10.01 Combustion, Oxidation, and Reduction
1. Combustion Reactions
Definition:
- Combustion is a chemical reaction where a substance reacts with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. It is an exothermic reaction.
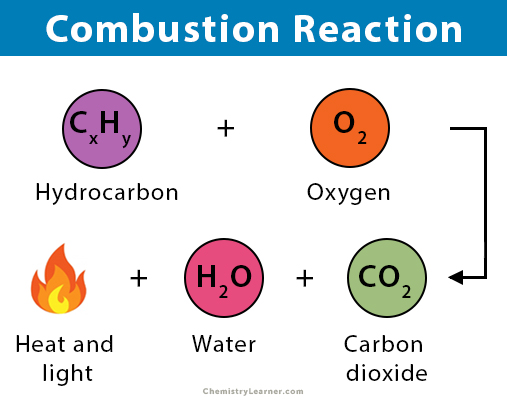
Characteristics of Combustion:
- Exothermic: Releases energy.
- Requires Oxygen: Oxygen is a key reactant.
- Produces Oxides: Typically carbon dioxide and water when hydrocarbons burn completely.
Common Combustion Reactions:
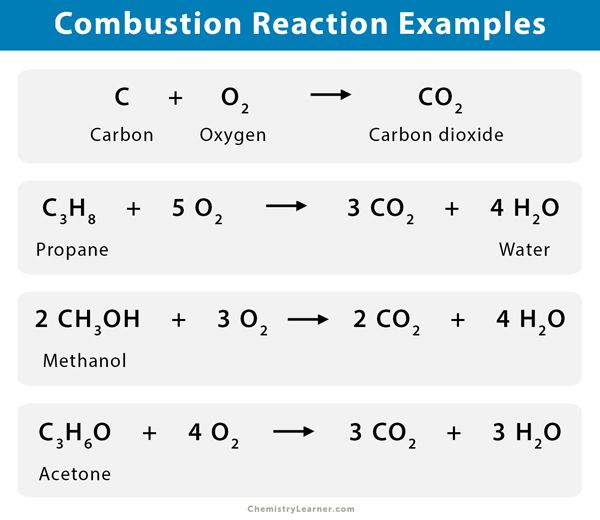
- Complete Combustion of Methane (Natural Gas):CH4(g)+2O2(g)→CO2(g)+2H2O(g)
- Methane (CH₄): Main component of natural gas.
- Products: Carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water vapor (H₂O).
- Combustion of Glucose in Respiration:C6H12O6(s)+6O2(g)→6CO2(g)+6H2O(l)+heat
- Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆): Derived from carbohydrates in food.
- Process: Respiration in biological cells.
- Products: Carbon dioxide, water, and energy (heat).
Key Terms:
- Fuel: A substance like methane that combusts readily, releasing significant energy.
2. Oxidation and Reduction (Redox) Reactions
Definitions:
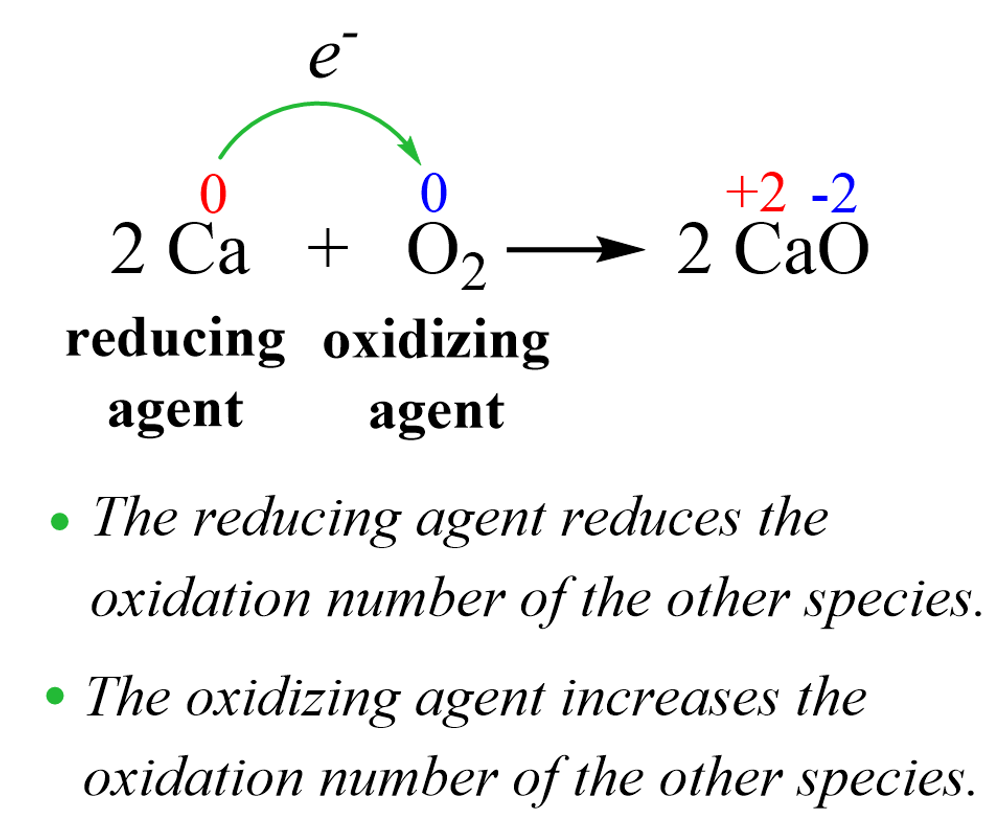
- Oxidation: Gain of oxygen or loss of electrons by a substance.
