02.02 Building Blocks of Life
Key Elements in Living Organisms:
- Four Main Elements (make up over 99% of atoms in all living organisms):
- Hydrogen (H)
- Carbon (C)
- Oxygen (O)
- Nitrogen (N)
Role of Carbon in Organic Molecules:
- Carbon’s Unique Bonding Ability:
- Can form long chains or rings by bonding with other carbon atoms.
- These structures act as carbon skeletons for organic molecules.
- Functional Groups:
- Other atoms/groups attach to carbon skeletons, allowing for functional diversity in molecules.
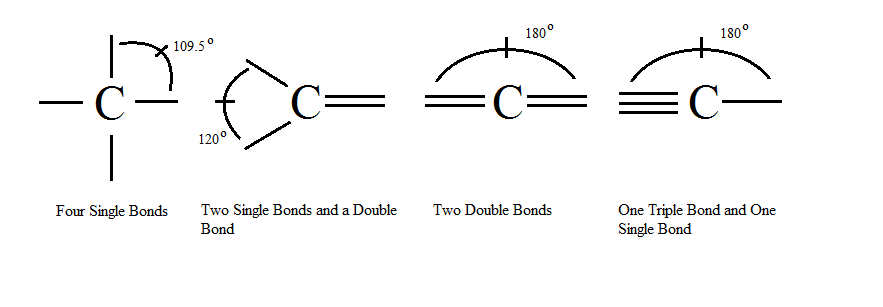
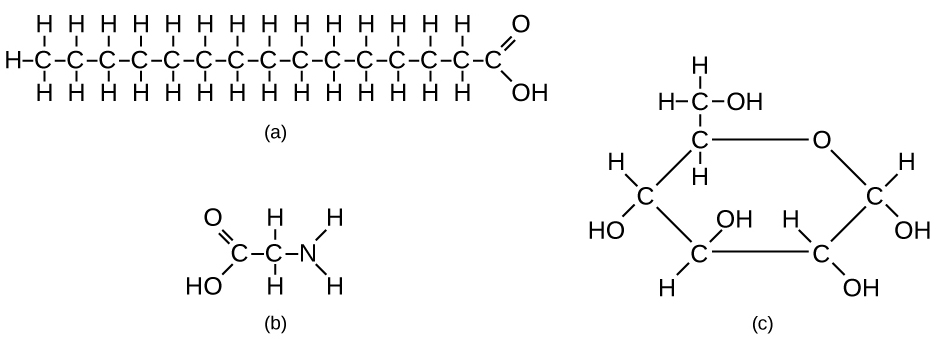
Types of Biological Molecules and Their Building Blocks:
- Simple Biological Molecules (serve as building blocks for complex molecules):
- Monosaccharides: Simple sugars (e.g., glucose), building blocks of polysaccharides.
- Amino Acids: Building blocks of proteins.
- Fatty Acids and Glycerol: Components of lipids.
- Nucleotides (Organic Bases): Contain nitrogenous bases, building blocks of nucleic acids.
Complex Biological Molecules (formed from simple molecules):
- Polysaccharides: Formed from chains of monosaccharides (e.g., starch, glycogen).
- Proteins: Made of amino acid chains; perform structural, enzymatic, and regulatory roles.
- Lipids: Formed from fatty acids and glycerol; function in energy storage and cell membrane structure.
- Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA): Composed of nucleotides; store and transmit genetic information.
Summary of Building Block Relationships:
- Monosaccharides ➔ Polysaccharides
- Amino Acids ➔ Proteins
- Fatty Acids + Glycerol ➔ Lipids
- Nucleotides ➔ Nucleic Acids
Practise Questions
Question 1
List the four main elements found in living organisms and briefly explain their significance. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Hydrogen (H): Found in water and organic molecules; crucial for energy transfer in cellular respiration. (1 mark)
- Carbon (C): Forms the backbone of organic molecules, capable of creating long chains and rings. (1 mark)
- Oxygen (O): Essential for cellular respiration and found in water, carbohydrates, and other organic molecules. (1 mark)
- Nitrogen (N): Found in amino acids and nucleotides, crucial for protein and nucleic acid synthesis. (1 mark)
- These elements make up over 99% of atoms in living organisms, forming the basis of life. (1 mark)
Question 2
Explain why carbon is central to the structure of organic molecules. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Carbon has four valence electrons, allowing it to form four covalent bonds. (1 mark)
- It can bond with other carbon atoms to form long chains or rings, creating diverse structures. (1 mark)
- These chains and rings act as carbon skeletons for organic molecules. (1 mark)
- Functional groups attach to carbon skeletons, providing chemical diversity and reactivity. (1 mark)
- Carbon’s versatility makes it the foundation of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. (1 mark)
Question 3
Describe the relationship between simple and complex biological molecules, providing examples. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Simple molecules act as building blocks for complex biological molecules. (1 mark)
- Monosaccharides (e.g., glucose) combine to form polysaccharides (e.g., starch, glycogen). (1 mark)
- Amino acids link via peptide bonds to form proteins, which perform structural and enzymatic roles. (1 mark)
- Fatty acids and glycerol join to form lipids, key for energy storage and membrane structure. (1 mark)
- Nucleotides, which contain nitrogenous bases, form nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) that store genetic information. (1 mark)
- This hierarchical structure underpins the complexity of biological systems. (1 mark)
Question 4
How do monosaccharides serve as building blocks for polysaccharides? Provide an example. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Monosaccharides are simple sugars (e.g., glucose) with the general formula (CH₂O)ₙ. (1 mark)
- They join via glycosidic bonds through condensation reactions. (1 mark)
- Chains of monosaccharides form polysaccharides like starch in plants or glycogen in animals. (1 mark)
- Polysaccharides serve as energy storage molecules or structural components (e.g., cellulose in plant cell walls). (1 mark)
- Example: Glucose units combine to form starch, a key energy reserve in plants. (1 mark)
Question 5
