2022 Specimen Paper
Specimen Paper
Q1
Which definition of the magnification of a drawing of a leaf is correct?
A the actual size of the leaf multiplied by the magnification of the microscope
B the measured difference in size between the leaf and a drawing of the leaf
C the increase in size of the leaf when observed using a microscope
D the size of the drawing of the leaf divided by the actual size of the leaf
D
Image size (I) = Actual size (A) x Magnification (M)
M = I/A
Q2
The electron micrograph shows part of two cells.
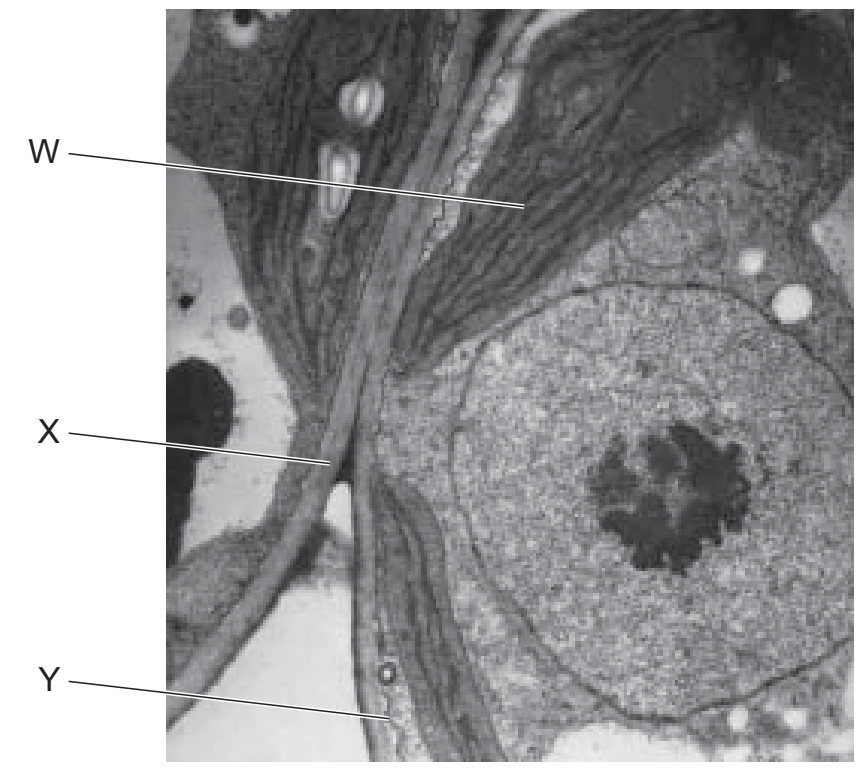
Which labelled features identify these cells as eukaryotic?
A W, X and Y
B W and X only
C W only
D X only
C
W = Chloroplasts (found in plants)
Q3
Plant cells are stained and viewed using a student microscope. The light source is natural light. What could be clearly visible at x400 magnification?
A cristae of mitochondria
B grana of chloroplasts
C nucleoli
D ribosomes
C

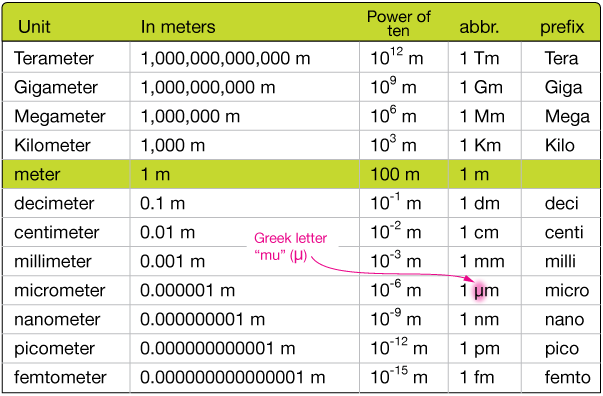
Q4
Which lengths are equivalent to 1μm?
1 1000 mm
2 0.001 nm
3 0.001 mm
4 1 000 000 nm
5 0.01 mm
6 1000 nm
A 1 and 4
B 2 and 5
C 3 and 4
D 3 and 6
D
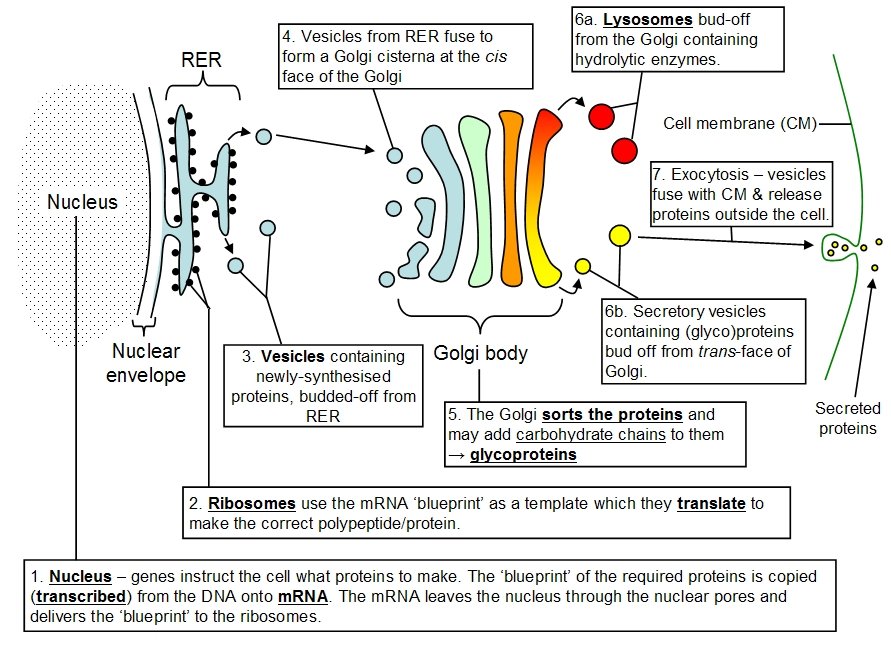
Q5
Some secretory cells synthesise and release glycoproteins. What is the correct sequence of some of the events that occur in a secretory cell?
