03.02 Chemical Bonding
a. Overview
Definition:
- Chemical bonding refers to the strong forces that hold atoms or ions together in chemical substances. These bonds are essential for the formation of molecules and compounds, determining their structure, properties, and behavior.
Types of Bonding:
- Covalent Bonding:
- Description: Involves the sharing of electrons between non-metal atoms.
- Example: Hydrogen gas (H₂), where two hydrogen atoms share electrons.
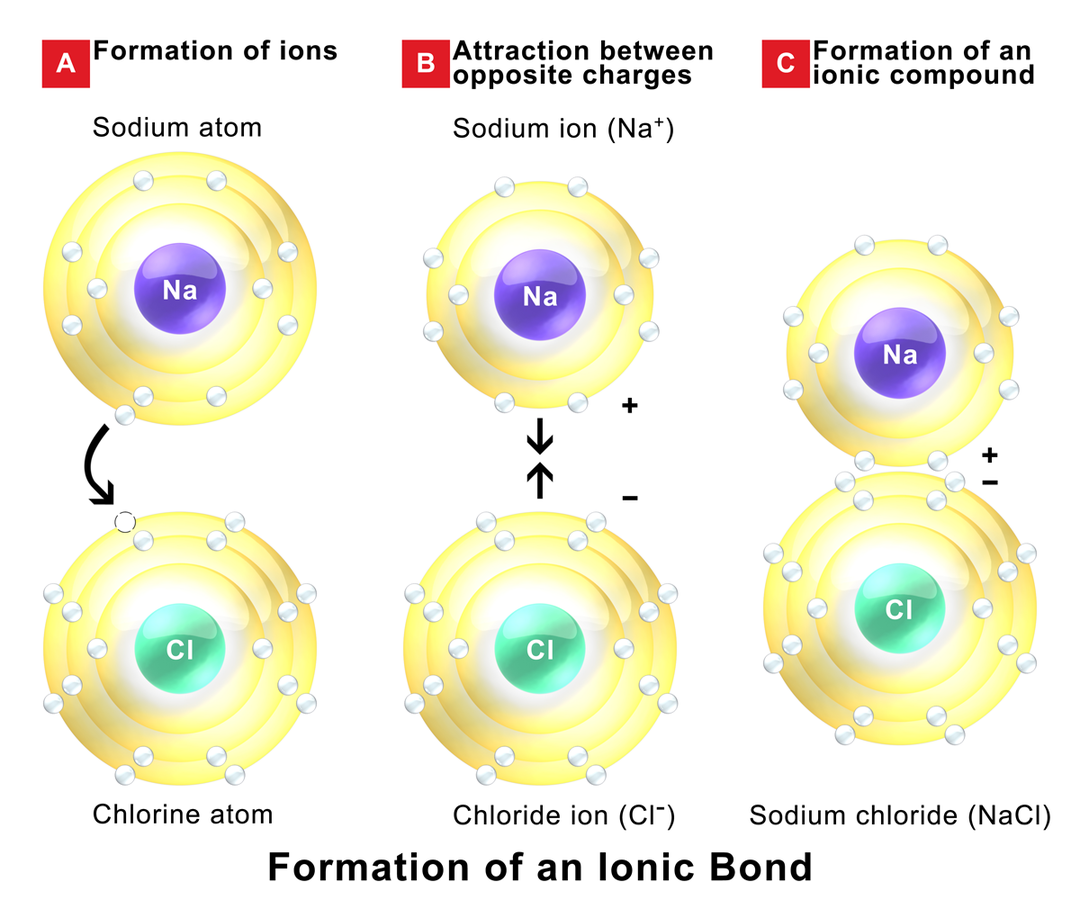
- Ionic Bonding:
- Description: Involves the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal, resulting in the formation of ions.
- Example: Sodium chloride (NaCl), where sodium (Na) donates an electron to chlorine (Cl).
- Metallic Bonding:
- Description: Involves the delocalization of electrons within a lattice of metal atoms, allowing electrons to move freely.
- Example: Copper (Cu), where electrons flow freely, giving metals their characteristic properties like conductivity and malleability.
b. Covalent Bonding in Non-Metals
Formation:
- Atoms form covalent bonds by sharing electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, typically resembling that of noble gases.
