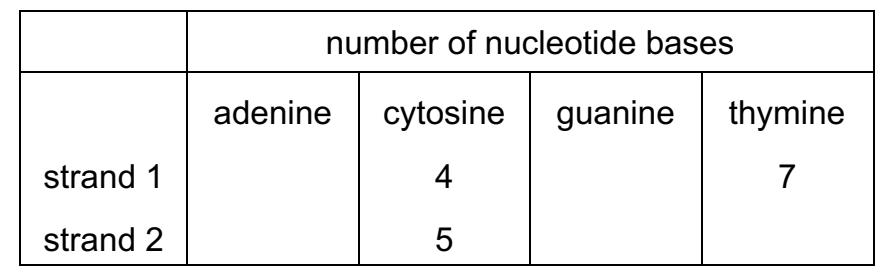
How many nucleotides containing thymine were present in strand 2?
A 2
B 4
C 5
D 7
A
Chargaff’s rules state that DNA from any species of any organism should have a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio of purine and pyrimidine bases (i.e., A+G=T+C ) and, more specifically, that the amount of guanine should be equal to cytosine and the amount of adenine should be equal to thymine.
Therefore, if thre are 9 cytosines, then there is 9 guanines. 18 – 9 = 9. There can therefore be only 9 total thymines. Strand 1 already contins 7, so 9 -7 = 2.
Q21
The diagram shows a strand of DNA and mRNA during transcription.
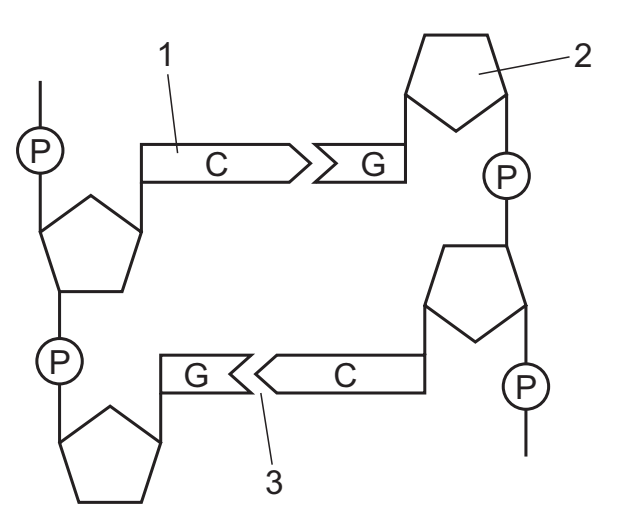
Which row correctly identifies 1, 2 and 3?
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| A B C D | purine purine pyrimidine pyrimidine | deoxyribose ribose deoxyribose ribose | two hydrogen bonds three hydrogen bonds two hydrogen bonds three hydrogen bonds |
D
Q22
Two students were discussing the involvement of DNA and RNA in transcription and translation.
Student 1 always stated correct facts.
Student 2 gave further information, which was sometimes correct.
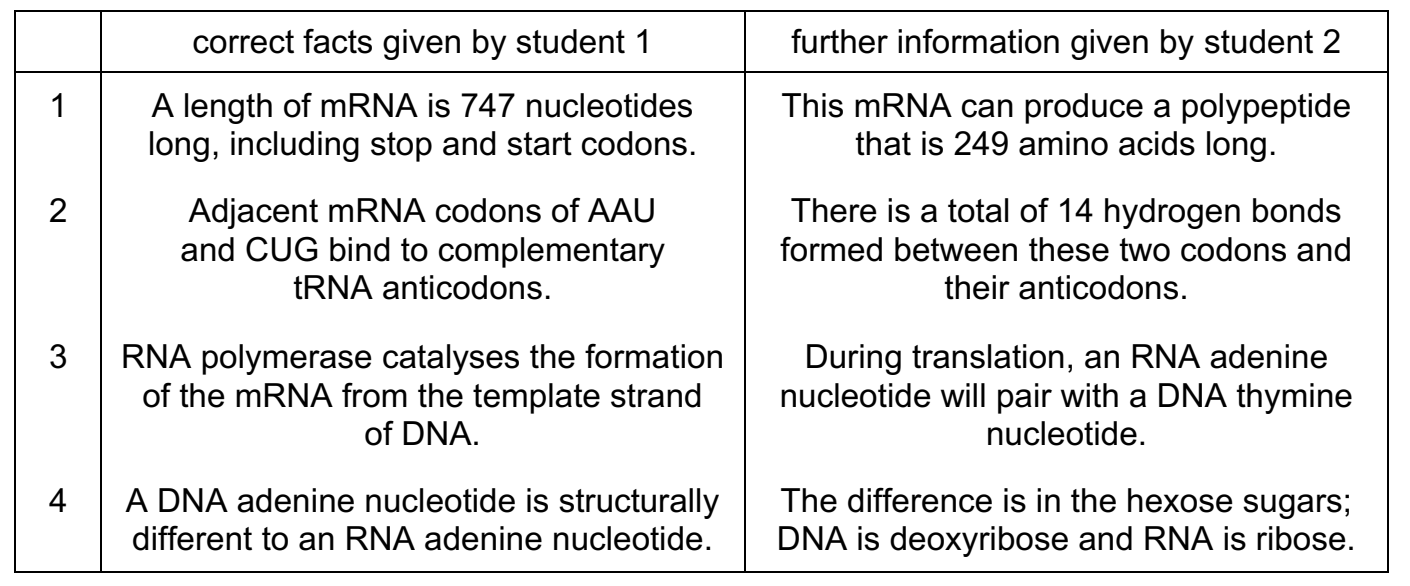
Which further information, given by student 2, is correct?
A 1 and 4
B 2 and 3
C 2 only
D 4 only
C
AAU = 2 + 2 + 2 (number of hydrogen bonds formed by each nucleotide)
CUG = 3 + 2 + 3 (number of hydrogen bonds formed by each nucleotide)
= 14.

Q23
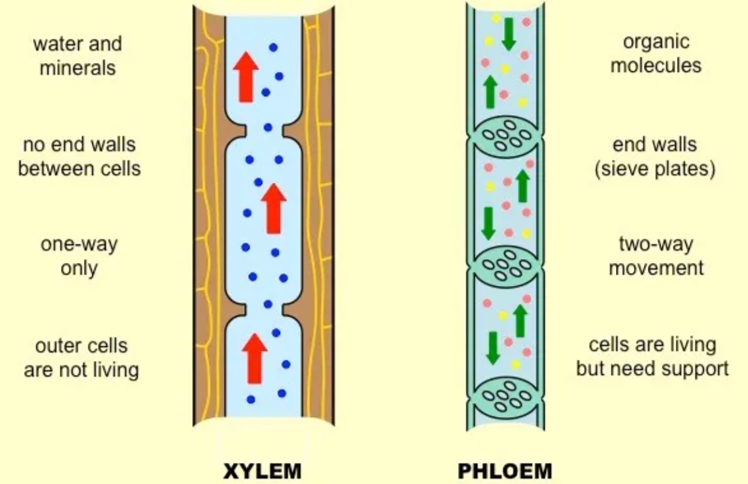
Which descriptions of the adaptations of xylem vessel elements to their function are correct?
1 They have pits between vessels allowing water to pass from one vessel to another.
2 They are thickened with lignin to stop them collapsing when the column of water is under tension.
3 They form a continuous hollow tube through the plant providing little resistance to water movement.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 3 only
C 2 only
D 2 and 3 only
A
Q24
The diameter of a tree trunk usually decreases slightly during the day.
Which changes in environmental factors during the day could cause the diameter to decrease even more?