1 exocytosis
2 products accumulate in secretory vesicles
3 mRNA binds to ribosomes
4 synthesis of glycoproteins
A 3, 4, 1, 2
B 3, 4, 2, 1
C 4, 3, 1, 2
D 4, 3, 2, 1
B
Q6
A scientist used a blender to break open a sample of animal cells and release the organelles. The extracted mixture was spun in a centrifuge at a low speed. The heaviest type of organelle sank to the bottom of the centrifuge tube to form a solid pellet, pellet 1.
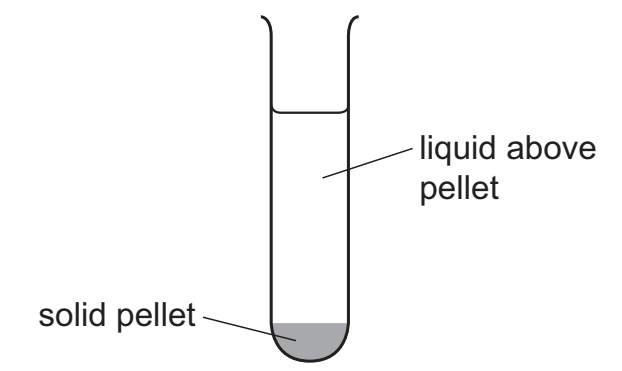
The liquid above pellet 1 was poured into a clean centrifuge tube and spun at a higher speed. The next heaviest organelle sank to the bottom to form a solid pellet, pellet 2.
The scientist repeated this procedure twice more to obtain pellet 3 and pellet 4, each containing a single type of organelle.
What is the function of the type of organelle extracted in pellet 3?
A digestion of old cell organelles
B production of ATP by respiration
C synthesis of mRNA
D synthesis of protein
A
Pallet 4 has ribosome sized objects (or smaller).
Q7
What is the general formula for amylose?
A (C5H10O5)n
B (C5H10O6)n
C (C6H12O6)n
D (C6H10O5)n
D
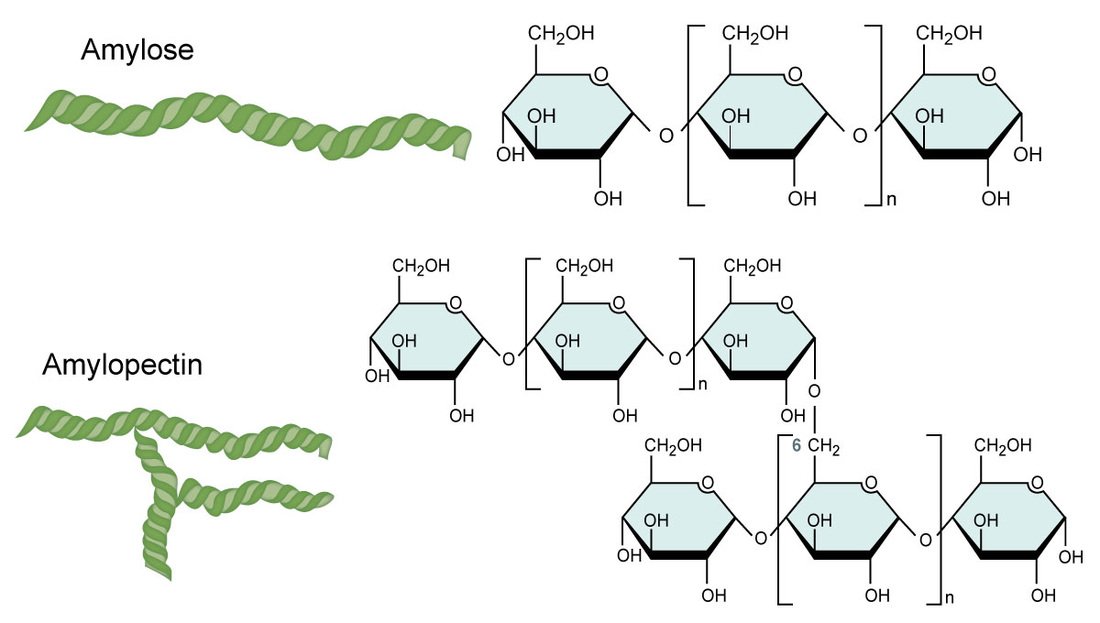
Amylose/Amylopectin: [C6H10O5]n
Q8
Which statement describes how the molecular structure of starch is suited to its function?