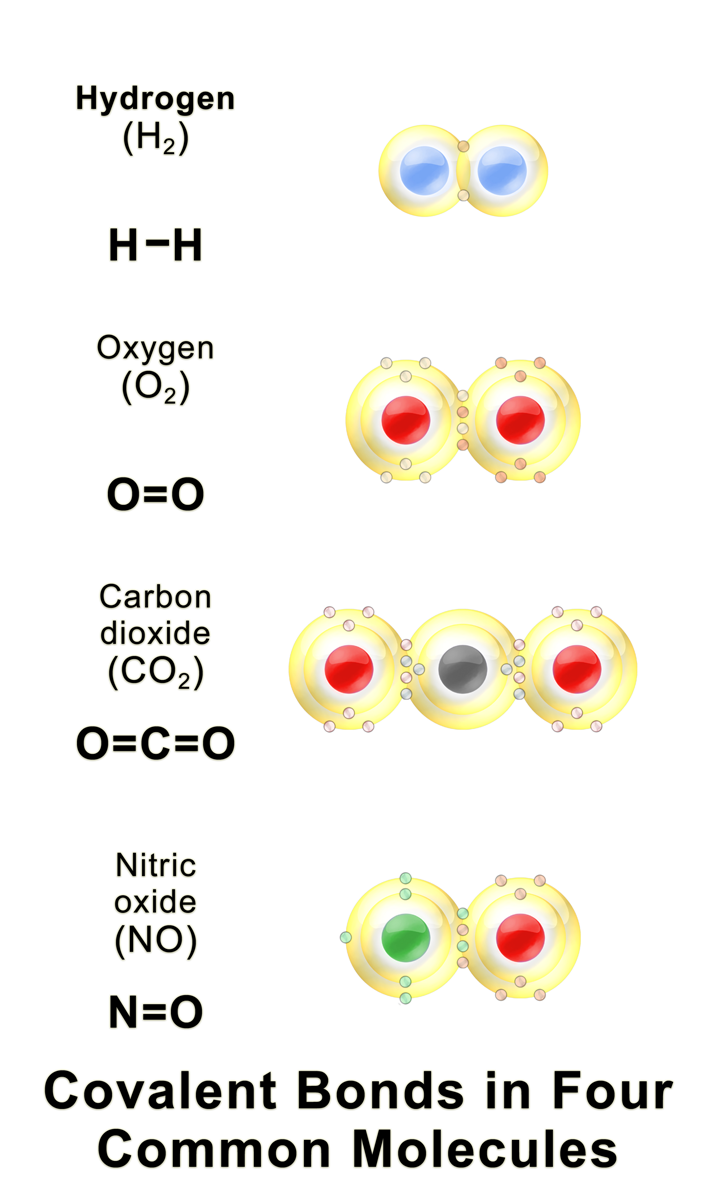
Types of Covalent Bonds:
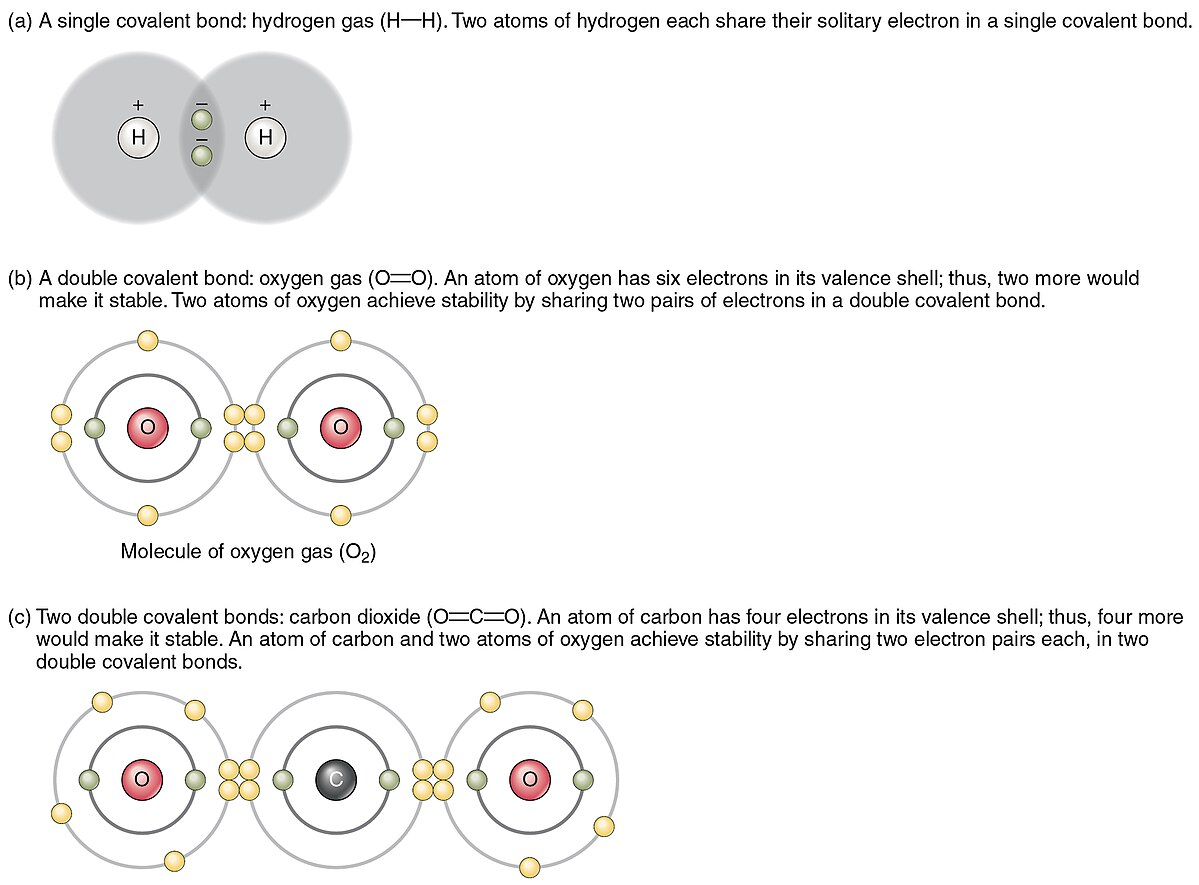
- Single Bond:
- Description: Sharing of one pair of electrons (2 electrons) between two atoms.
- Example:
- Hydrogen (H₂): H–H
- Chlorine (Cl₂): Cl–Cl
- Double Bond:
- Description: Sharing of two pairs of electrons (4 electrons) between two atoms.
- Example:
- Oxygen (O₂): O=O
- Triple Bond:
- Description: Sharing of three pairs of electrons (6 electrons) between two atoms.
- Example:
- Nitrogen (N₂): N≡N
Illustrative Examples:
- Single Bond:
H2: H shares one electron with another H (H–H)
- Double Bond:
O2: O shares two electrons with another O (O=O)
- Triple Bond:
N2: N shares three electrons with another N (N≡N)
c. Diatomic Molecules
Definition:
- Diatomic molecules are molecules composed of two atoms bonded together. They can consist of two identical atoms or two different atoms.
Examples of Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules (same atoms):
- Hydrogen (H₂):
- Structure: H–H
- Uses: Hydrogen fuel, ammonia production.
- Oxygen (O₂):