- Reduction: Loss of oxygen or gain of electrons by a substance.
- Redox Reaction: A reaction involving both oxidation and reduction.
Important Concepts:
- Oxidizing Agents: Substances that oxidize others and are themselves reduced (e.g., oxygen, hydrogen peroxide).
- Reducing Agents: Substances that reduce others and are themselves oxidized (e.g., hydrogen, carbon, carbon monoxide).
General Principles:
- Oxidation Never Occurs Alone: It is always paired with reduction.
- Electron Transfer: Oxidation involves loss of electrons; reduction involves gain of electrons.
Key Definitions:
- Redox Reaction: Reaction involving the transfer of electrons between two species, resulting in oxidation of one and reduction of the other.
3. Examples of Redox Reactions
Example A: Oxidation of Copper
- Reaction: 2Cu(s)+O2(g)→2CuO(s)
- Process:
- Oxidation: Copper (Cu) loses oxygen to form copper(II) oxide (CuO).
- Reduction: Oxygen gains electrons to form oxide ions.
Reverse Reaction: Reduction of Copper(II) Oxide
- Reaction: CuO(s)+H2(g)→Cu(s)+H2O(g)
- Process:
- Reduction: Copper(II) oxide loses oxygen to regenerate copper.
- Oxidation: Hydrogen gains oxygen to form water.
Example B: Reduction of Zinc Oxide by Carbon
- Reaction: ZnO(s)+C(s)→Zn(s)+CO(g)
- Process:
- Reduction: Zinc oxide loses oxygen to form zinc metal.
- Oxidation: Carbon gains oxygen to form carbon monoxide.
4. Industrial Importance of Redox Reactions
Extraction of Metals:
- Reduction of Metal Oxides:
- Example: Extraction of Iron from Hematite (Fe₂O₃) in a Blast Furnace:
- Reduction of Carbon Dioxide: CO2(g)+C(s)→2CO(g)
- Reduction of Iron(III) Oxide: Fe2O3(s)+3CO(g)→2Fe(s)+3CO2(g)
- Reducing Agents Used: Carbon, carbon monoxide.
- Example: Extraction of Iron from Hematite (Fe₂O₃) in a Blast Furnace:
- Extraction of Other Metals:
- Metals like Zinc, Lead, Copper: Extracted by reducing their oxides with carbon.
5. Everyday Oxidation Reactions
a. Corrosion:
- Definition: The chemical attack on metals by substances like oxygen and water.
- Example: Rusting of Iron:
4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) + 6H2O(l) → 4Fe(OH)3(s)- Product: Rust (Iron(III) oxide-hydroxide).
- Impact: Weakens structures like cars, railings, and bridges.
b. Rancidity:
- Definition: Oxidation of fats and oils in food, leading to unpleasant taste and smell.
- Prevention Methods:
- Adding antioxidants.
- Storing in refrigerators or airtight containers to slow oxidation.
6. Key Vocabulary
- Combustion: Chemical reaction with oxygen, releasing energy.
- Respiration: Biological combustion of glucose in cells to release energy.
- Redox Reaction: Involving both oxidation and reduction.
- Oxidizing Agent: Substance that causes another to oxidize, itself gets reduced.
- Reducing Agent: Substance that causes another to reduce, itself gets oxidized.
- Corrosion: Chemical degradation of metals due to reaction with environment.
- Rancid: Oxidized organic material, particularly fats and oils.
Examples:
1. Which of these reactions involve oxidation and reduction?
Reactions:
- A. Hexane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- B. Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide
- C. Calcium Carbonate → Calcium Oxide + Carbon Dioxide
- D. Magnesium + Copper(II) Oxide → Magnesium Oxide + Copper
- E. Hydrochloric Acid + Sodium Hydroxide → Sodium Chloride + Water
Answer:
- Reactions A, B, and D are redox reactions.
- A. Combustion of Hexane: Hydrocarbon oxidizes to CO₂ and H₂O.
- B. Magnesium Combustion: Magnesium oxidizes to MgO.
- D. Magnesium reducing Copper(II) Oxide: Magnesium reduces CuO to Cu while being oxidized to MgO.
- Reactions C and E are non-redox reactions:
- C. Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate: Thermal decomposition.
- E. Neutralization Reaction: Acid-base reaction without electron transfer.
2. Which of these reactions usually involve burning?
Answer:
- Reactions A and B involve burning:
- A. Combustion of Hexane is a typical burning process.
- B. Magnesium burning in oxygen is a combustion reaction.
3. What type of reaction has happened to the copper(II) oxide in equation D?
Equation D: Mg(s)+CuO(s)→MgO(s)+Cu(s)
Answer:
Mg acts as the reducing agent, getting oxidized to MgO.
Reduction Reaction:
Copper(II) Oxide (CuO) is reduced to Copper (Cu)
Quizzes
Quiz: Combustion and Redox Reactions
Your score: 0 / 10