B
Q25
A student wanted to find out the rate of transpiration using a potometer as shown.

The student was told to work out a value for transpiration using the units mm3, m–2 and hour–1.
Which measurements would the student need to take?
A volume of water in the reservoir, length of the capillary tubing, temperature and how many leaves are on the shoot
B volume of water in the reservoir, radius of the capillary tubing, time and surface area of the leaves
C distance air bubble moves, radius of the capillary tubing, time and surface area of the leaves
D distance air bubble moves, length of the capillary tubing, temperature and how many leaves are on the shoot
C
Q26
In plants, assimilates such as sucrose are loaded from source cells into sieve tube elements. The assimilates are then transported from source to sink.
What is needed to transport sucrose from source cells through phloem tissue to sink cells?
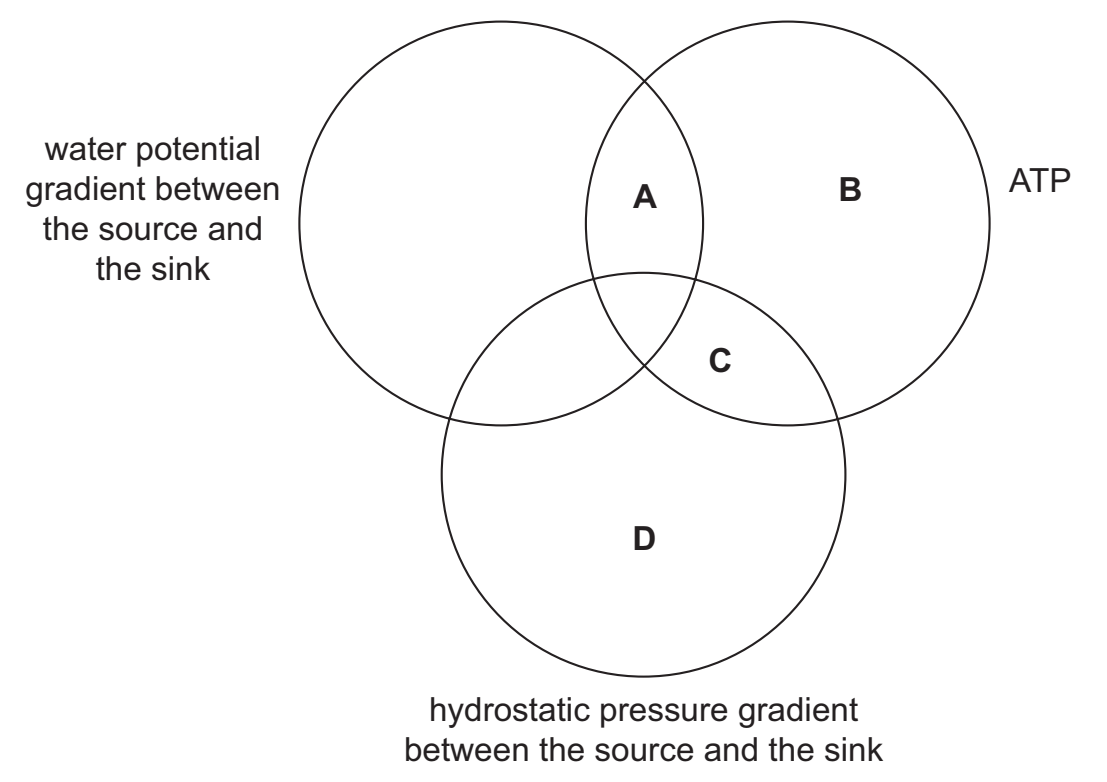
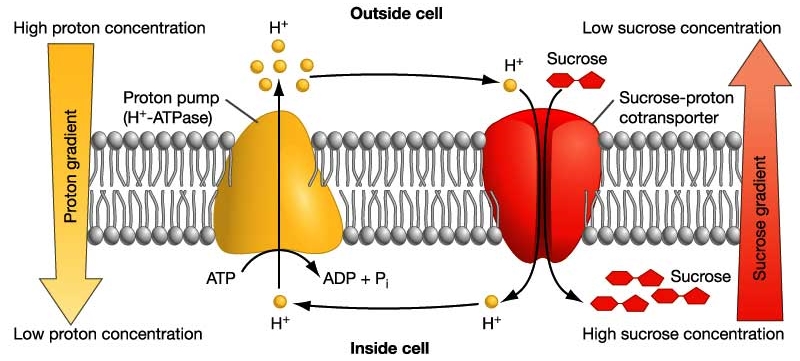
C

Q27
The sinoatrial node initiates the cardiac cycle.
What is the correct order in which the chambers of the heart contract?
A atria and ventricles at the same time
B both atria then both ventricles
C left atrium, then left ventricle, then right atrium, then right ventricle
D right atrium, then right ventricle, then left atrium, then left ventricle
B
Q28
The graph shows pressure changes in different parts of the heart during a mammalian cardiac cycle. W, X, Y and Z indicate when a valve opens or closes.
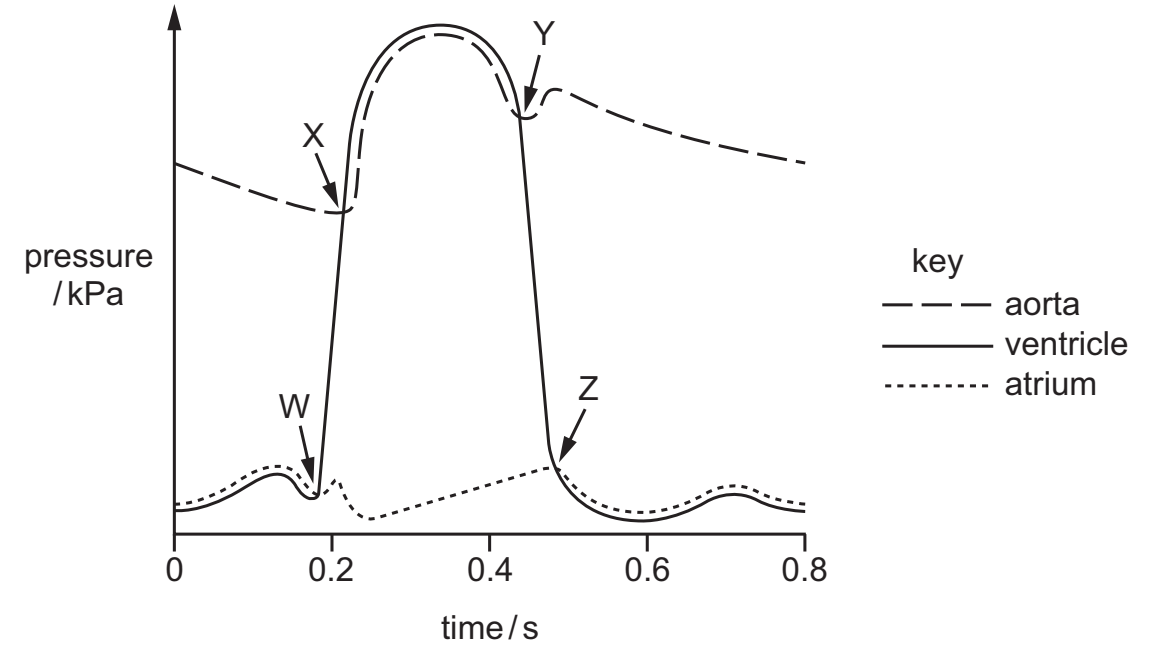
Which row is correct?
| W | X | Y | Z | |
| A B C D | opens opens closes closes | closes opens opens closes | closes closes closes opens | opens opens opens opens |
C
Q29
What can combine with the haem group of a haemoglobin molecule?
1 oxygen
2 carbon dioxide
3 carbon monoxide
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 3 only
C 1 only
D 2 and 3 only
B
Carbaminohemoglobin is a compound of hemoglobin and carbon dioxide, and is one of the forms in which carbon dioxide exists in the blood.
Q30
What is the main reaction occurring in blood capillaries at the gas exchange surface in a human lung?
A Carbonic acid dissociates into carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions.
B Carbonic anhydrase converts carbon dioxide into hydrogencarbonate ions.
C Carbon dioxide combines with haemoglobin to form carbaminohaemoglobin.
D Carbon dioxide is produced from hydrogencarbonate ions by carbonic anhydrase.
D