- Structure: O=O
- Uses: Essential for respiration, combustion.
- Nitrogen (N₂):
- Structure: N≡N
- Uses: Inert atmosphere for chemical reactions, fertilizer production.
- Halogens (e.g., Chlorine Cl₂, Bromine Br₂):
- Chlorine (Cl₂): Cl–Cl
- Bromine (Br₂): Br–Br
- Uses: Disinfectants, bleach, industrial synthesis.
Examples of Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules (different atoms):
- Hydrogen Chloride (HCl):
- Structure: H–Cl
- Uses: Production of hydrochloric acid, PVC manufacturing.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- Structure: C≡O
- Uses: Industrial processes, fuel.
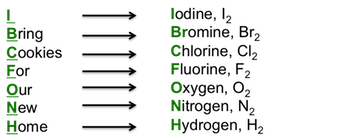
d. Chemical Formulas and Bond Diagrams
Chemical Formula
Definition:
- A chemical formula indicates the elements present in a compound and their respective ratios.
Examples:
- Hydrochloric Acid: HCl
- Carbon Dioxide: CO₂
- Water: H₂O
- Methane: CH₄
Bond Diagrams (Dot-and-Cross Diagrams)
Definition:
- Bond diagrams visually represent the sharing of electrons between atoms in a molecule using dots and crosses.