A Amylose has a branched structure and amylopectin is coiled to give a compact molecule for transport.
B In the breakdown of amylose and amylopectin, many condensation reactions release stored energy.
C In the formation of amylose and amylopectin, many hydrolysis reactions allow the release of stored energy.
D Amylose and amylopectin form a complex that is insoluble and so does not affect the water potential of the cell.
D
Q9
Cows and whales are mammals that produce milk to feed their babies. Newborn whales grow faster than newborn cows. Milk contains fatty acids with a range of chain lengths.
The table shows the percentage of fatty acids of different chain lengths in cow milk and whale milk.
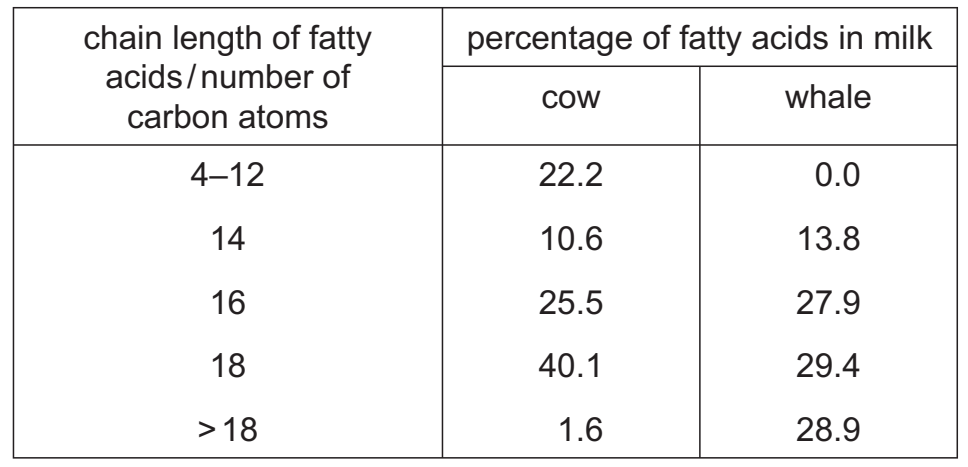
Which statement about the ratio of short fatty acids (4–16 carbon atoms) to long fatty acids (18 or more carbon atoms) in the milk of cows and whales is correct?
A The ratio in cow milk is higher because newborn cows need more energy than newborn
whales.
B The ratio in cow milk is lower because newborn cows need less energy than newborn whales.
C The ratio in whale milk is higher because newborn whales need less energy than newborn cows.
D The ratio in whale milk is lower because newborn whales need more energy than newborn cows.
D
Q10
The structure of phospholipids includes:
1 polar phosphate heads
2 hydrophobic fatty acid chains
3 saturated fatty acid chains.
What are essential for the formation of a phospholipid bilayer in a cell surface membrane?
A 1 and 2
B 1 and 3
C 2 and 3
D 3 only
A
Q11
The diagram shows the molecular structure of a peptide.
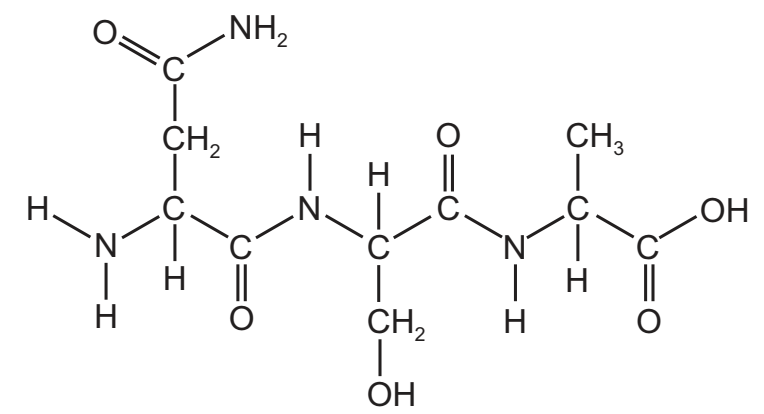
Which molecules would result from the complete hydrolysis of the peptide?
C
Q12
The diagram shows a haemoglobin molecule.