Q31
Which reactions take place in blood that is passing through active tissues?
1 HbO8 → Hb + 4O2
2 HbO8 + H+ → HHb + 4O2
3 HCO3– + H+ → H2CO3
4 H2O + CO2 → H2CO3
A 1, 2, 3 and 4
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 1, 3 and 4 only
D 2 and 3 only
B

Q32
Which row shows the tissues that are present in the wall of the trachea and in the wall of the bronchus?
| cartilage | squamous epithelium | goblet cells | |
| A B C D | ✓ ✓ ✓ x | ✓ ✓ x ✓ | ✓ x ✓ x |
key
✓= present
x = not present
C
Alveoli has squamous epithelial cells, whereas the bronchi has colomnar cells.

Q33
In some cases where a person has lung disease, the partial pressure of oxygen in the pulmonary veins is less than the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli.
What could explain the difference in partial pressure of oxygen?
1 A high proportion of alveoli are collapsed and do not have enough alveolar capillaries.
2 The partial pressure of oxygen in the pulmonary arteries is lower than in the alveolar air.
3 The rate of diffusion of oxygen from the alveolar air to the surrounding alveolar capillaries is too slow.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
C
Q34
How many times must a molecule of carbon dioxide pass through a cell surface membrane as it diffuses from the plasma, through a cell in the capillary wall, into an alveolus?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
D
Q35
Which disease is spread by a vector?
A AIDS / HIV
B cholera
C malaria
D measles
C
Q36
Which statement explains why a one-dose vaccination programme for measles has not yet
eliminated the disease?
A Many infants under the age of eight months have passive immunity.
B Some children need several booster doses to develop full immunity.
C The one-dose measles vaccine has a success rate of 93%.
D The virus does not often change its antibodies.
B
Q37
What has contributed to the increase in antibiotic resistance in bacteria?
1 increased use of vaccines for animal diseases
2 mutations in bacterial DNA
3 patients not completing their antibiotic treatment
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
D
Q38
What explains why monoclonal antibodies can be used to target cancer cells?
A Cancer cells have different antigens from normal body cells.
B Specific cancer drugs can be attached to the monoclonal antibody.
C They secrete a type of antigen that binds to a specific antibody.
D They are secreted by hybridomas of cancer cells and B-lymphocytes.
A
Q39
Which statements correctly describe lymphocytes?
1 Each B-lymphocyte has the ability to make several types of antibody molecules.
2 Some B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes become memory cells.
3 Plasma cells secrete antibodies into the blood plasma.
4 Some T-lymphocytes stimulate macrophages to kill infected cells.
A 1, 2, 3 and 4
B 1, 2 and 3 only
C 1 and 4 only
D 2, 3 and 4 only
D
Q40
A country introduced a measles vaccination during a measles epidemic. Later, it was realised that vaccinated children were more likely to survive childhood than
unvaccinated children, even when there were no measles epidemics. The vaccine had given the children some protection against other pathogenic infections.
Which statement could account for this extra protection?
A B-lymphocytes produced memory cells which gave the children passive immunity to these infections.
B Memory cells produced plasma cells which secreted anti-measles antibodies that bound to antigens that closely resembled measles antigens.
C Memory cells produced plasma cells which secreted anti-measles antibodies that bound to any antigen.
D T-lymphocytes produced memory cells which gave the children natural immunity against these other infections.
B
May/June Summer (13)
Q1
Which set of measurements is correct?
| diameter of capillary | diameter of red blood cell | thickness of cell surface membrane of red blood cell | ||
| A B C D | 7 μm 7 μm 0.7 mm 0.7 mm | 7 μm 7 nm 7 μm 0.7 mm | 7 nm 7 nm 7 nm 7 μm |
A


