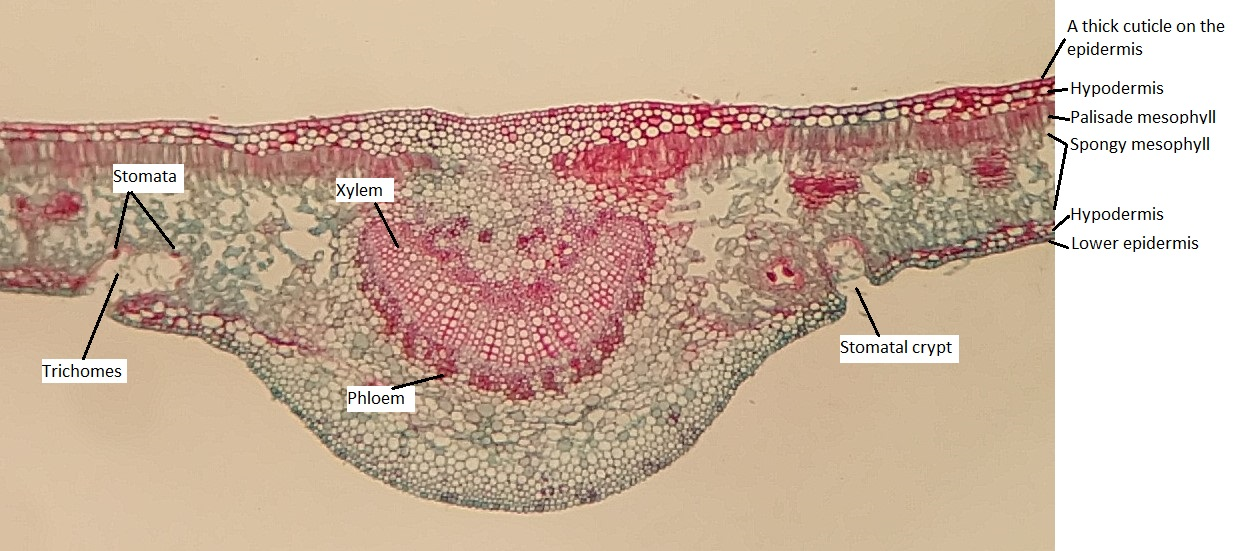
7.06 Xerophytes
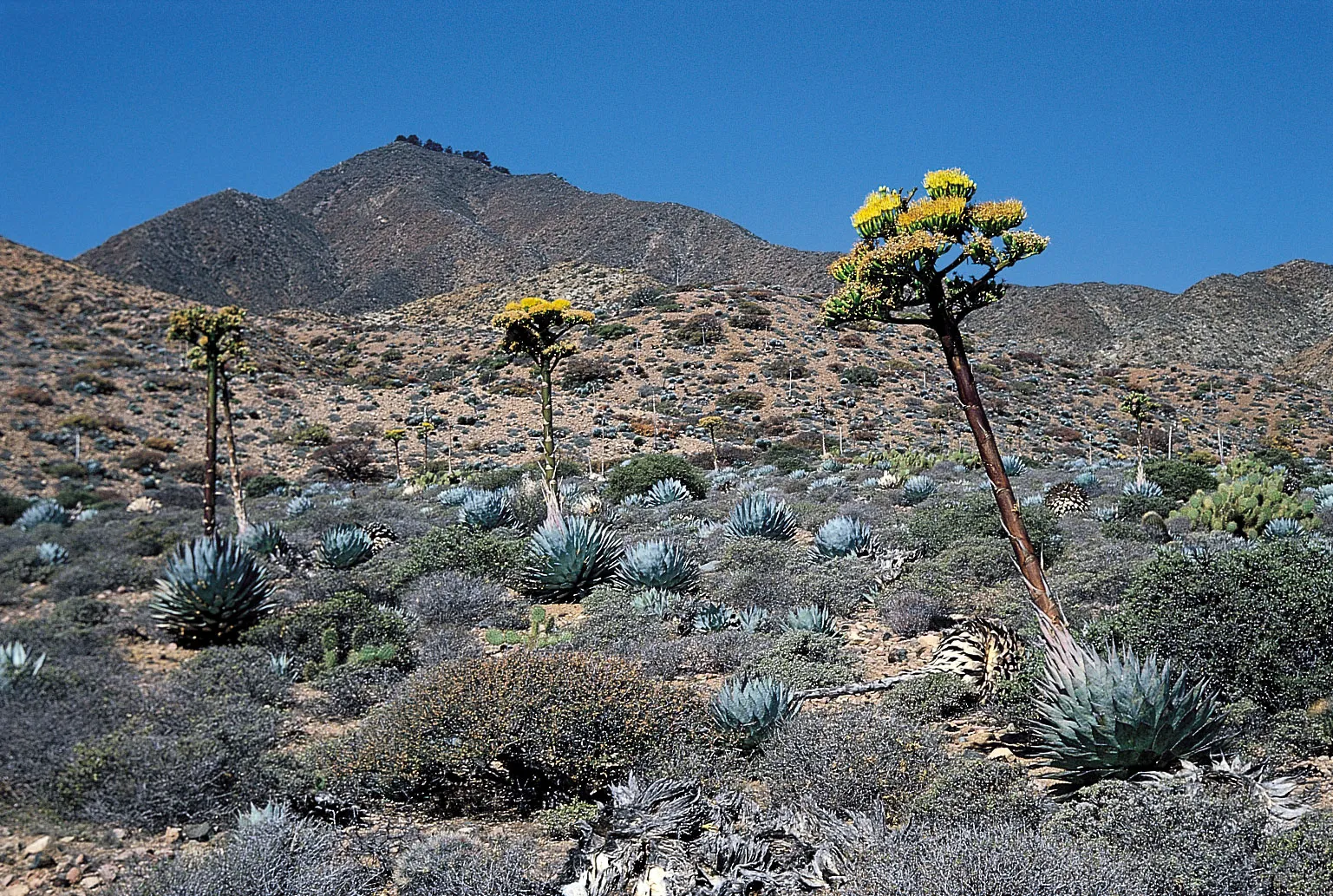

Definition:
- Xerophytes: Plants adapted to live in environments with limited water availability.
Question
Explain two structural adaptations of xerophytes that help them survive in dry environments. For each adaptation, describe how it reduces water loss.
Thick, waxy cuticle:
- The waxy cuticle forms a waterproof layer on the leaf surface.
- This reduces water evaporation by minimizing transpiration through the epidermis, helping the plant retain water.