Symbols:
- Dots (•): Represent electrons from one atom.
- Crosses (×): Represent electrons from another atom.
Example: Hydrogen Chloride (HCl):
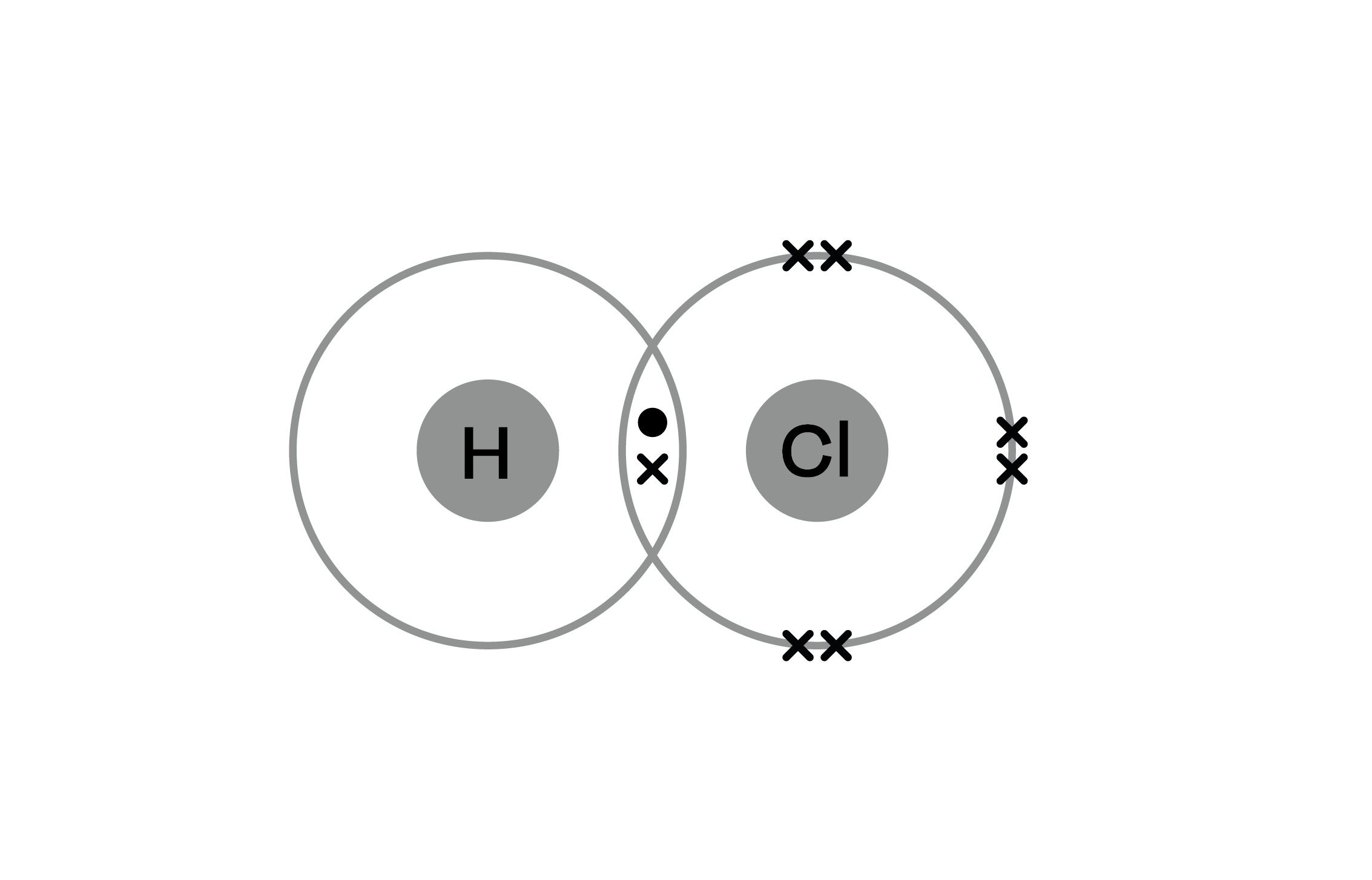
- Explanation:
- Hydrogen (H) shares one electron with Chlorine (Cl).
- Chlorine shares one electron with Hydrogen.
- This sharing results in a single covalent bond (H–Cl).