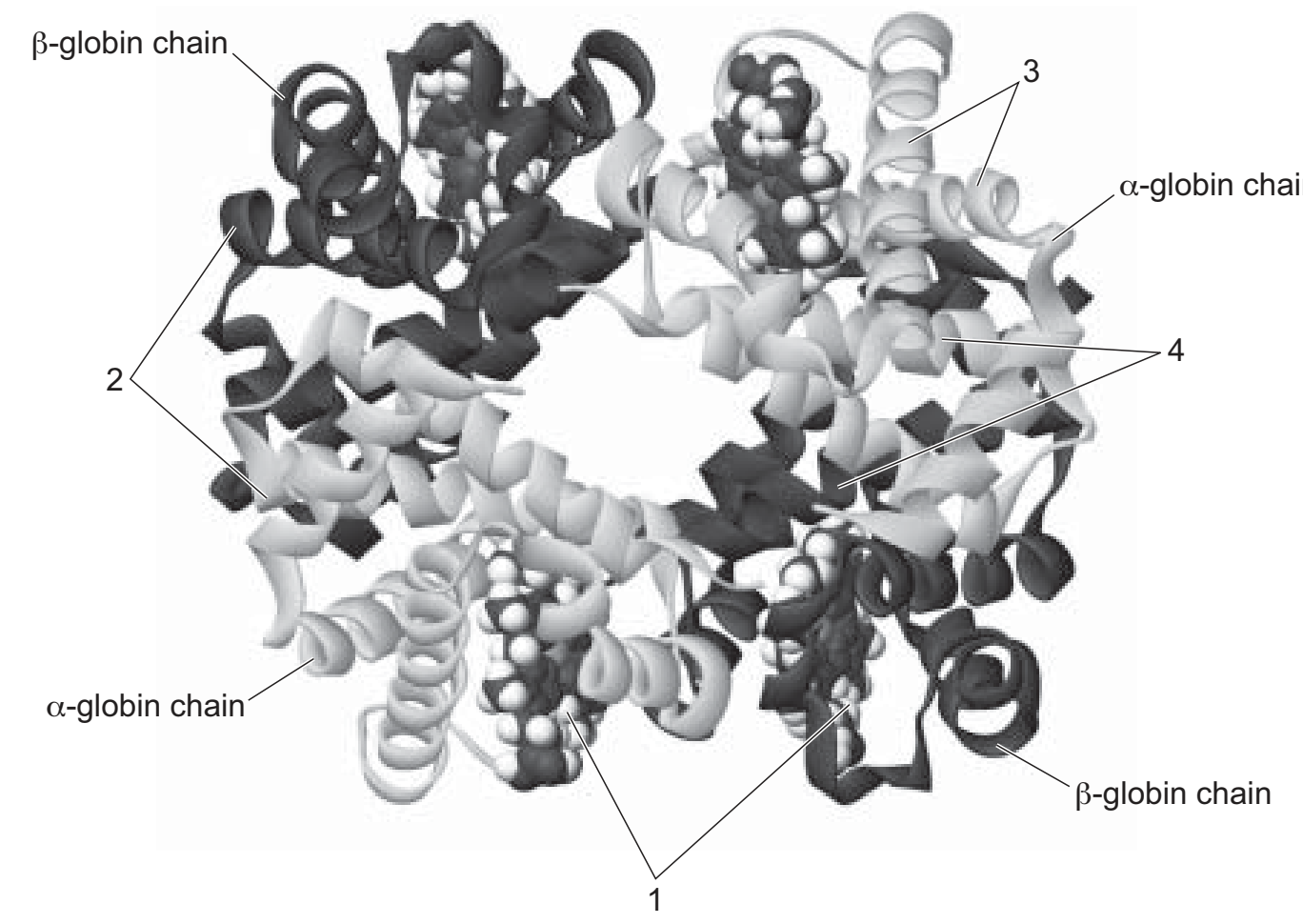
Which row identifies the different parts of the molecule?
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| A | α-helix | β-pleated sheet | oxygen binding site | hydrophobic amino acids |
| B | oxygen binding site | hydrophilic amino acids | α-helix | hydrophobic amino acids |
| C | haem group | hydrophobic amino acids | α-helix | hydrophilic amino acids |
| D | hydrophobic amino acids | β-pleated sheet | haem atom | oxygen binding site |
B
Q13
A student investigated the effect of enzyme concentration on the rate of hydrolysis of protein in milk. When the enzyme and milk were mixed, the protein was hydrolysed and the mixture changed from cloudy to clear. The student investigated five different enzyme concentrations and recorded the time taken for the mixture to become clear.
What is an appropriate control for this investigation?
A Carrying out an experiment where the enzyme solution is replaced with water.
B Carrying out each experiment in a thermostatically controlled water-bath at 35 °C.
C Repeating each experiment three times for each of the five enzyme concentrations.
D Using the same volume of enzyme solution for each of the five experiments.
A
Q14
What determines the specificity of an enzyme?
1 the covalent and other bonding between R groups of the polypeptide
2 the optimum pH of the enzyme
3 the covalent peptide bonds between amino acids of the polypeptide
4 the shape of the substrate molecule
A 1, 2, 3 and 4
B 1 and 3 only
C 1 only
D 2, 3 and 4 only
C
Q15
The graph shows the effect of temperature on the rate at which the enzyme in a biological washing powder digests and removes fruit juice stains.