Q2
The diagram shows an eyepiece graticule and part of a stage micrometer scale as seen using x100 magnification.
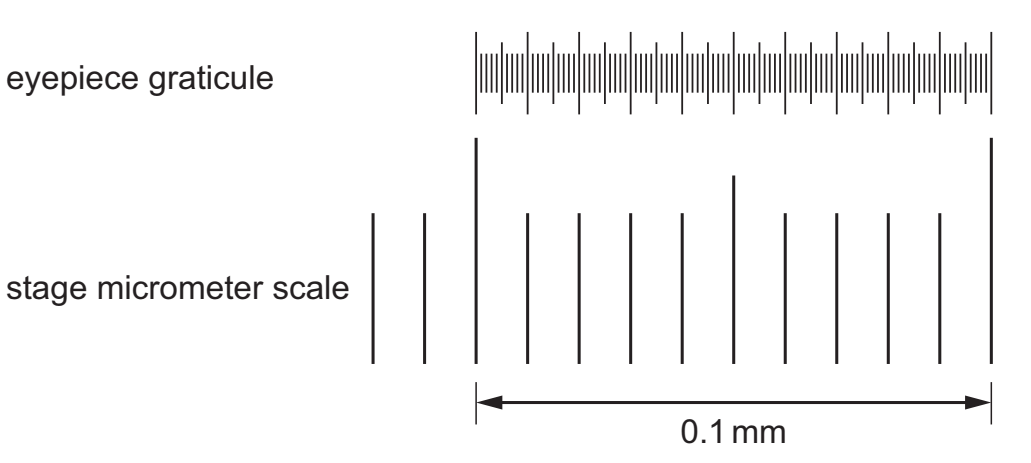
Which is the correct method for calculating the value of one eyepiece graticule unit in micrometres (μm)?
A divide 100 by 0.1 then multiply by 1000
B divide 100 by 0.1 then multiply by 1000 divided by 100
C multiply 0.1 by 1000 then divide by 100
D multiply 0.1 by 1000 then divide by 100 then divide again by 100
C
0.1mm x 1,000 = 100μm
100 EPG : 100μm
1 EPG : 1 μm (divide both sides by 100)
Q3
A prokaryotic cell, 1 μm in diameter, is magnified 50,000 times on an electron micrograph. What is the diameter as shown in the electron micrograph?
A 0.5 mm
B 5 mm
C 50 mm
D 500 mm
C
Micrograph means an image. So in other words they are asking you what is the image size.
1 μm ÷ 1000 = 0.001mm
I = AM
I = 0.001mm x 50,000
I = 50 mm
Q4
Which cell structures contain DNA?
1 mitochondria
2 chloroplasts
3 centrioles
4 nucleolus
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1, 2 and 4
C 1, 3 and 4
D 2, 3 and 4
B
Centrioles do not have DNA. They are microtubles.
Q5
Four students were asked to match the function with the appearance of some cell structures in an animal cell.
The functions were listed by number.
1 mRNA passes through to the ribosome
2 synthesis of polypeptides
3 synthesis of lipids
The appearances were listed by letter.
V membranes which surround an enclosed inner cavity
W non-membrane bound, spherical structures
X a double membrane interspersed with pores
Y non-membrane bound, cylindrical structures
Z membrane-bound sacs, arranged as a flattened stack
Which student correctly matched the numbered function with the appearance of the cell structure?
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| A B C D | V V X X | X Z W Z | Z W V V |
C
Nucleus –> Ribosomes –> Endoplasmic Reticulum
Q6
Which row is correct for structures found in eukaryotic cells?
| circular DNA | 70S ribosomes | 80S ribosomes | |
| A B C D | present present present absent | present present absent present | present absent present absent |
A
80S = Animal cells.
70S = Mitochondria (inside animal cells).
Circular DNA = Mitochondria has circular DNA.
Q7
Four solutions were tested for the presence of four different biological molecules. The appearance of the solutions after each test are shown in the table.
| solution | Benedict’s following acid hydrolysis | Benedict’s | biuret | emulsion |
| 1 2 3 4 | blue green red yellow | blue blue green yellow | purple purple purple blue | cloudy clear cloudy clear |
Which solutions contained molecules with ester bonds?
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 3 only
C 2, 3 and 4
D 2 and 4 only
B
Ester bonds = fats.
We test fats with the emulsion test.
Fats goes milky/cloudy in the presence of fats.
1 and 3 = B.
Q8
The diagrams represent two monosaccharides with the same molecular formula (C6H12O6). Both can exist in an alpha (α) or beta (β) form as shown.
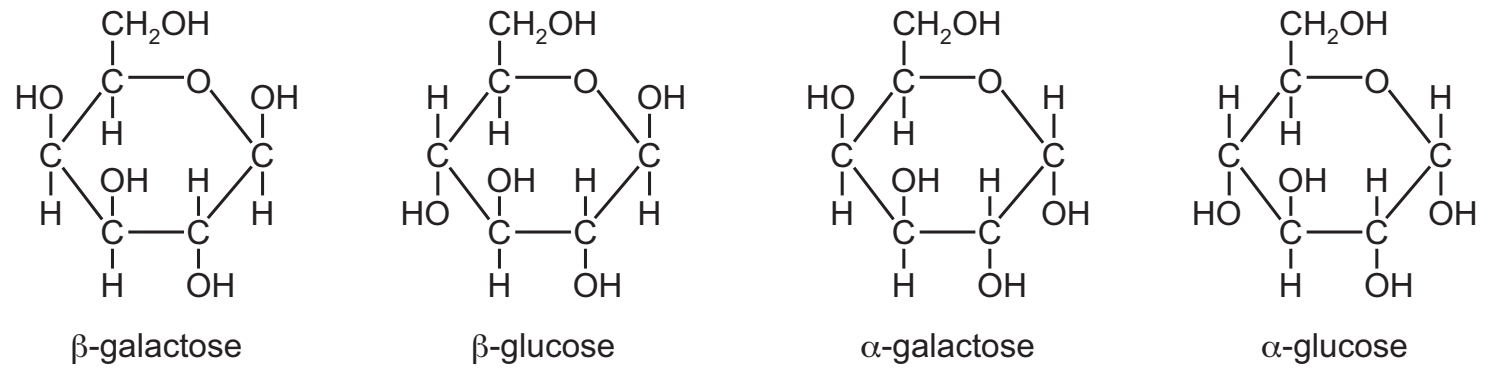
The diagram shows a lactose molecule formed by condensation between glucose and galactose.
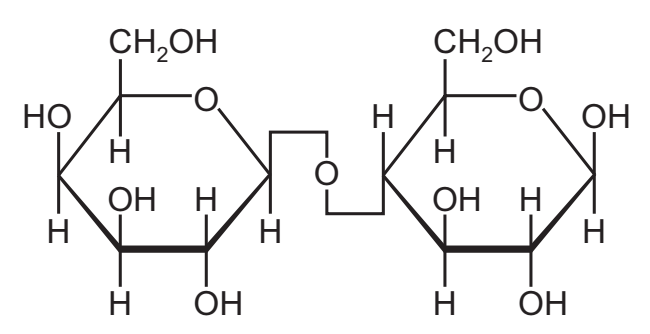
Which molecules have condensed to form lactose?
A α-glucose and α-galactose
B α-glucose and β-galactose
C β-glucose and α-galactose
D β-glucose and β-galactose
D
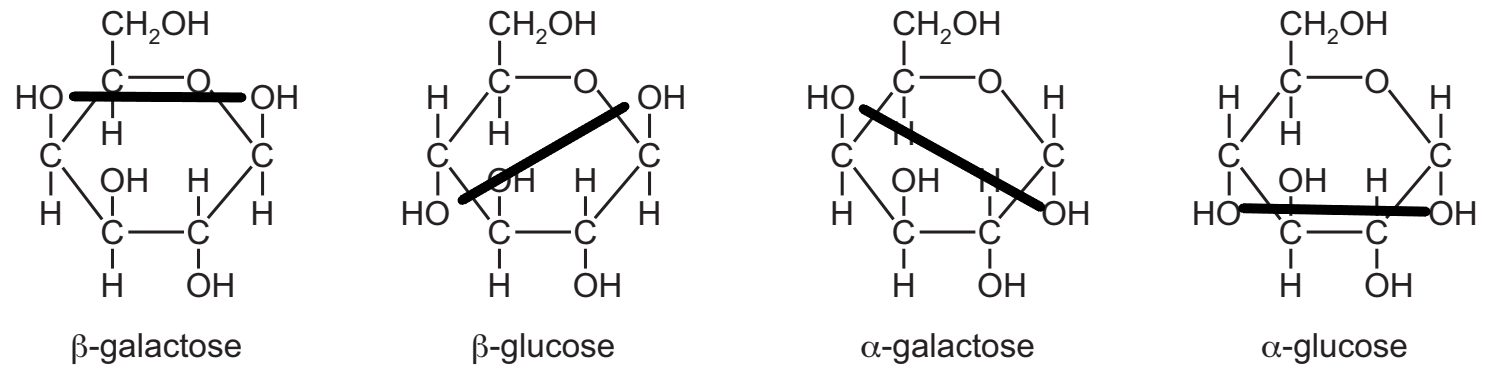

Q9
One type of covalent bond between two monomers is shown.