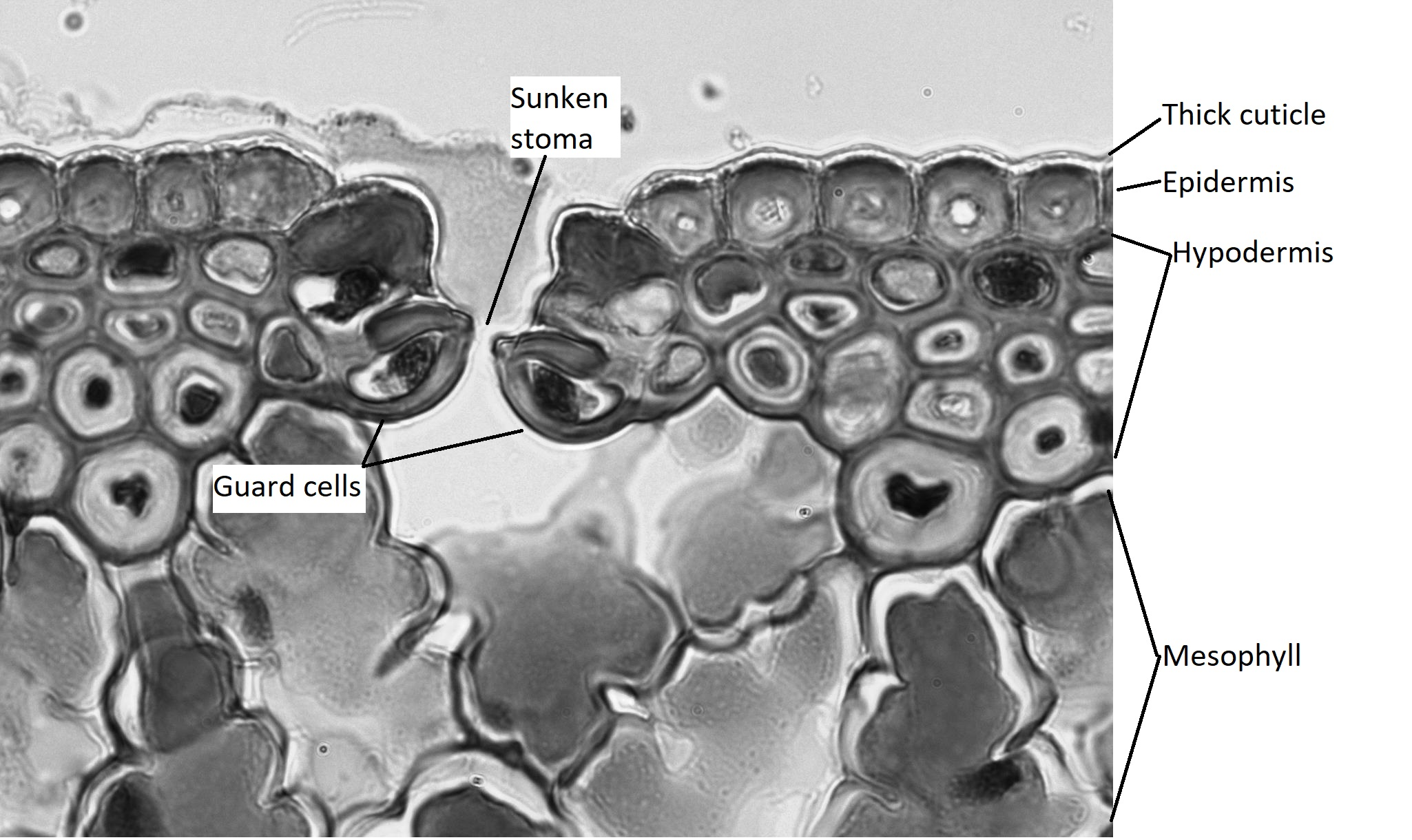
Sunken stomata:
- Stomata are located in pits or depressions on the leaf surface.
- This traps humid air around the stomata, reducing the water vapor concentration gradient between the leaf and the surrounding air, which slows down transpiration.

Key Adaptations of Xerophytes to Minimize Water Loss:
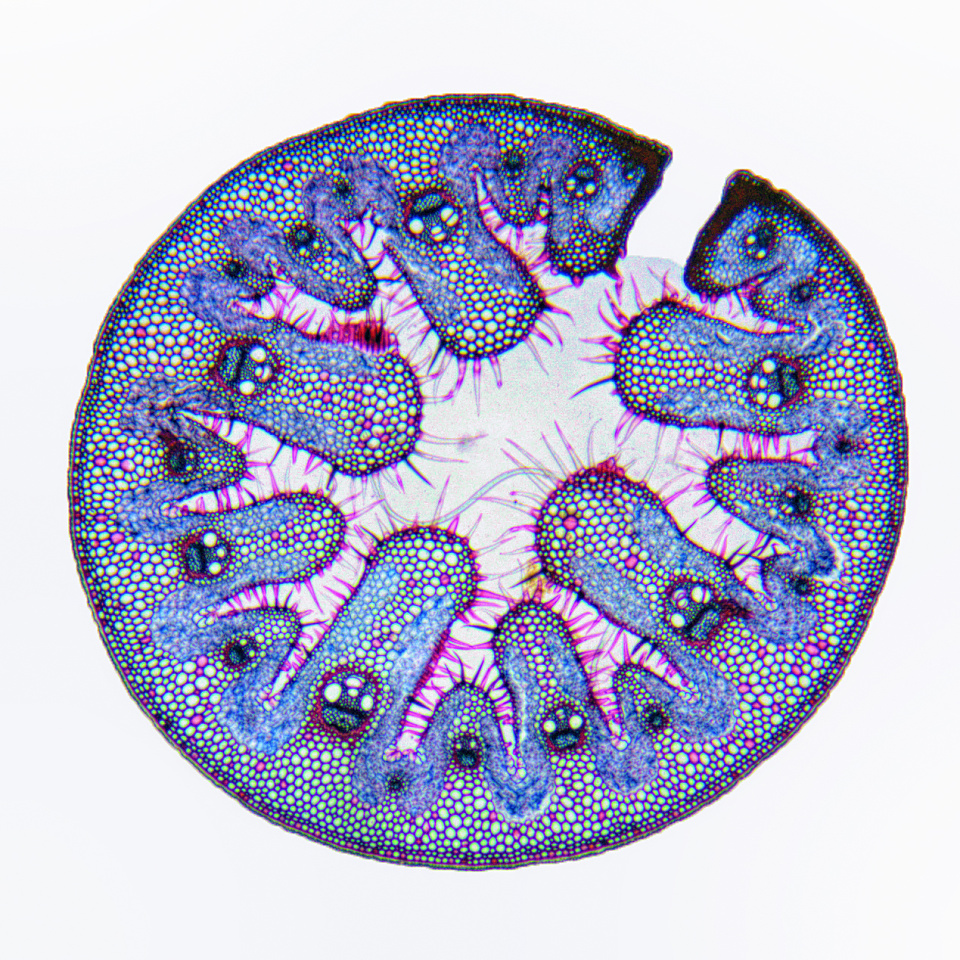
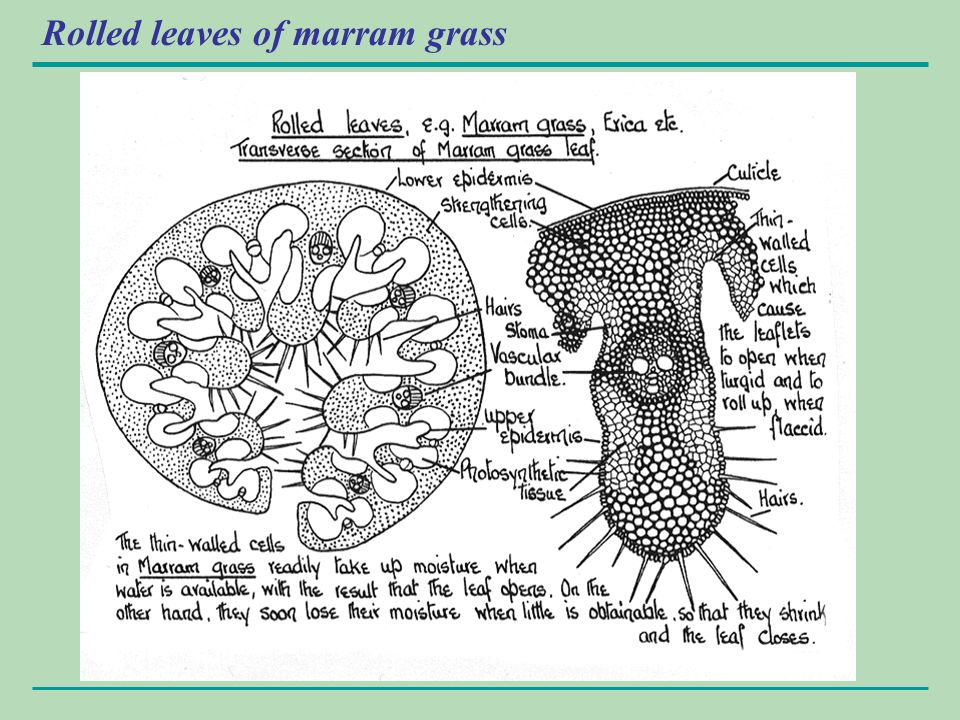
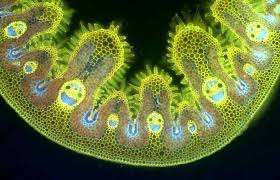
Rolled Leaves (e.g., Marram Grass – Ammophila arenaria):
- Leaf Structure: Leaves roll up due to the shrinkage of hinge cells, exposing a thick waterproof cuticle on the outside.