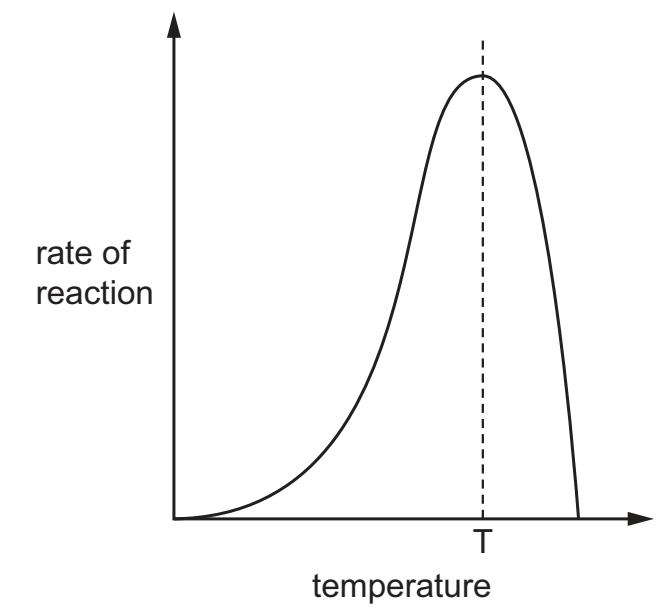
Which statements explain the shape of the graph at temperatures higher than T?
1 Bonds are broken between the R groups of the amino acids in the polypeptide chains of
the enzyme.
2 There are more collisions between the enzyme and its substrate.
3 The tertiary structure of the enzyme is altered.
4 The shapes of the active site and the substrate are no longer complementary.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1, 2 and 4
C 1, 3 and 4
D 2, 3 and 4
C
Q16
Which statement describes carrier proteins in cell surface membranes?
A Carrier proteins are found on the outer surface of the membranes allowing cell recognition.
B Carrier proteins are involved in moving substances through the membranes by either active transport or passive transport.
C Carrier proteins allow the binding of ligand molecules, which causes changes within cells.
D Carrier proteins are involved in moving substances through the membranes by passive
transport through water-filled pores.
B
Q17
What happens to a typical bacterium when it is placed in surroundings that have a higher water potential than the water potential inside the cell?
A The bacterium bursts because the cell wall has no structural function.
B The bacterium dies because water leaves the cell by osmosis.
C There is no change because the cell wall is impermeable to water.
D There is a net movement of water into the bacterium.
D
Q18
By which process do hydrogencarbonate ions leave red blood cells?
A active transport
B endocytosis
C facilitated diffusion
D phagocytosis
C
Q19
In an experiment, fluorescent dyes were attached to proteins on the outer surface of cell surface membranes. Fluorescent dyes of one colour were attached to proteins of a living human cell and fluorescent dyes of a different colour were attached to proteins of a living mouse cell.
The human cell and the mouse cell were then fused to form a hybrid cell.
At first, the proteins attached to different fluorescent dyes remained separate, but after 40 minutes the proteins were distributed randomly across the hybrid cell surface membrane.
What does this experiment show?
A Proteins are found only on the outer surface of cell surface membranes.
B Proteins in the outer layer of a bilayer do not penetrate into the inner layer.
C Proteins move freely in the phospholipids of a bilayer.
D The cell surface membranes of the two cells are bilayers.
C
Q20
The diagram shows the mitotic cell cycle. During which phase is DNA replicated?
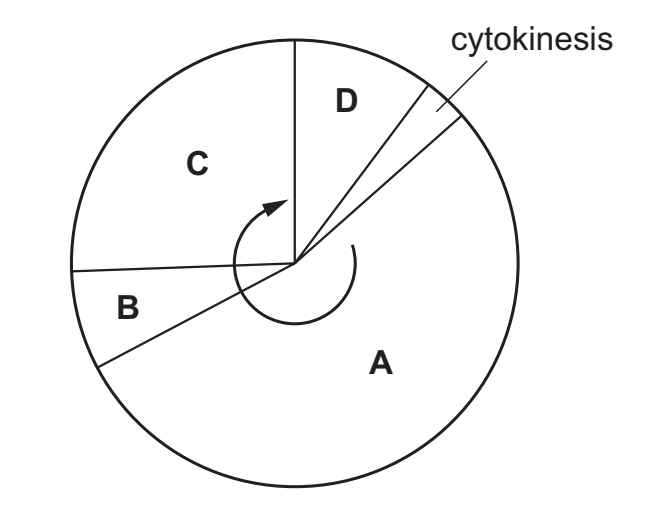
B
Q21
Bacterial cells divide by a process called binary fission. Which macromolecules must be synthesised for binary fission?
1 cell membrane proteins and RNA
2 DNA and peptidoglycan
3 enzymes and cellulose
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 3 only
B
Q22
The electron micrograph shows a group of human chromosomes.