Which molecules contain this type of covalent bond?
A amylopectin, amylase, glycogen and starch
B amylopectin, amylase and glycogen only
C amylopectin, glycogen and starch only
D amylase, glycogen and starch only
C

Q10
Which statements about carbohydrates and triglycerides are correct?
1 They form polymers.
2 They contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
3 They are used as energy stores.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 3 only
C 1 only
D 2 and 3 only
D
A polymer is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules, or macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Triglycerides does not consist of identical repeating units.
Q11
Which molecules contain at least three double bonds?
A saturated fatty acid, collagen and haemoglobin
B collagen and saturated fatty acid
C haemoglobin and collagen
D saturated fatty acid and haemoglobin
C

Q12
The diagrams show the structures of two amino acids. One contains two amino (–NH2) groups, labelled 1 and 2. The other contains two carboxylic (–COOH) groups, labelled 3 and 4.
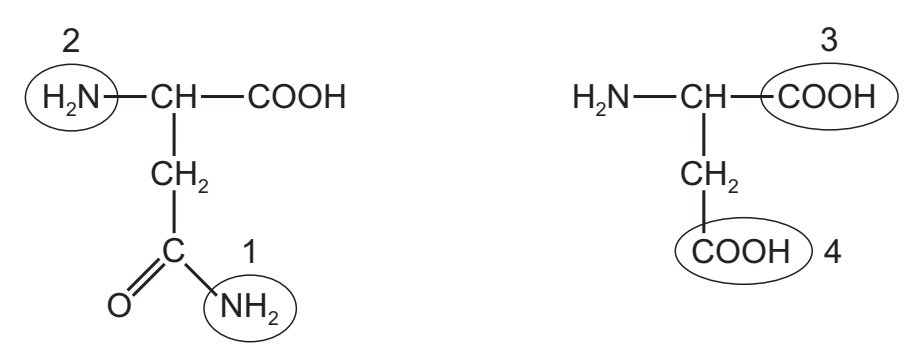
A peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids. Which groups form the peptide bond?
A 1 and 4
B 2 and 3
C 2 and 4
D 1 and 3
B


Q13
Which row about the structure of proteins is correct?
| primary structure | secondary structure | tertiary structure | quaternary structure | |
| A | is the number of amino acids present in a protein | is the right-handed spiral formed by the primary structure | is the result of cross-bonding between specific amino acids in the primary structure | is the sub-unit polypeptides that link together to form a protein |
| B | is the order of amino acids present in a protein encoded by DNA | is the coiling of a chain of amino acids to form a β-pleated sheet or an α-helix | is the shape formed by the folding of a polypeptide and is held together by hydrogen bonds | contains two types of polypeptide that interact forming the shape of a protein |
| C | is the result of translation of an mRNA molecule by a ribosome into a chain of amino acids | occurs because of an attraction between hydrogen and oxygen atoms in the peptide bonds | is the result of ionic and hydrogen bonds, disulfide bridges and hydrophobic interactions between amino acids | is formed by four polypeptides and an additional reactive group attached to the protein |
| D | is the sequence of amino acids in a protein coded by an mRNA molecule | is formed by hydrogen bonding between amino acids forming the primary structure | is formed as a result of interaction of the side chains of amino acids in the primary structure | is formed by the linking together of more than one polypeptide to form a protein |
D

Q14
The enzyme β-galactosidase can catalyse the hydrolysis of four substrates with similar structures.
Each substrate gives a different Km value. For which substrate does β-galactosidase have the highest affinity?
| substrate | Km / mol dm–3 | |
| A B C D | 1 2 3 4 | 4 x 10–3 1 x 10–3 2 x 10–4 1 x 10–4 |
D
Arrange the numbers from smallest to highest. 1 x 10–4 = 0.0001 is the smallest.

Q15
An investigation was carried out on the effect of temperature on the activity of an enzyme when it is immobilised and when it is non-immobilised (free in solution). The product of the enzymecatalysed reaction causes a decrease in pH.
The graph shows the results of the investigation.
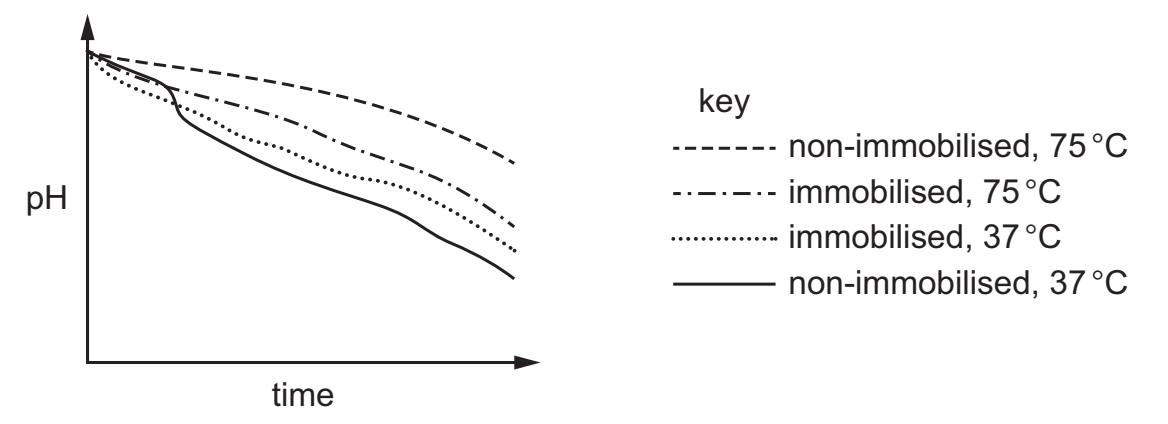
Which would give the highest yield of product?
A immobilised, 37 °C
B immobilised, 75 °C
C non-immobilised, 37 °C
D non-immobilised, 75 °C
C
The product of the enzymecatalysed reaction causes a decrease in pH – therefore the product concentration is directed correlated acidity of the medium. More acidic = higher product yield. The line which lies the closest to the x-axis therefore will have the lowest pH and therefore also the highest product yield.
Q16
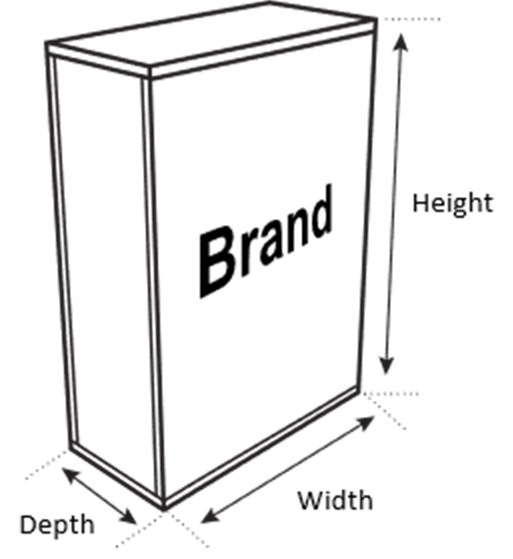
An indicator mixed with agar forms a pink colour. The pink-coloured agar becomes colourless when put in acid. Blocks of pink-coloured agar are cut to different sizes and put in acid. All other variables are kept constant.
Which block becomes colourless most quickly?
A 3 mm x 30 mm x 30 mm
B 6 mm x 6 mm x 6 mm
C 6 mm x 12 mm x 12 mm
D 12 mm x 12 mm x 12 mm
A
The object with the lowest value for either height, depth or width will have the highest diffusion rate. This is because the distance to diffuse through that dimension of the object is least. Acid will be able to penetrate the object much faster at that point/side.
Q17
Three identical plant cells were put into one of three different concentrations of sugar solution, 10%, 5% and 2.5%. The cells were left for 50 minutes and then observed using a light microscope.
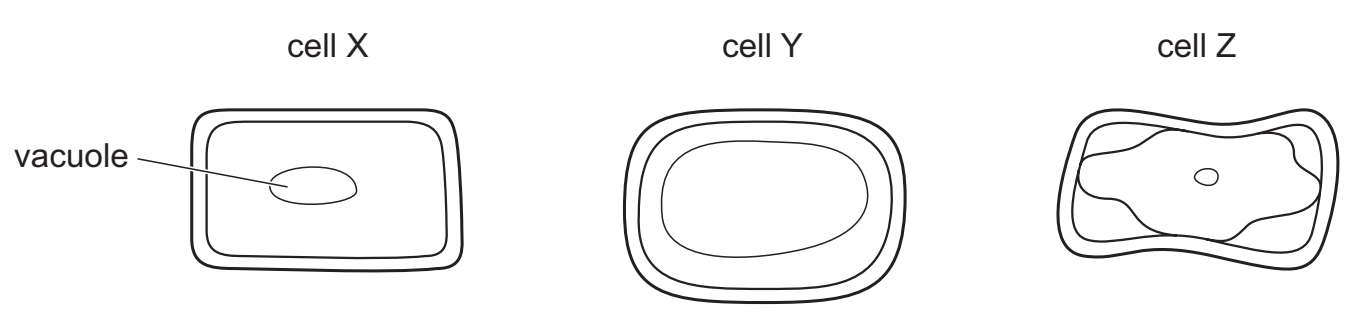
Which statement is not correct?
A Cell X has the same water potential as the sugar solution it was put into.
B Cell Y is turgid and cell Z is plasmolysed.
C Cell Y was put into the 2.5% sugar solution.
D Cell Z had a more negative water potential than the sugar solution it was put into.
D
Remember: the more negative the water potential value, the more solutes it has suspended in it. Which means it has a higher “water pulling” ability. Pure water has a water potential of zero.
Cell Z clearly lost water which means that the solution outside the sell was able to “pull water” from it. It therefore had to have had a more negative water potential (relative to the cytoplasm).