Outline the role of amino acids and how they form proteins. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Amino acids are the monomers of proteins, each containing an amino group (-NH₂), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a variable R group. (1 mark)
- Amino acids link via peptide bonds formed in condensation reactions. (1 mark)
- Chains of amino acids fold into specific 3D structures, forming proteins. (1 mark)
- Proteins perform various roles, including structural (e.g., collagen), enzymatic (e.g., amylase), and regulatory (e.g., insulin). (1 mark)
- The sequence of amino acids determines the protein’s function and specificity. (1 mark)
Question 6
Describe the structure and function of nucleotides in forming nucleic acids. (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Nucleotides are the monomers of nucleic acids and consist of three parts:
- A phosphate group.
- A pentose sugar (ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA).
- A nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil). (1 mark)
- Nucleotides link via phosphodiester bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of another. (1 mark)
- This linkage forms a sugar-phosphate backbone in nucleic acids. (1 mark)
- DNA stores genetic information, while RNA plays roles in protein synthesis. (1 mark)
- The nitrogenous bases pair via hydrogen bonds (A-T, C-G in DNA) to form the double-helix structure. (1 mark)
- Example: ATP (a modified nucleotide) acts as an energy carrier in cells. (1 mark)
Question 7
Explain the role of fatty acids and glycerol in forming lipids. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Fatty acids consist of a hydrocarbon chain and a carboxyl group (-COOH), while glycerol is a 3-carbon alcohol with hydroxyl groups (-OH). (1 mark)
- Lipids are formed by condensation reactions, creating ester bonds between fatty acids and glycerol. (1 mark)
- Triglycerides (three fatty acids + glycerol) function as energy storage molecules. (1 mark)
- Phospholipids (two fatty acids + glycerol + phosphate group) form the structural basis of cell membranes. (1 mark)
- Lipids are hydrophobic, playing a key role in forming barriers that separate cellular environments. (1 mark)
Question 8
Discuss the importance of nitrogen in biological molecules. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Nitrogen is a key component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. (1 mark)
- It is also found in nucleotides, which make up DNA and RNA. (1 mark)
- Nitrogen is essential for the synthesis of nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, etc.), crucial for genetic information storage. (1 mark)
- It is a component of chlorophyll, vital for photosynthesis in plants. (1 mark)
- Nitrogen availability affects the production of proteins and nucleic acids, influencing growth and reproduction. (1 mark)
Question 9
Summarize the relationship between carbon skeletons and functional groups in organic molecules. (5 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Carbon skeletons form the backbone of organic molecules, consisting of chains or rings of carbon atoms. (1 mark)
- Functional groups, such as hydroxyl (-OH), carboxyl (-COOH), and amino (-NH₂), attach to carbon skeletons. (1 mark)
- These groups determine the chemical properties and reactivity of the molecule. (1 mark)
- Example: The carboxyl group makes fatty acids acidic, while the amino group allows amino acids to form peptide bonds. (1 mark)
- This diversity enables carbon-based molecules to perform various biological functions, including energy storage and enzymatic activity. (1 mark)
Question 10
What is the significance of chemical evolution in the origin of life? (6 marks)
Mark Scheme:
- Chemical evolution hypothesizes that simple carbon-based molecules formed before life began. (1 mark)
- These molecules combined to create more complex organic compounds, acting as building blocks for life. (1 mark)
- Example: Monosaccharides, amino acids, and nucleotides formed polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids, respectively. (1 mark)
- Functional groups added diversity, enabling molecules to interact and catalyze reactions. (1 mark)
- Chemical evolution provided the foundation for biological molecules essential for metabolism, reproduction, and cellular structure. (1 mark)
- This process is believed to have led to the first self-replicating systems, a key step in the origin of life. (1 mark)