Another Example: Water (H₂O):
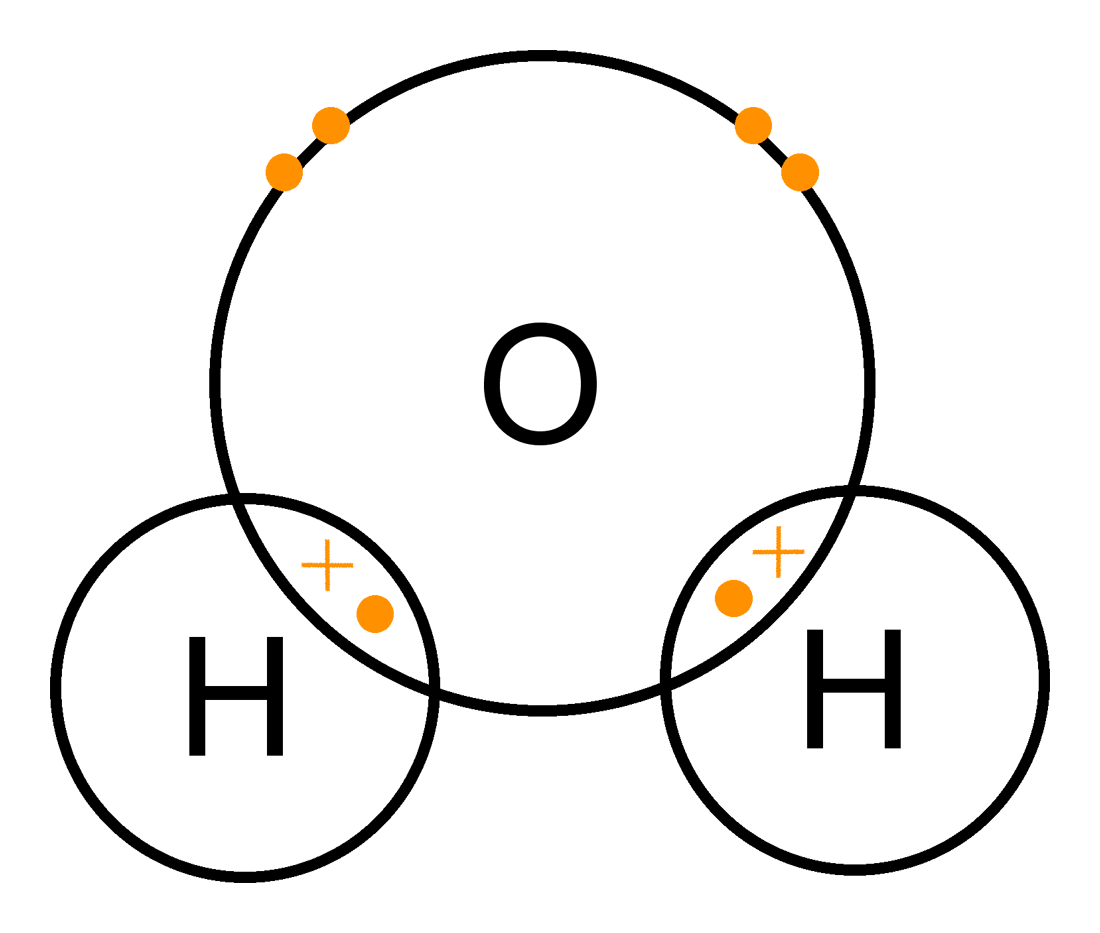
- Explanation:
- Each Hydrogen (H) shares one electron with Oxygen (O).
- Oxygen shares two electrons (one with each H), forming two single bonds.
e. Multiple Covalent Bonds
Definition:
- Multiple covalent bonds involve the sharing of more than one pair of electrons between two atoms, leading to double or triple bonds.
Examples:
- Oxygen (O₂):
- Type of Bond: Double bond
- Structure: O=O
- Explanation: Two pairs of electrons are shared between the two oxygen atoms.
- Nitrogen (N₂):
- Type of Bond: Triple bond
- Structure: N≡N
- Explanation: Three pairs of electrons are shared between the two nitrogen atoms.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂):
- Type of Bonds: Two double bonds
- Structure: O=C=O
- Explanation: Each oxygen atom shares two pairs of electrons with the central carbon atom.