Q18
How many copies of each different DNA molecule are found in a cell at the start of each of these stages of the mitotic cell cycle?
| G2 of interphase | prophase | cytokinesis | |
| A B C D | 1 1 2 2 | 1 2 1 2 | 2 1 2 2 |
D
Replication takes place after G1 phase, i.e, during the S phase.
Q19
Hydra are simple animals which can reproduce asexually. The photomicrograph shows an adult hydra with a new hydra developing while attached to the side of the adult animal.

Which processes have occurred in the two hydra?
1 DNA replication
2 growth
3 mitosis
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
A
Q20
The diagram represents a nucleotide containing thymine.
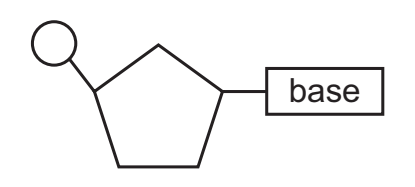
Which statements about this nucleotide are correct?
1 Thymine is a pyrimidine.
2 Base pairing occurs with two hydrogen bonds.
3 The carbohydrate can be ribose or deoxyribose.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
B
Q21
Some of the events that occur during transcription are listed.
1 Bonds break between complementary bases.
2 Bonds form between complementary bases.
3 Sugar-phosphate bonds form.
4 Free nucleotides pair with complementary nucleotides.
Before the mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus, which events occur twice during transcription?
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1, 3 and 4
C 2, 3 and 4
D 1 and 2 only
D
Q22
The table shows the DNA triplet codes for some amino acids.
| amino acid | DNA triplet code | amino acid | DNA triplet code |
| arginine arginine arginine asparagine asparagine cysteine cysteine STOP | GCA GCC GCG TTA TTG ACA ACG ATC | glycine glycine glycine lysine lysine proline proline valine | CCA CCG CCT TTC TTT GGA GGC CAC |
The base sequence on the DNA template strand coding for part of a polypeptide is shown.
CCA TTC ACG GCG TTA GCA
Two mutations occur in this sequence during DNA replication.
Which mutated DNA would result in a polypeptide with one different amino acid?
A CCA ATC ACG GCG TTG GCA
B CCA TTC ACA GCA TTA GCA
C CCA TTC ACG CCG TTA GCC
D CCT TTC ACG GCG TTA GCC
C
Q23
A gene codes for the sequence of amino acids in a single polypeptide. Haemoglobin consists of two α-globins and two β-globins.
How many genes are needed to code for a single haemoglobin molecule?
A 1
B 2
C 4
D 8
B
Q24
Which properties of water molecules are important in the upward flow of water through the xylem?
1 Water molecules are attracted to each other by hydrogen bonding.
2 Water molecules are attracted to cellulose by adhesion.