- Cuticle: Contains cutin, a fatty, water-resistant substance that reduces water loss.
- Stomatal Placement: Stomata are located only on the upper epidermis, opening into the enclosed, humid area within the roll to limit water loss.
- Hairs: Trap a layer of moist air inside the roll, decreasing the water vapor diffusion gradient, reducing transpiration.
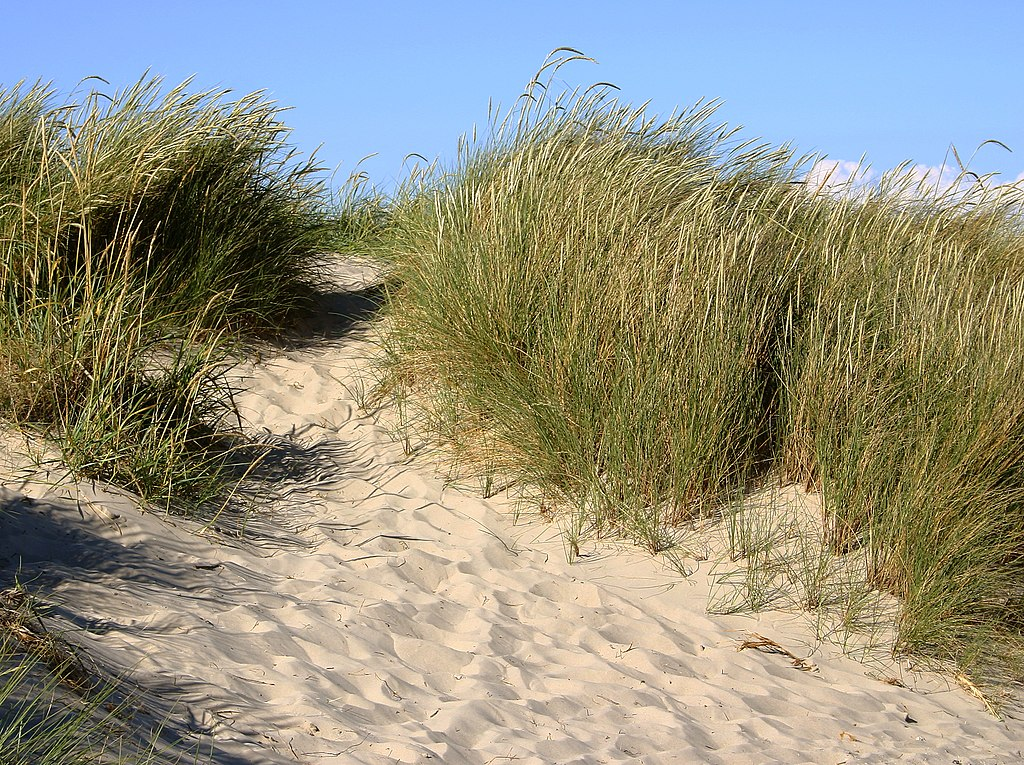

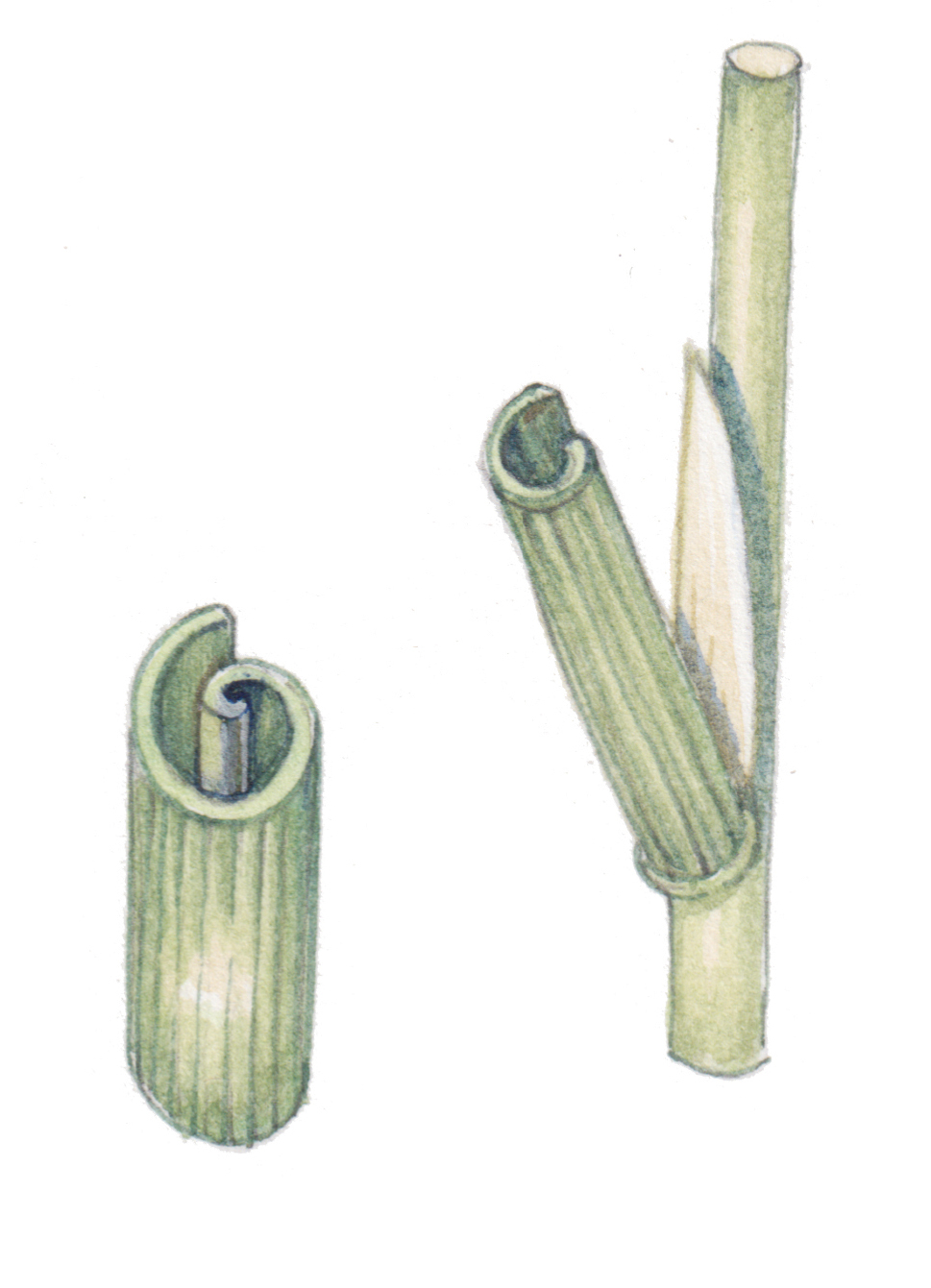
Question
Explain how rolled leaves in xerophytes like Marram grass (Ammophila arenaria) help reduce water loss in dry environments.
Rolled Leaves:
- The leaf rolls up to trap moist air inside the rolled structure.
- This creates a region of high humidity near the stomata, reducing the water vapor concentration gradient between the inside of the leaf and the surrounding dry air.
- Fewer stomata are exposed directly to the air, which minimizes water loss through transpiration.
- Additionally, the rolled shape reduces the overall leaf surface area exposed to wind, further limiting water loss.
Reduced Leaves (e.g., Opuntia – Cactus):
- Leaf Modification: Leaves are reduced to spines, lowering surface area and thus reducing water loss.
- Photosynthesis Location: Flattened, water-storing stems take over photosynthesis.
- Defense Mechanism: Spines deter animals from eating the plant, protecting water stores.