- Ethylene (C₂H₄):
- Type of Bond: Double bond between carbon atoms
- Structure: H₂C=CH₂
- Explanation: Each carbon shares two pairs of electrons with the other carbon and single bonds with hydrogen atoms.
f. Simple Covalent Compounds
Definition:
- Simple covalent compounds are molecules formed by non-metal atoms bonded together through covalent bonds.
Examples and Structures:
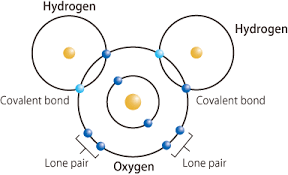
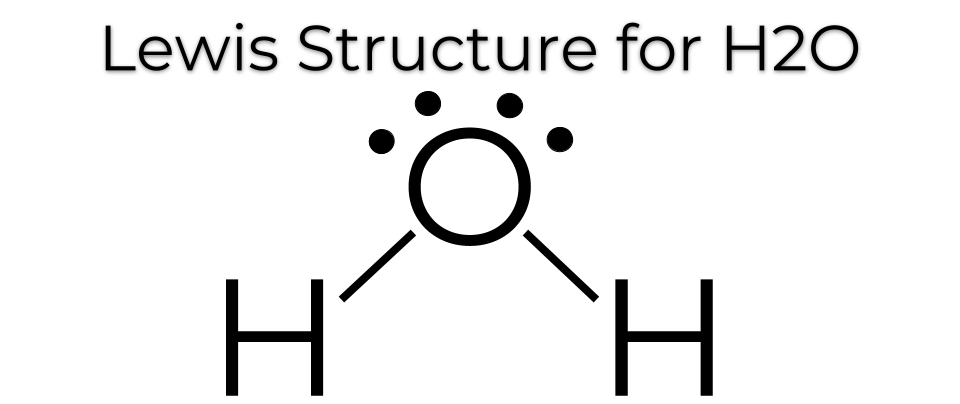
1.Water (H₂O):
- Structure: Two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.
- Properties: Polar molecule, high boiling point, essential for life.
- Bond Diagram:
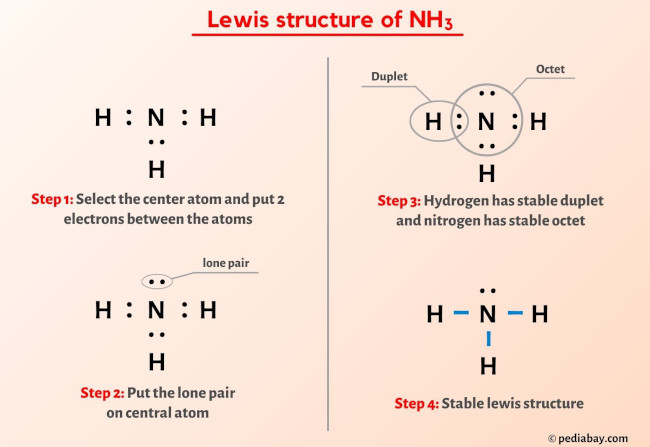
2. Ammonia (NH₃):
- Structure: Three hydrogen atoms bonded to one nitrogen atom.
- Properties: Weak base, pungent smell, used in fertilizers.
- Lewis Bond Diagram:
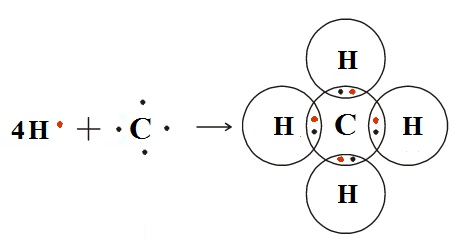
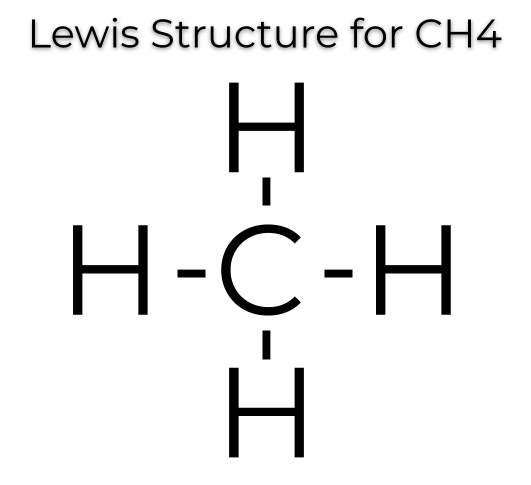
3. Methane (CH₄):
- Structure: Four hydrogen atoms bonded to one carbon atom
- Properties: Main component of natural gas, simplest hydrocarbon.