3 Water molecules have high cohesion in water columns.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
A
Q25
The graph shows the rate of water absorption and the rate of water loss by a plant during one 24-hour period. The plant was growing in natural conditions.
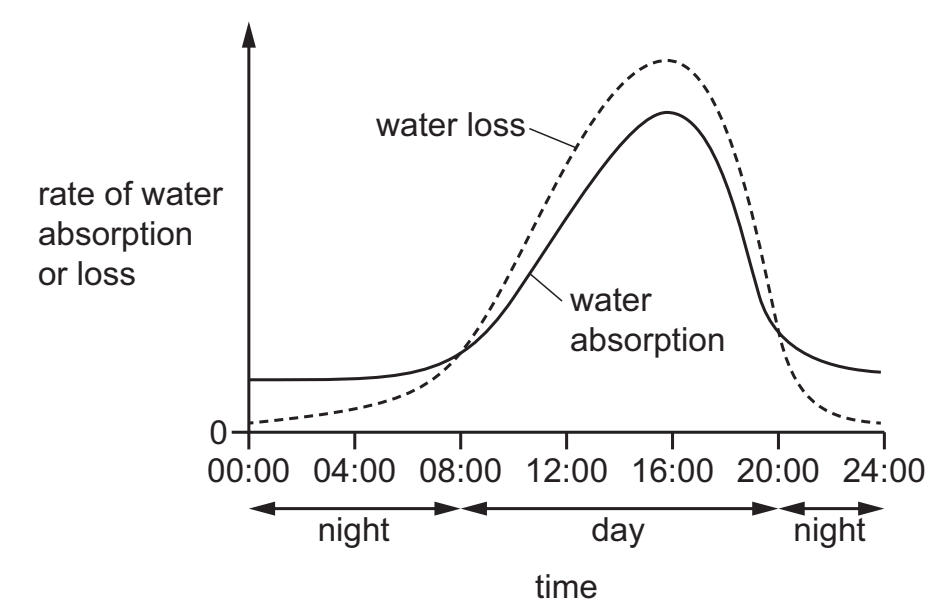
What may be concluded from the graph?
1 The rate of water absorption and the rate of water loss peak at 16:00.
2 The rate of water loss is greater than the rate of water absorption for 12 hours.
3 The rate of water absorption is greater than the rate of water loss at night.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
A
Q26
Which statements explain why a stem is cut under water and connected to a potometer under water?
1 to prevent plasmolysis of xylem vessel elements
2 to prevent the collapse of xylem vessel elements
3 to prevent air entering xylem vessel elements
A 1, 2 and 3
B 2 and 3 only
C 1 only
D 3 only
D
Q27
Sucrose moves into an actively dividing shoot tip from a phloem sieve tube element. Which changes to the water potential and the volume of liquid in the phloem sieve tube element are correct?
| water potential becomes | volume of liquid | |
| A B C D | less negative less negative more negative more negative | decreases increases decreases increases |
A
Q28
Sucrose is loaded into phloem sieve tubes from companion cells. What is the correct order of statements that explains this mechanism?
1 Hydrogen ions diffuse into companion cells through co-transporter proteins.
2 Hydrogen ions are pumped out of companion cells by active transport.
3 Sucrose diffuses into phloem sieve tubes via plasmodesmata.
4 Sucrose is co-transported along with hydrogen ions.
A 1 → 2 → 4 → 3
B 1 → 4 → 2 → 3
C 2 → 1 → 4 → 3
D 4 → 1 → 2 → 3
C
Q29
Which components are found in arteries?
B
Q30
Which diagram correctly shows the direction of the flow of blood through the heart?
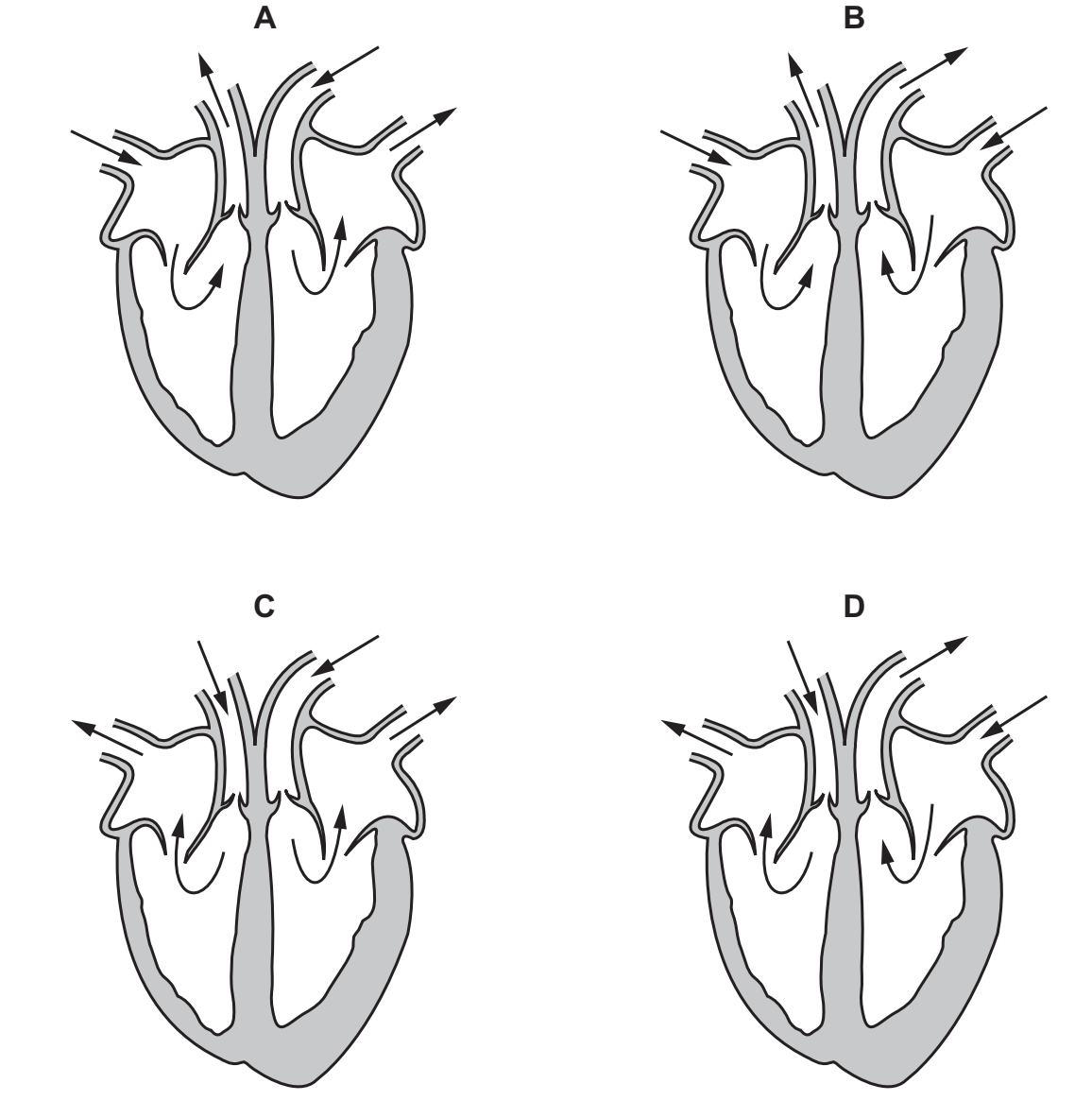
B
Q31
Which row correctly identifies the pulmonary artery?
| thickness of blood vessel wall /mm | oxygen content of blood inside vessel | blood pressure / mmHg | |
| A B C D | 1.30 2.10 0.15 0.20 | deoxygenated oxygenated oxygenated deoxygenated | 15–30 80–120 5–15 3–8 |
A
Q32
What is found in all blood vessels, lymph and tissue fluid?
1 carbon dioxide
2 glucose
3 white blood cells
4 antibodies
A 1, 2, 3 and 4
B 1, 2 and 3 only
C 1, 3 and 4 only
D 2 and 4 only
A
Q33
At high altitudes, the oxygen content of the air may be a third of that at sea level. As a person slowly climbs a mountain, their body gradually adjusts to the high altitude.
What is increased during this period of adjustment?