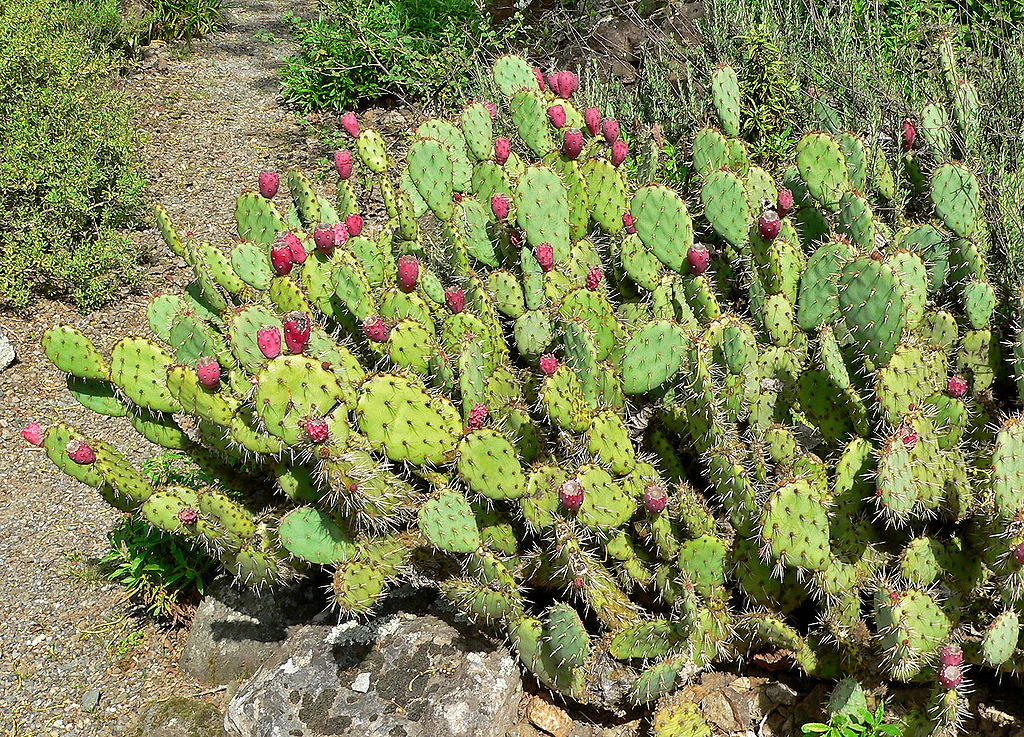
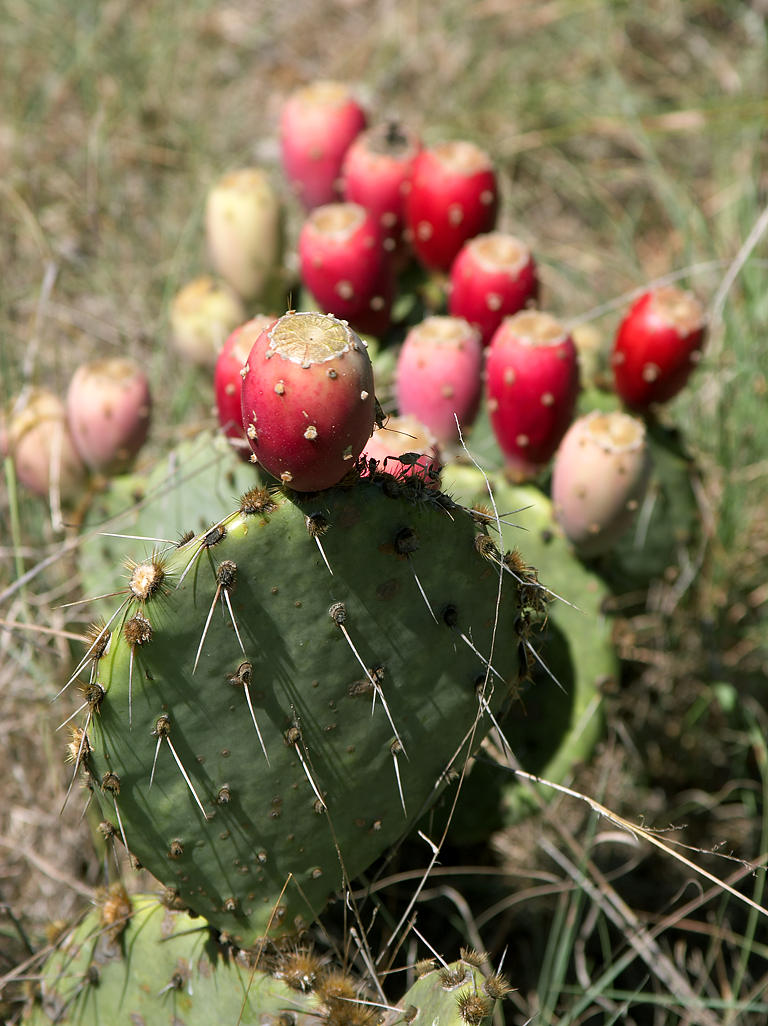


Needle-Like Leaves (e.g., Sitka Spruce):
- Leaf Form: Needle-shaped leaves minimize surface area exposed to the air, reducing transpiration.
- Waterproofing: Leaves are covered in a thick wax layer.
- Sunken Stomata: Stomata are located in grooves or pits, reducing exposure to air currents and minimizing water loss.
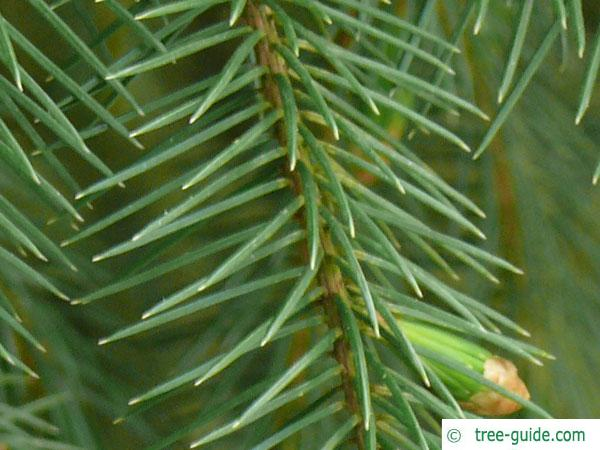


Question
Describe how the reduced leaves in xerophytes, such as Opuntia (Cactus), help the plant survive in arid conditions. Include the role of stems and an additional benefit of this adaptation.
Reduced Leaves (Spines):
- Leaves are modified into spines, which significantly reduce the surface area available for water loss through transpiration.
- This adaptation conserves water in dry environments.
Photosynthesis in Stems:
- Photosynthesis occurs in the flattened, green stems (also called cladodes), which are water-storing structures.
- The thick, fleshy stems help store water and minimize evaporation.
Defense Mechanism:
- The spines act as a deterrent to herbivores, preventing animals from eating the cactus and accessing its water stores.