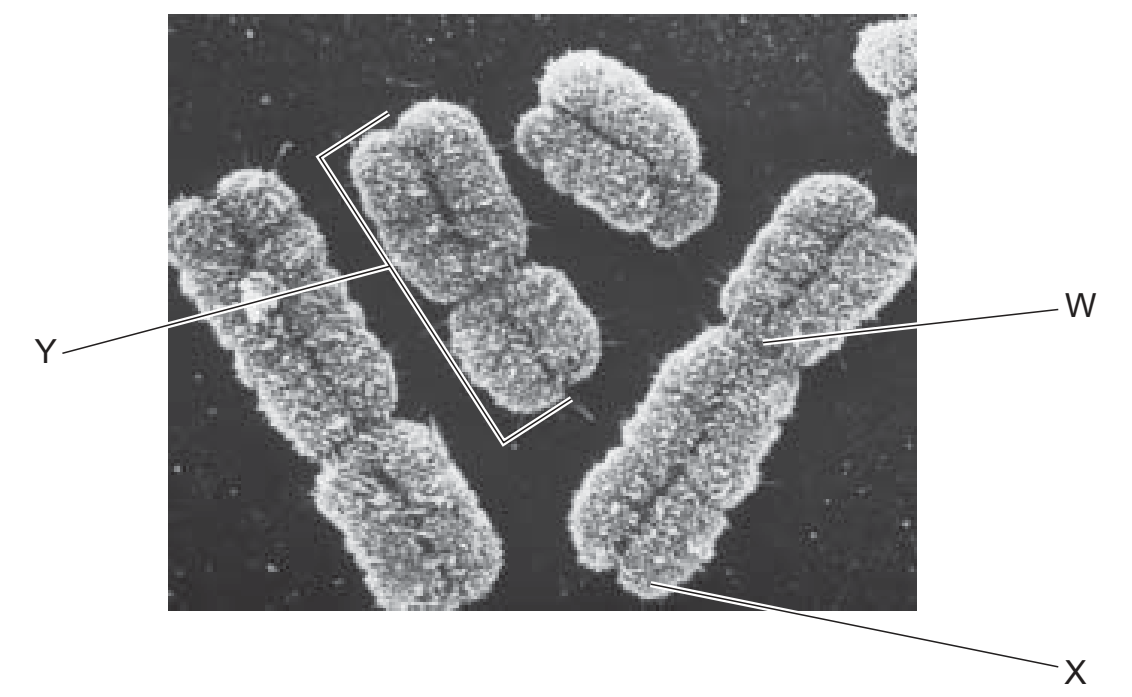
Which label is correct for each of the structures labelled W, X and Y?
| W | X | Y | |
| A B C D | centriole centriole centromere centromere | centromere centromere telomere telomere | chromatid microtubule chromatid microtubule |
C
Q23
Which statement about the behaviour of chromosomes during mitosis is correct?
A They attach to the spindle fibres to contain them within the nucleus.
B They condense to prevent further translation of genes.
C They reach the poles of the cell and begin to uncoil.
D They replicate to produce sufficient DNA to form two new nuclei.
C
Q24
Gene mutations can occur by substitution, deletion or insertion. What is the smallest part of a DNA molecule that can be changed by a gene mutation?
A base
B codon
C gene
D nucleotide
D
Q25
Which statements about mRNA are correct?
1 mRNA can form base pairs.
2 mRNA can form hydrogen bonds.
3 mRNA is single stranded.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
A
Q26
The table shows the role of four different proteins involved in DNA replication.
| protein | helicase | topoisomerase | single-strand binding protein | DNA polymerase |
| role | unwinds the parental DNA double helix | breaks and rejoins the DNA strands | binds to separated DNA strands to stabilise them | synthesises strand of DNA |
Which row shows the functions of these proteins?
| helicase | topoisomerase | single-strand binding protein | DNA polymerase | |
| A | adds DNA nucleotides to the 3′ end of a growing polynucleotide strand | prevents original strands re-forming complementary base pairs | enables tension caused by unwinding to be released | makes strands available as templates |
| B | enables tension caused by unwinding to be released | prevents original strands re-forming complementary base pairs | makes strands available as templates | adds DNA nucleotides to the 3c end of a growing polynucleotide strand |
| C | enables tension caused by unwinding to be released | makes strands available as templates | adds DNA nucleotides to the 3′ end of a growing polynucleotide strand | prevents original strands re-forming complementary base pairs |
| D | makes strands available as templates | enables tension caused by unwinding to be released | prevents original strands re-forming complementary base pairs | adds DNA nucleotides to the 3′ end of a growing polynucleotide strand |
D
Q27
Which type of sugar and which type of bond are found in a DNA molecule?
| type of sugar | type of bond | |
| A B C D | disaccharide disaccharide monosaccharide monosaccharide | glycosidic phosphodiester peptide hydrogen |
D
Q28
The diagrams represent transverse sections of three plant organs.