- Bond Diagram:
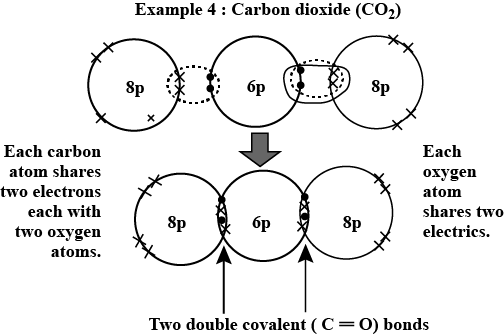
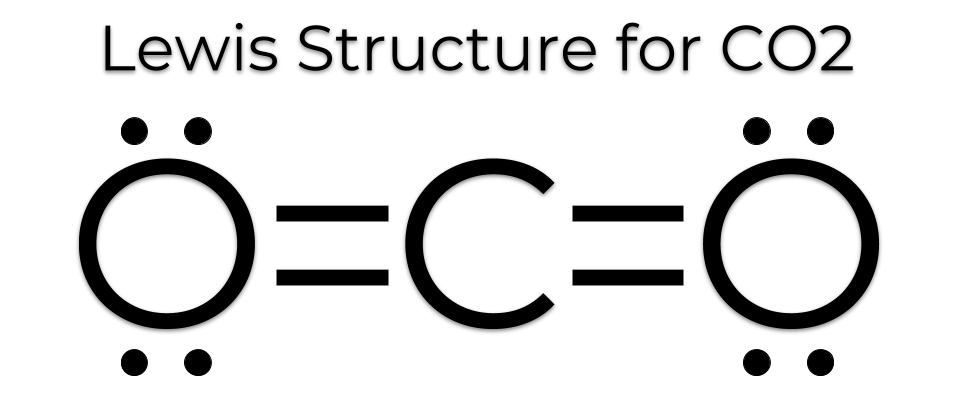
4. Carbon Dioxide (CO₂):
- Structure: One carbon atom double-bonded to two oxygen atoms.
- Bond Diagram: O=C=O
- Properties: Gas at room temperature, greenhouse gas, product of respiration.
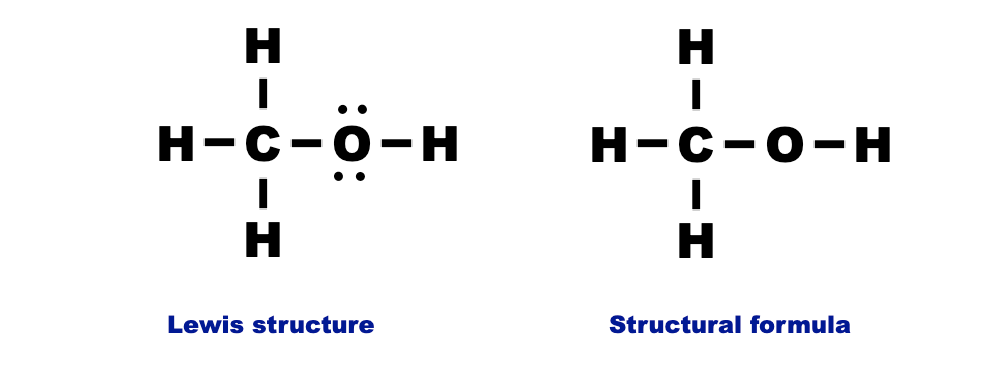
5. Methanol (CH₃OH):
- Structure: Combination of a methyl group (CH₃) and a hydroxyl group (OH).
- Properties: Alcohol, used as a solvent and fuel.
- Bond Diagram:
Additional Examples:
- Properties: Pollutant, used in the production of sulfuric acid.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- Structure: Triple bond between carbon and oxygen with a lone pair on each atom.
- Bond Diagram: C≡O
- Properties: Toxic gas, used in industrial processes.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂):
- Structure: One sulfur atom double-bonded to two oxygen atoms.
- Bond Diagram: S=O