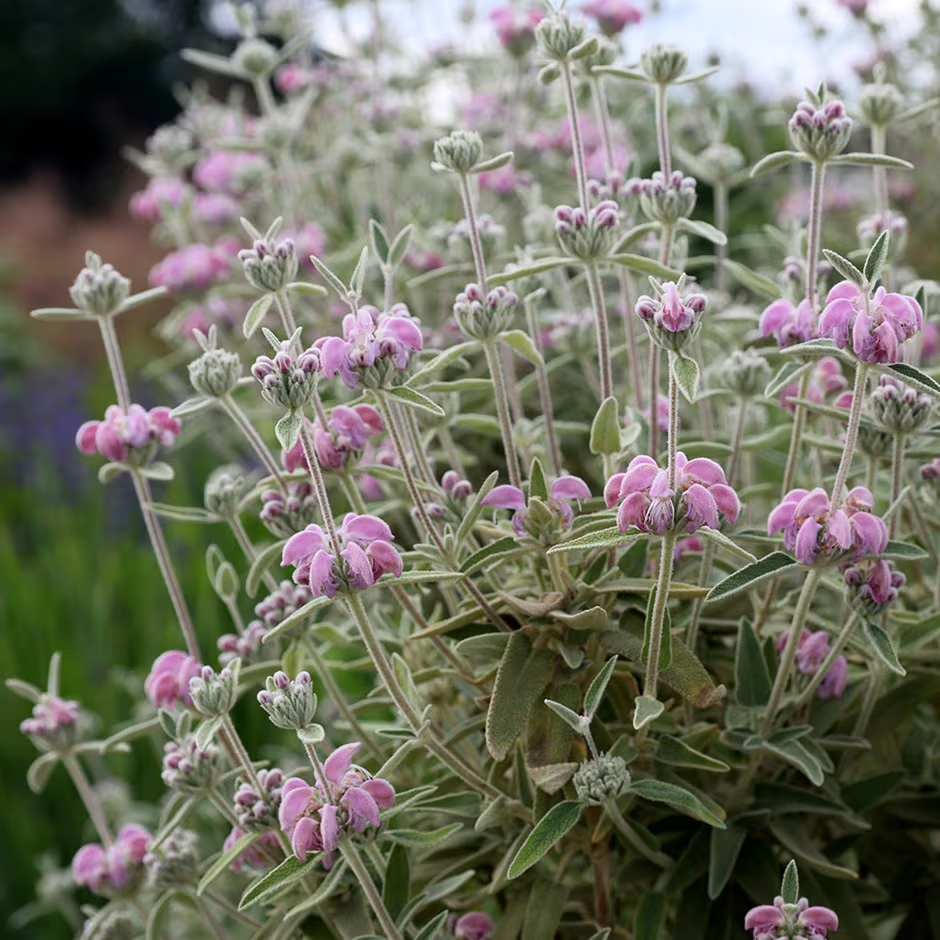
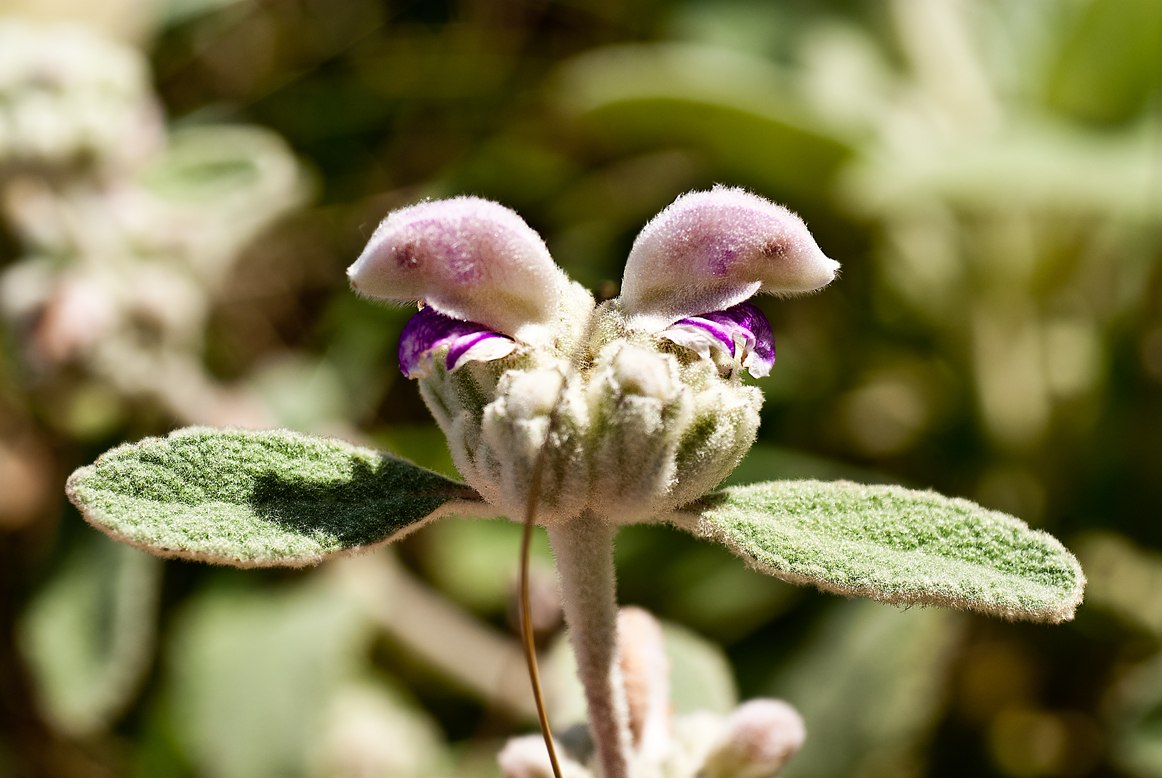
Trichomes (e.g., Phlomis italica):
- Leaf Hairs (Trichomes): Hair-like structures on leaf surfaces trap moisture and reduce water loss, similar to the hairs on marram grass.
- Habitat: Common in small shrubs in Mediterranean dry habitats.


Question
Explain how trichomes (leaf hairs) in xerophytes like Phlomis italica reduce water loss and help the plant survive in dry environments.
Trichomes (Leaf Hairs):
- The hair-like structures on the leaf surface trap a layer of moist air close to the leaf.
- This reduces the water vapor concentration gradient between the leaf and the surrounding dry air, slowing down transpiration.
Additional Effect:
- Trichomes can also reflect sunlight, reducing the leaf surface temperature and lowering evaporation rates.
Habitat Adaptation:
- Phlomis italica is commonly found in Mediterranean dry habitats, where water conservation is essential for survival during long dry periods.
Succulent Stems (e.g., Euphorbia canariensis):
- Stem Adaptation: Swollen stems store water for long-term use.
- Photosynthesis: Stems carry out photosynthesis, reducing reliance on leaf structures.
- Wax Coating: Thick wax layer reduces water loss by forming a barrier.
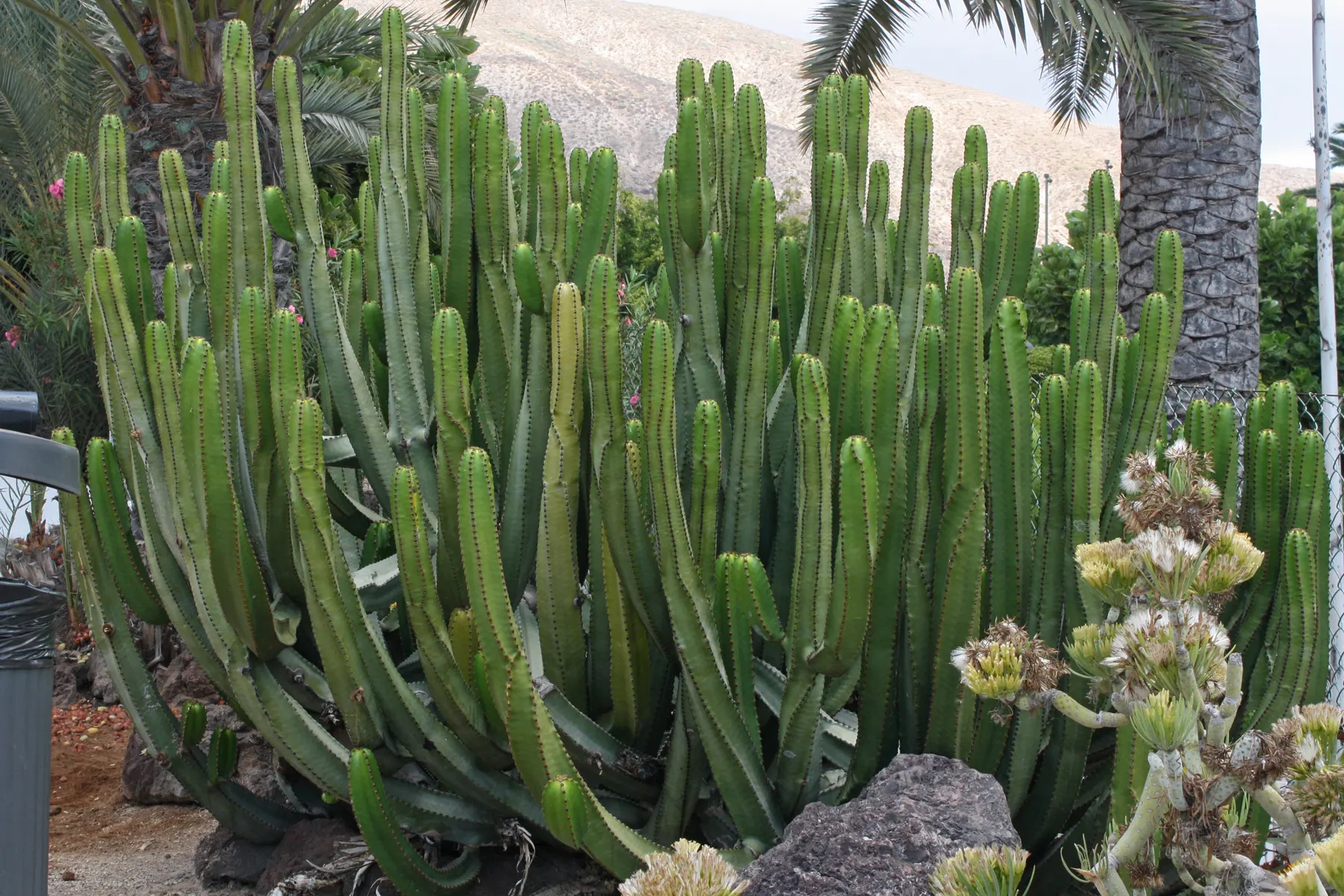
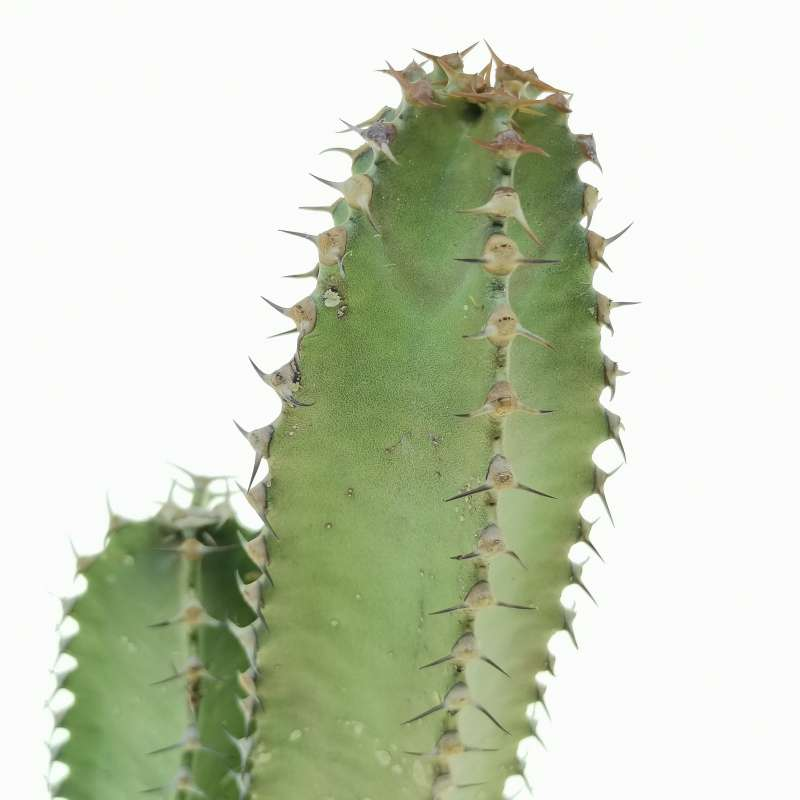


Explain how the succulent stems in xerophytes like Euphorbia canariensis are adapted to survive in dry environments. Include their role in photosynthesis and water conservation.
Water Storage in Succulent Stems:
- The stems are swollen and fleshy, allowing them to store large amounts of water.
- This water is used during periods of drought, helping the plant survive long dry spells.
Photosynthesis in Stems:
- The stems carry out photosynthesis (instead of leaves), reducing the need for large leaves that would otherwise lose water through transpiration.
- This adaptation ensures the plant can still produce food while conserving water.
Wax Coating:
- A thick waxy layer covers the stem, creating a waterproof barrier that reduces water loss through evaporation.
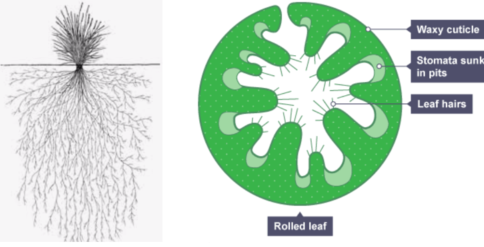
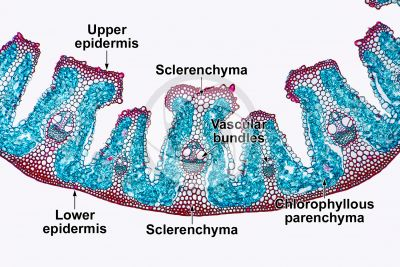
Practical Study of Xerophytes (e.g., Marram Grass – Ammophila arenaria):
- Observation under Microscopy:
- Use a light microscope to examine a transverse section (TS) of a marram grass leaf.
- Low-Power Plan Drawing: Create an annotated drawing of the leaf, focusing on unique xerophytic features.
- High-Power Detail: Draw detailed structures, including:
- Sunken stomata at the bottom of grooves in the upper epidermis.
- Hinge cells aiding in leaf rolling.
- Hairs on the upper epidermis to trap moisture.
- Thick cuticle on the lower epidermis, which lacks stomata for additional water retention.
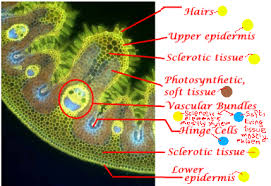
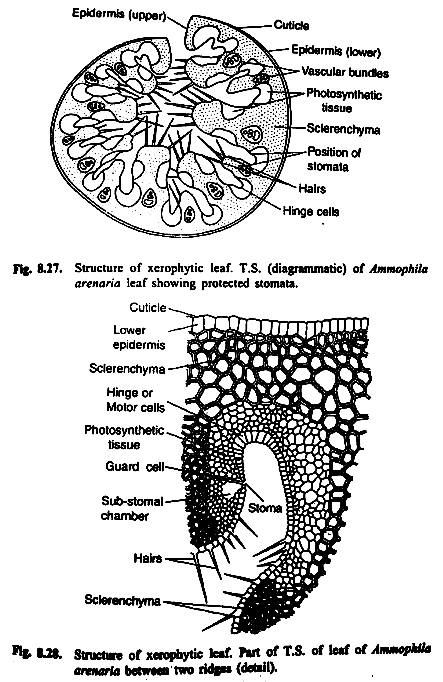
Question
Describe four adaptations of Marram Grass (Ammophila arenaria) that reduce water loss in dry, windy environments such as sand dunes.
Sunken Stomata:
- Stomata are located at the bottom of deep grooves in the upper epidermis.
- This traps humid air near the stomata, reducing the water vapor concentration gradient and minimizing transpiration.
Hinge Cells:
- Specialized hinge cells allow the leaf to roll up under dry conditions.
- This reduces the surface area exposed to wind and traps moisture inside the rolled leaf.
Leaf Hairs (Trichomes):
- Hairs on the upper epidermis trap water vapor near the leaf surface.
- This creates a humid microclimate, reducing the rate of water loss through transpiration.
Thick Cuticle:
- A thick, waxy cuticle on the lower epidermis, which lacks stomata, acts as a waterproof layer.
- This prevents excessive water loss through evaporation.
Key Terms:
- Trichomes: Hair-like structures on the leaf surface that trap moisture and reduce evaporation.
- Xerophyte: Plant adapted to survive in low-water environments.
- Cuticle: Protective layer made of cutin, covering the epidermis to reduce water loss.