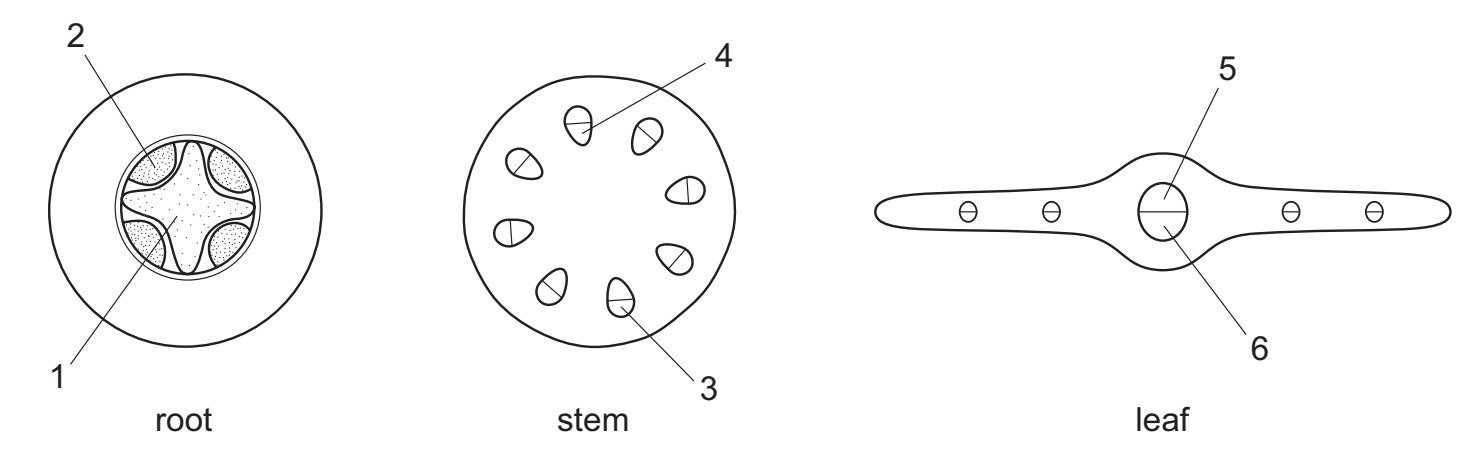
Which row is correct for phloem?
| ROOT | STEM | LEAF | |
| A B C D | 1 1 2 2 | 3 4 3 4 | 5 6 6 5 |
C
Q29
Sucrose moves from a phloem sieve tube element into a root cell. Which changes to the water potential and the volume of liquid in the phloem sieve tube element are correct?
| water potential | volume of liquid | |
| A B C D | becomes higher becomes higher becomes lower becomes lower | decreases increases decreases increases |
A

Q30
Which statements about water movement in plants are correct?
1 Water can pass through cell walls containing layers of cellulose fibres.
2 Water can pass through cell walls containing rings or spirals of lignin.
3 Water cannot pass through a band of suberin in cell walls.
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
A
Q31
The photomicrograph is a transverse section of a leaf.
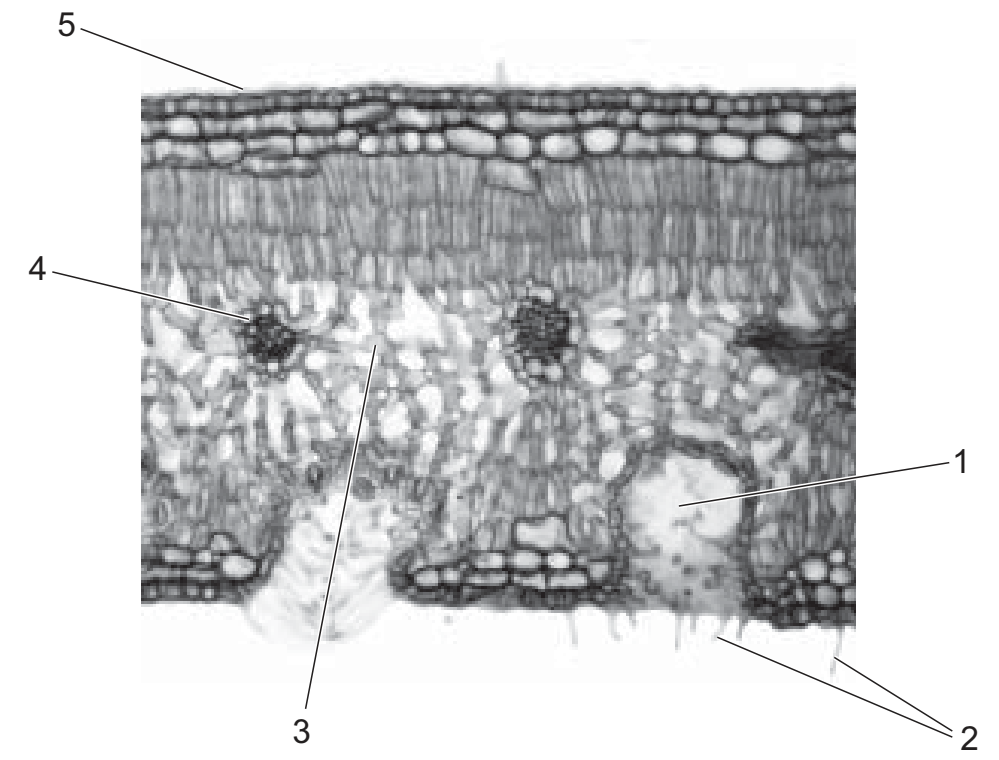
Which labelled features are characteristic adaptations of many xerophytes?
A 1, 3, 4 and 5
B 1, 2 and 3
C 1, 2 and 5
D 2, 3, 4 and 5
C
Q32
A maize crop is growing successfully in a field in which the water potential of the soil is –40 kPa.
What is the most likely water potential of the cell sap in the root hair cell?
A –60 kPa
B –40 kPa
C –20 kPa
D 0 kPa
A
The cytoplasm has more solutes (absorbed from the soil via active and passive transport). This lower water potential ensures that water in the soil moves into the root hair cells via osmosis.