A the concentration of haemoglobin in the red blood cells
B the oxygen-carrying capacity of the haemoglobin
C the number of red blood cells per mm3 of blood
D the rate at which haemoglobin releases oxygen into the tissues
C
Q34
Which row correctly shows features present in terminal bronchioles?
| cartilage | cilia | smooth muscle | |
| A B C D | ✓ ✓ x x | ✓ x ✓ ✓ | x ✓ ✓ x |
key:
✓= present
x = not present
C
Q35
The photomicrograph shows a section through lung tissue.
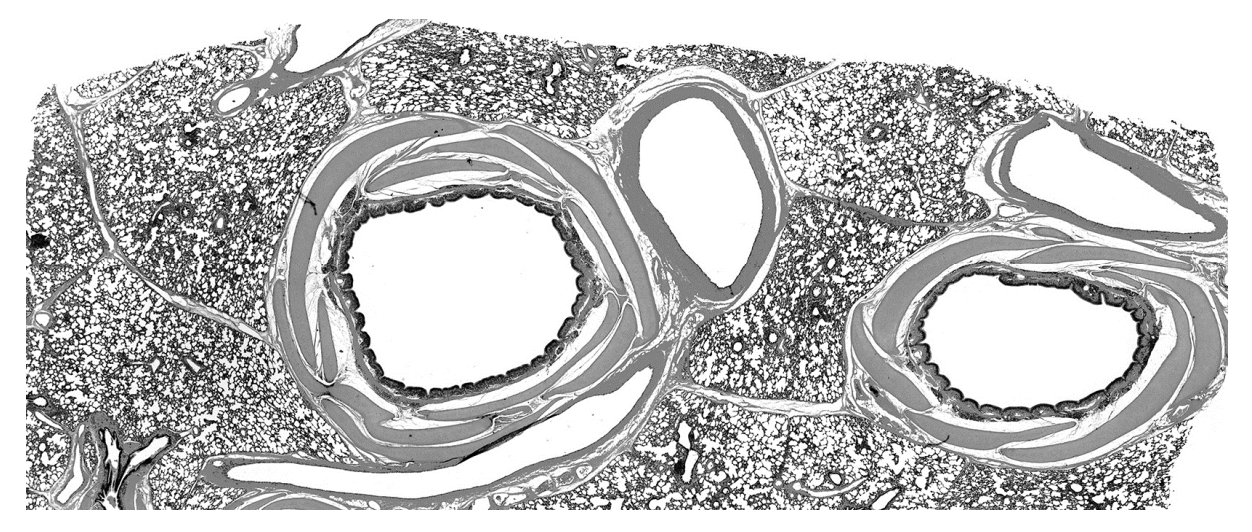
Which structures are present in this photomicrograph?
| artery | vein | bronchus | trachea | |
| A B C D | ✓ ✓ x x | ✓ x ✓ x | ✓ x x ✓ | x ✓ ✓ ✓ |
key:
✓= present
x = not present
A
Q36
The symptoms of two diseases are listed.
| disease 1 | disease 2 |
| coughing up blood pain when breathing loss of weight | shortness of breath difficulty breathing out fatigue |
Which row identifies diseases 1 and 2?
| disease 1 | disease 2 | |
| A B C D | chronic bronchitis emphysema lung cancer lung cancer | emphysema lung cancer chronic bronchitis emphysema |
D
Q37
Disease transmission can be reduced in different ways.
+ antibiotic therapy for sufferers
+ vaccination for non-sufferers
+ more living space per person
The transmission of which disease can be reduced by all of these methods?
A cholera
B TB
C malaria
D measles
B
Q38
What do pathogens of HIV / AIDS, malaria and TB have in common?
| cell surface membrane | genes | ribosomes | |
| A B C D | ✓ ✓ x x | ✓ x ✓ ✓ | ✓ x ✓ x |
key
✓ = common to all three pathogens
x = not common to all three pathogens
D
Q39
The diagram shows the immune response following infection by a virus.
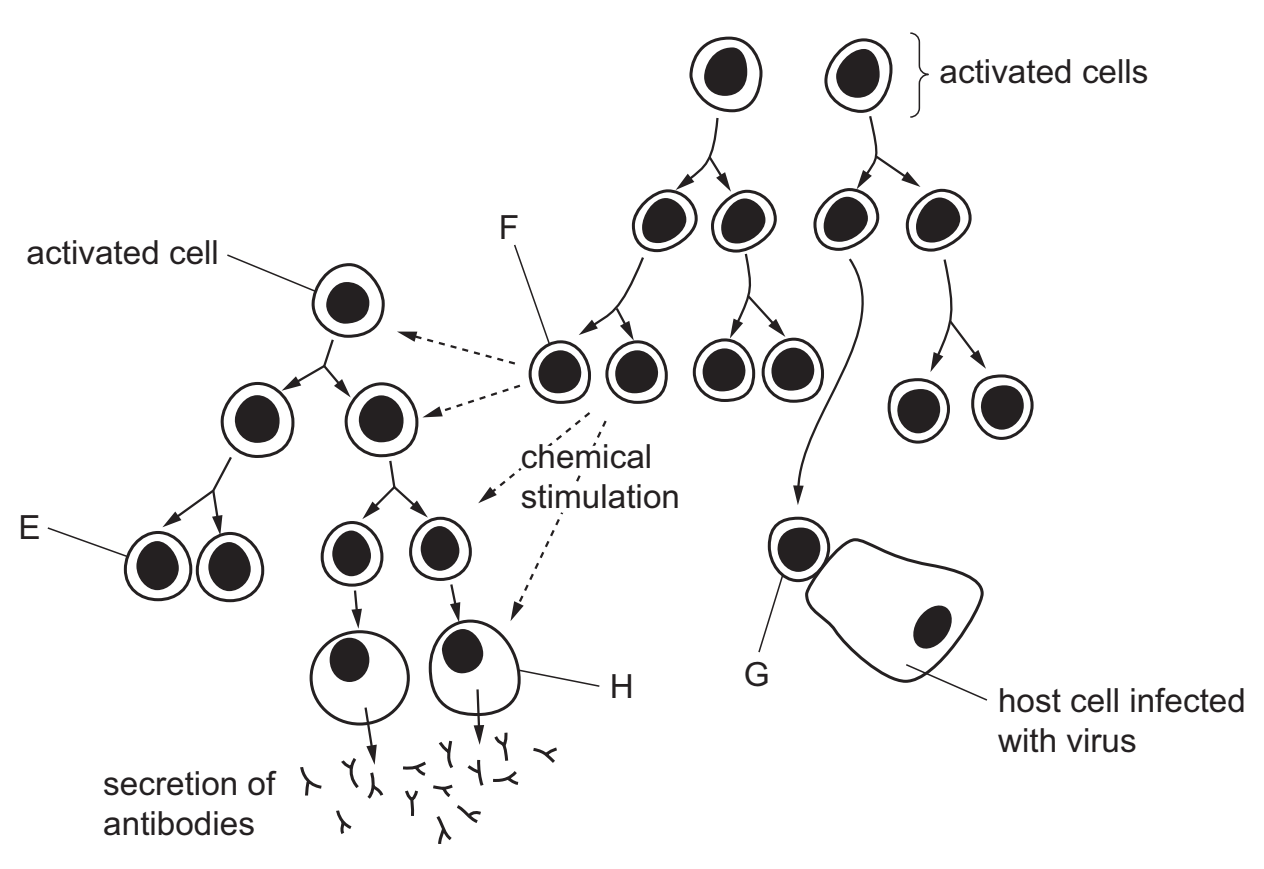
Which row identifies the cells labelled E, F, G and H?
| E | F | G | H | |
| A B C D | B-memory cell B-memory cell plasma cell T-killer cell | T-helper cell T-memory cell T-memory cell B-memory cell | T-killer cell macrophage T-helper cell macrophage | plasma cell plasma cell B-memory cell T-helper cell |
A
Q40
Monoclonal antibodies are used to test for the presence of the hormone HCG in the urine of a human female during early pregnancy.
Which statements describe how the monoclonal antibodies used in this test are produced?
1 HCG is injected into a mouse, and plasma cells in the mouse produce antibodies specific to HCG.
2 Antibodies are extracted from the mouse and then fused with cancer cells to produce hybridoma cells.
3 Single hybridoma cells are cultured and they divide by mitosis to produce a clone of hybridoma cells.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
C