Practice Questions 1
Question 1
Define xerophytes and explain the primary challenge they face in their natural habitats. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Definition of Xerophytes:
- Xerophytes are plants adapted to live in environments with limited water availability. (1 mark)
- Primary Challenge – Water Scarcity:
- They face the challenge of conserving water to survive in arid and semi-arid regions. (1 mark)
- Adaptations Necessitated by Water Scarcity:
- Develop structural and physiological adaptations to minimize water loss and maximize water uptake. (1 mark)
- Environmental Conditions:
- Typically inhabit deserts, steppes, and dry shrublands where precipitation is low. (1 mark)
- Survival Strategies:
- Implement strategies such as reduced leaf area, thick cuticles, and specialized root systems. (1 mark)
Question 2
List and describe two structural adaptations of xerophytes that help reduce water loss. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Thick, Waxy Cuticle:
- Description: A thick, waxy layer covering the leaf surface.
- Function: Forms a waterproof barrier, reducing transpiration by minimizing water evaporation through the epidermis. (2 marks)
- Sunken Stomata:
- Description: Stomata located in pits or depressions on the leaf surface.
- Function: Traps humid air around the stomata, lowering the water vapor concentration gradient and thus reducing transpiration. (2 marks)
- Leaf Hairs (Trichomes):
- Description: Hair-like structures on the leaf surface.
- Function: Trap moisture and create a humid microenvironment, decreasing the rate of water loss through transpiration. (2 marks)
Question 3
Explain how rolled leaves in xerophytes like Marram grass (Ammophila arenaria) help reduce water loss. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Leaf Rolling Mechanism:
- Leaves roll up due to the shrinkage of hinge cells, exposing a thick waterproof cuticle on the outside. (1 mark)
- Trapping Moist Air:
- The rolled structure traps humid air inside, creating a high humidity environment near the stomata. (1 mark)
- Reduction of Surface Area:
- Reduces the overall leaf surface area exposed to wind and sun, minimizing water loss through transpiration. (1 mark)
- Sunken Stomata Protection:
- Fewer stomata are directly exposed to the air, further limiting water loss. (1 mark)
- Moisture Conservation:
- The trapped moist air lowers the water vapor concentration gradient, reducing the rate of transpiration. (1 mark)
Question 4
Describe how reduced leaves in xerophytes like Opuntia (Cactus) contribute to water conservation. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Leaf Modification to Spines:
- Leaves are reduced and modified into spines, significantly lowering the surface area available for water loss through transpiration. (1 mark)
- Photosynthesis in Stems:
- Flattened, green stems take over the role of photosynthesis, reducing the need for large leaves that would otherwise lose more water. (1 mark)
- Water Storage in Stems:
- Fleshy stems store water, providing a reservoir during drought conditions. (1 mark)
- Defense Mechanism:
- Spines deter herbivores, preventing them from accessing and consuming the plant’s water stores. (1 mark)
- Minimized Evaporation:
- The reduced leaf surface and protected stems minimize evaporation, ensuring efficient water use. (1 mark)
Question 5
Explain how trichomes (leaf hairs) in xerophytes like Phlomis italica reduce water loss. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Moisture Trapping:
- Trichomes trap a layer of moist air close to the leaf surface, reducing the water vapor concentration gradient between the leaf and the air. (1 mark)
- Reduction of Transpiration Rate:
- The trapped moist air slows down transpiration, as water vapor has a lower gradient to diffuse out. (1 mark)
- Reflection of Sunlight:
- Trichomes can reflect sunlight, lowering the leaf surface temperature and reducing evaporation rates. (1 mark)
- Wind Barrier:
- They act as a physical barrier against wind, which can otherwise increase transpiration by removing moisture from the leaf surface. (1 mark)
- Microclimate Creation:
- Trichomes help in creating a microclimate around the leaf, enhancing water retention within the plant tissues. (1 mark)
Question 6
Describe the role of succulent stems in xerophytes like Euphorbia canariensis and how they aid in water conservation. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Water Storage in Stems:
- Succulent stems are swollen and fleshy, allowing them to store large amounts of water for use during dry periods. (1 mark)
- Photosynthesis in Stems:
- Stems carry out photosynthesis, reducing the reliance on leaves and thereby minimizing water loss through transpiration. (1 mark)
- Thick Waxy Cuticle:
- A thick waxy layer on the stems forms a waterproof barrier, reducing water loss through evaporation. (1 mark)
- Reduced Surface Area:
- Succulent stems often have a compact shape, reducing the surface area exposed to the air and limiting water loss. (1 mark)
- Protective Structures:
- The robust structure of succulent stems protects the stored water from physical damage and harsh environmental conditions. (1 mark)
Question 7
Explain how sunken stomata in xerophytes like Marram grass (Ammophila arenaria) help reduce water loss. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Location in Pits or Depressions:
- Stomata are located in pits or depressions on the leaf surface, creating a protected environment. (1 mark)
- Trapping Humid Air:
- The sunken position traps humid air around the stomata, reducing the water vapor concentration gradient between the leaf and the surrounding air. (1 mark)
- Minimized Exposure to Wind:
- Being in depressions reduces the direct exposure of stomata to wind, which can otherwise increase transpiration rates. (1 mark)
- Lower Transpiration Rates:
- The humid microenvironment near sunken stomata slows down water loss through transpiration. (1 mark)
- Water Conservation:
- By limiting water loss, sunken stomata help the plant retain water, essential for survival in dry, windy environments. (1 mark)
Question 8
Discuss how the thick cuticle in xerophytes contributes to their survival in arid environments. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Waterproof Barrier:
- The thick cuticle acts as a waterproof layer, preventing excessive water loss through evaporation. (1 mark)
- Minimized Transpiration:
- By reducing the permeability of the leaf surface, the thick cuticle lowers the rate of transpiration. (1 mark)
- Protection Against Environmental Stress:
- The cuticle protects the plant from harsh sunlight, wind, and pathogens, which can exacerbate water loss. (1 mark)
- Enhanced Water Retention:
- Helps the plant retain water within its tissues, ensuring a steady supply during periods of scarcity. (1 mark)
- Structural Support:
- The thick cuticle adds to the structural integrity of leaves and stems, aiding in physical resilience against environmental factors. (1 mark)
Question 9
Compare the adaptations of xerophytes with rolled leaves and reduced leaves in terms of their effectiveness in water conservation. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Rolled Leaves – Water Trapping:
- Rolled leaves trap moist air inside the rolled structure, creating a humid microenvironment around the stomata, thus reducing transpiration. (2 marks)
- Rolled Leaves – Reduced Surface Area Exposure:
- The rolled shape decreases the surface area exposed to wind and sunlight, limiting water loss through transpiration. (2 marks)
- Reduced Leaves – Surface Area Minimization:
- Reduced leaves, such as spines, significantly lower the surface area available for water loss, enhancing water conservation. (1 mark)
- Reduced Leaves – Specialized Photosynthesis in Stems:
- Photosynthesis occurs in the water-storing stems, reducing the need for large leaves that would otherwise lose more water. (1 mark)
- Overall Effectiveness:
- Both adaptations effectively minimize water loss, but rolled leaves additionally protect stomata and create humid conditions, while reduced leaves also provide defense against herbivores. (1 mark)
Question 10
Explain how the structural adaptations of xerophytes are beneficial in their typical habitats. Use examples from the key adaptations listed. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Thick, Waxy Cuticle:
- Benefit: Reduces water loss in arid environments by preventing excessive transpiration.
- Example: Marram grass has a thick cuticle to retain water in sand dune habitats. (2 marks)
- Sunken Stomata:
- Benefit: Minimizes water loss by trapping humid air around stomata, reducing the transpiration rate.
- Example: Marram grass places stomata in deep pits to conserve water in dry, windy conditions. (2 marks)
- Rolled Leaves:
- Benefit: Reduces surface area exposed to wind and sunlight, and traps moist air to lower transpiration.