Q33
The contraction of the heart is coordinated through electrical impulses passing through the cardiac muscle.
What is the correct order of part of the sequence of these impulses?
A right and left atria → sinoatrial node → atrioventricular node → ventricular walls
B sinoatrial node → right and left atria → atrioventricular node → Purkyne tissue
C sinoatrial node → right and left atria → Purkyne tissue → atrioventricular node
D right and left atria → sinoatrial node → Purkyne tissue → ventricular walls
B
Q34
Which features allow the aorta to withstand high blood pressures?
A collagen fibres and elastin fibres
B collagen fibres and smooth muscle
C elastin fibres and endothelium
D endothelium and smooth muscle
A
Collagen is protein molecules made up of amino acids. It provides structural support to the extracellular space of connective tissues. Due to its rigidity and resistance to stretching, it is the perfect matrix for skin, tendons, bones, and ligaments.
The main components of elastic fibers, elastin and fibrillin-containing microfibrils play a structural and mechanical role in the arteries and their essential function is to provide elasticity and resilience to the tissues.
Q35
Which row is correct for the pulmonary artery?
| blood carried | thickness of wall | lumen size | |
| A B C D | oxygenated oxygenated deoxygenated deoxygenated | thin thick thin thick | large small large small |
D
Q36
The graph shows oxygen dissociation curves of adult haemoglobin in different carbon dioxide concentrations, 1 and 2.
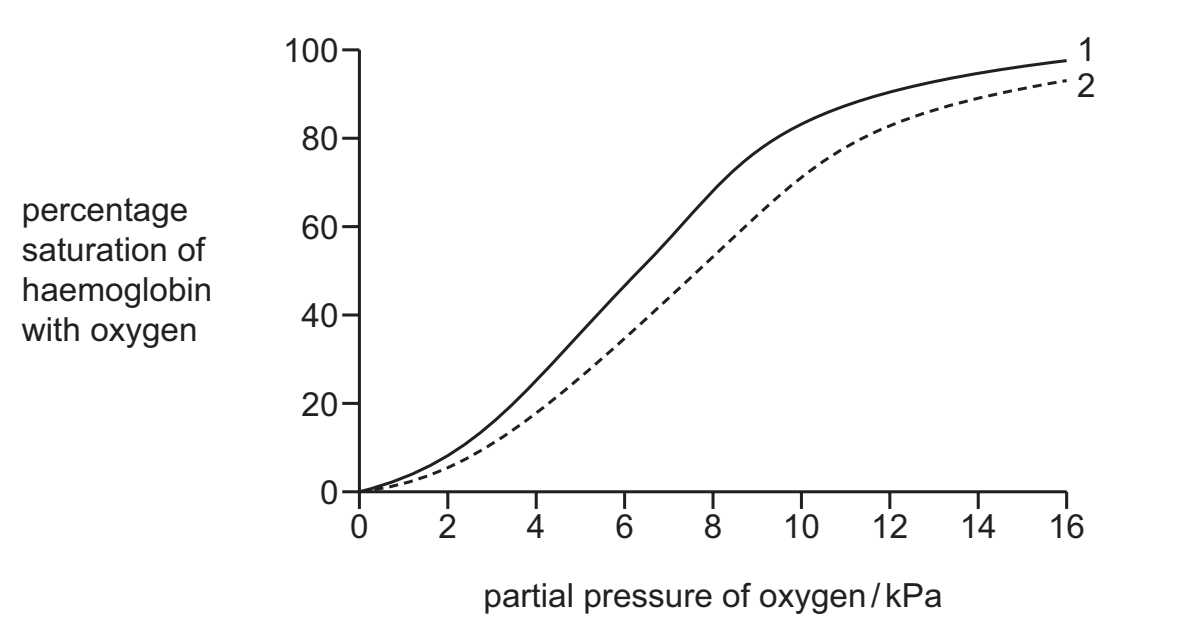
Which conditions could change the shape of curve 1 to the shape of curve 2?
A increased carbon dioxide concentration causing a decrease in pH
B increased carbon dioxide concentration causing an increase in pH
C decreased carbon dioxide concentration causing a decrease in pH
D decreased carbon dioxide concentration causing an increase in pH
A
Q37
What maintains the necessary concentration gradients for carbon dioxide and oxygen in the lungs?
A good ventilation of the lungs
B large surface area of the alveoli
C the capillaries are close to the walls of the alveoli
D the walls of the alveoli are thin
A
Q38
Which cells and tissues are present in the trachea?

B
Q39
The global mortality figures for some diseases in 2013 are shown in the table.
| cause of death | millions of deaths |
| HIV / AIDS TB malaria cholera | 1.50 1.40 1.03 0.02 |
How many millions of people died in 2013 from the bacterial diseases listed in the table?
A 0.02
B 1.42
C 2.45
D 2.90
B
(HIV and Malaria are not bacterial)
Q40
Why is it difficult for B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes to respond to the antigens on pathogens that are intracellular parasites?
A The antigens are constantly mutating.
B The antigens can destroy the lymphocytes.
C The lymphocytes do not encounter the antigens.
D The lymphocytes do not recognise the antigens.
C