- Example: Marram grass rolls its leaves to create a humid microclimate and protect against water loss in sand dunes. (2 marks)
Describe how CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) photosynthesis is an adaptation in some xerophytes and explain how it helps in water conservation. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Definition of CAM Photosynthesis:
- CAM is a type of photosynthesis where stomata open at night to minimize water loss. (1 mark)
- Stomatal Opening at Night:
- Stomata open during the cooler, more humid night conditions, reducing water evaporation. (1 mark)
- CO₂ Fixation at Night:
- CO₂ is fixed into organic acids at night and stored in vacuoles. (1 mark)
- Daytime Stomatal Closure:
- Stomata close during the day to prevent water loss while releasing CO₂ from organic acids for photosynthesis. (1 mark)
- Water Conservation:
- By opening stomata at night and closing them during the day, CAM plants significantly reduce transpiration and conserve water. (1 mark)
Question 12
Explain how the root system of xerophytes like mesquite trees contributes to their survival in arid environments. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Deep Taproot System:
- Mesquite trees have an extensive deep taproot that can reach groundwater sources. (1 mark)
- Access to Deep Water:
- The deep roots access water reserves that are unavailable to plants with shallower roots. (1 mark)
- Efficient Water Uptake:
- The taproot system allows for efficient water uptake during rare rainfall events. (1 mark)
- Stable Anchorage:
- Provides strong anchorage in sandy or loose soils, preventing the plant from being uprooted by wind. (1 mark)
- Minimized Surface Rooting:
- Reduces competition with other plants for surface water and nutrients, ensuring water availability for the mesquite. (1 mark)
Question 13
Compare and contrast xerophytes with mesophytes in terms of their water usage and habitat. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Water Usage – Xerophytes:
- Low water usage, adapted to arid and semi-arid environments. (1 mark)
- Water Usage – Mesophytes:
- Moderate to high water usage, thrive in moist environments. (1 mark)
- Leaf Structure – Xerophytes:
- Often have reduced, thick, or modified leaves (e.g., spines, rolled leaves) to minimize water loss. (1 mark)
- Leaf Structure – Mesophytes:
- Typically have broad, flat leaves with ample stomata for efficient gas exchange. (1 mark)
- Root Systems – Xerophytes:
- Possess deep taproots or extensive shallow roots for water acquisition. (1 mark)
- Root Systems – Mesophytes:
- Have moderate root systems optimized for efficient water uptake in consistently moist soils. (1 mark)
Question 14
Describe how the modification of leaves into spines in xerophytes like cacti helps in water conservation. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Reduction of Leaf Surface Area:
- Leaves are reduced into spines, significantly decreasing the surface area available for water loss through transpiration. (1 mark)
- Protection from Herbivores:
- Spines deter herbivores from eating the plant, protecting the plant’s water stores. (1 mark)
- Minimized Transpiration:
- With fewer leaf surfaces exposed, the overall transpiration rate is reduced, conserving water. (1 mark)
- Shade and Temperature Regulation:
- Spines can provide shade to the plant, lowering leaf temperature and reducing evaporation rates. (1 mark)
- Structural Support for Succulent Stems:
- Spines support succulent stems by adding rigidity and preventing physical damage, ensuring water storage structures remain intact. (1 mark)
Question 15
Explain how the presence of trichomes in xerophytes like Phlomis italica aids in water conservation. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Moisture Trapping:
- Trichomes trap a layer of moist air close to the leaf surface, reducing the water vapor concentration gradient. (1 mark)
- Reduction of Transpiration Rate:
- The trapped moist air slows down transpiration, decreasing the rate of water loss. (1 mark)
- Reflection of Sunlight:
- Trichomes can reflect sunlight, lowering the leaf surface temperature and reducing evaporation rates. (1 mark)
- Wind Barrier:
- They act as a physical barrier against wind, which can otherwise increase transpiration by removing moisture from the leaf surface. (1 mark)
- Microclimate Creation:
- Trichomes help in creating a microclimate around the leaf, enhancing water retention within the plant tissues. (1 mark)
Question 16
Discuss how succulent stems in xerophytes like Euphorbia canariensis contribute to both water storage and photosynthesis. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Water Storage in Succulent Stems:
- Succulent stems are swollen and fleshy, allowing them to store large amounts of water for use during dry periods. (1 mark)
- Photosynthesis in Stems:
- Stems carry out photosynthesis, reducing the need for large leaves that would otherwise lose more water through transpiration. (1 mark)
- Thick Waxy Cuticle:
- A thick waxy layer covers the stems, creating a waterproof barrier that reduces water loss through evaporation. (1 mark)
- Reduced Surface Area:
- Succulent stems often have a compact shape, reducing the surface area exposed to the air and limiting water loss. (1 mark)
- Efficient Water Use:
- Stored water in stems is used efficiently during drought conditions, ensuring the plant remains hydrated. (1 mark)
- Structural Support:
- The robust structure of succulent stems provides support and protects the stored water from physical damage and harsh environmental conditions. (1 mark)
Question 17
Explain how the thick cuticle in xerophytes reduces water loss and provide an example of a xerophyte that possesses this adaptation. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Waterproof Barrier:
- The thick cuticle acts as a waterproof layer, preventing excessive water loss through evaporation from the leaf surface. (1 mark)
- Reduced Transpiration:
- By lowering the permeability of the leaf surface, the thick cuticle reduces the rate of transpiration. (1 mark)
- Protection Against Environmental Stress:
- The cuticle protects the plant from harsh sunlight, wind, and pathogens, which can increase water loss. (1 mark)
- Enhanced Water Retention:
- Helps the plant retain water within its tissues, ensuring a steady supply during periods of scarcity. (1 mark)
- Example of Xerophyte:
- Marram Grass (Ammophila arenaria) possesses a thick waxy cuticle to retain water in sand dune habitats. (1 mark)
Question 18
Describe how the modification of leaves into spines in xerophytes like cacti serves a dual purpose beyond water conservation. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Defense Mechanism:
- Spines deter herbivores from eating the plant, protecting the plant’s water stores from being consumed. (1 mark)
- Shade Provision:
- Spines can provide shade to the plant’s surface, reducing leaf temperature and evaporation rates. (1 mark)
- Structural Support:
- Spines add rigidity and structural support to the plant, helping it maintain its shape and resist physical damage. (1 mark)
- Protection Against UV Radiation:
- Spines can help protect the plant from excessive UV radiation by blocking some of the harsh sunlight. (1 mark)
- Water Collection:
- In some species, spines can collect moisture from the air or dew, channeling it towards the stem for water absorption. (1 mark)
Question 19
Explain how the root modifications in xerophytes enhance their ability to absorb water efficiently. Provide an example. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Extensive Root Systems:
- Xerophytes often have extensive root systems, increasing the surface area for water absorption. (1 mark)
- Deep Taproots:
- Some xerophytes possess deep taproots that reach groundwater sources, ensuring access to water even during prolonged dry periods. (1 mark)
- Root Hairs:
- Root hairs increase the surface area for absorption and improve contact with soil particles, enhancing water uptake efficiency. (1 mark)
- Mycorrhizal Associations:
- Form symbiotic relationships with mycorrhizal fungi, which aid in the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. (1 mark)
- Example:
- Mesquite Trees (Prosopis spp.) have deep taproots that allow them to access deep water reserves in arid environments. (1 mark)
Question 20
Discuss how the adaptations of xerophytes influence their ecological roles in arid environments. Use at least two examples in your explanation. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Water Conservation and Survival:
- Adaptations like thick cuticles, rolled leaves, and succulent stems enable xerophytes to survive in arid environments with limited water. (1 mark)
- Habitat Stabilization:
- Xerophytes such as cacti and mesquite trees help in stabilizing soil and preventing erosion in desert ecosystems. (1 mark)
- Provision of Shelter and Food:
- Structures like spines provide shelter for animals, while fruit from xerophytes like cacti serve as food sources for various desert fauna. (1 mark)
- Carbon Fixation:
- Adaptations like CAM photosynthesis allow xerophytes to efficiently fix carbon dioxide, contributing to carbon cycling in arid ecosystems. (1 mark)
- Biodiversity Support:
- Xerophytes create microhabitats that support a variety of specialized organisms, enhancing biodiversity in harsh environments. (1 mark)
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal:
- Structural adaptations facilitate pollination by attracting specific pollinators and ensure effective seed dispersal in challenging conditions. (1 mark)
Quizzes
Quiz 1
Quiz 2