01.10 Past Paper Questions
Question 1
The table shows some properties of the Group I metals.
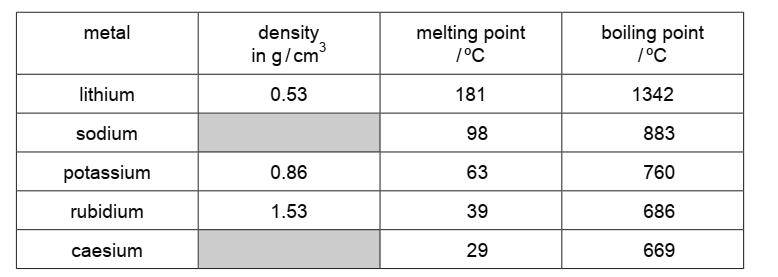
(a)(i) Describe the trend in boiling points of the Group I metals. [1 mark]
Answer:
The boiling points decrease down Group I metals.
Explanation:
- Trend Observation: As you move from lithium to caesium in Group I, the boiling points decrease as follows: Lithium (1342 °C) > Sodium (883 °C) > Potassium (760 °C) > Rubidium (686 °C) > Caesium (669 °C).
- Reason: This decrease occurs because the metallic bonding becomes weaker with increasing atomic size and decreasing ionization energy down the group. Larger atoms have their outer electrons further from the nucleus and are less tightly held, requiring less energy (lower temperature) to transition into the gaseous state.
(a)(ii) Predict the density of caesium. [1 mark]
Answer:
The density of caesium is 1.88 g/cm³ (range: 1.60–2.50 g/cm³).
Explanation:
Reasoning: Although atomic size increases down the group, the effect of higher atomic mass predominates, resulting in higher densities. The provided range (1.60–2.50 g/cm³) accounts for possible variations and measurement uncertainties.
Trend Consideration: Density generally increases down Group I due to the increase in atomic mass.
(a)(iii) Deduce the state of caesium at 20 °C. Explain your answer. [2 marks]
Answer:
Caesium is a solid at 20 °C.
Explanation:
Melting Point Consideration: The melting point of caesium is 28 °C.
Temperature Comparison: Since 20 °C is below the melting point, caesium remains in the solid state at this temperature.
Conclusion: Therefore, at 20 °C, caesium does not have enough thermal energy to overcome the forces holding its solid structure, and it remains solid.
(b) Complete the word equation for the reaction of rubidium with water. [2 marks]
Answer:
Rubidium + Water → Rubidium Hydroxide + Hydrogen Gas
Explanation:
- Reaction Type: Rubidium, an alkali metal, reacts with water in a single displacement reaction.
Products Formed:
- Rubidium Hydroxide (RbOH): A strong base formed from the reaction between rubidium and water.
- Hydrogen Gas (H₂): Released as a result of the reaction.
- Overall Reaction: This reaction is highly exothermic and vigorous, characteristic of Group I metals reacting with water.
(c) The dye, indigotin, is formed when compound F is exposed to air. The structure of compound F is shown below.
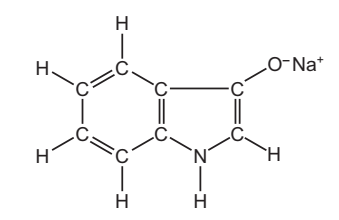
Complete the table and calculate the relative molecular mass of compound F. [2 marks]
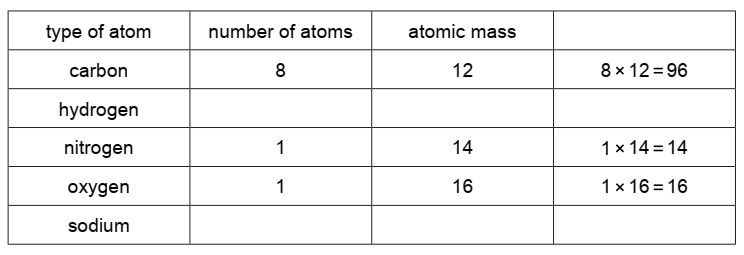
Calculation:
- Carbon: 8 atoms × 12 g/mol = 96 g/mol
- Hydrogen: 6 atoms × 1 g/mol = 6 g/mol
- Nitrogen: 1 atom × 14 g/mol = 14 g/mol
- Oxygen: 1 atom × 16 g/mol = 16 g/mol
- Sodium: 1 atom × 23 g/mol = 23 g/mol
Total Relative Molecular Mass = 96 + 6 + 14 + 16 + 23 = 155 g/mol
(d) Three dye mixtures, J, K and L, were spotted onto a piece of chromatography paper. Three pure dyes, X, Y and Z, were also spotted onto the same piece of paper. The diagram shows the results of this chromatography.
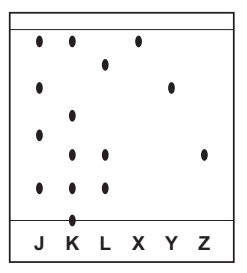
(d)(i) Suggest why the baseline was drawn in pencil and not in ink. [1 mark]
Answer:
The baseline was drawn in pencil because pencil marks do not smear or dissolve during chromatography, ensuring a clear and stable starting point for dye separation.
Explanation:
- Ink Solubility: Ink is soluble in many chromatography solvents and would spread or dissolve, interfering with the separation process.
- Pencil Stability: Graphite from pencil is insoluble in the solvents used, maintaining a sharp and precise baseline where the dyes can be applied without distortion.
(d)(ii) Which dye mixture, J, K or L, contains a dye which did not move during this chromatography? [1 mark]
Answer:
Mixture K contains a dye that did not move during chromatography.
Explanation:
- Observation from Diagram: In the chromatography results, Mixture K shows a spot that remains at the origin (baseline), indicating that this particular dye did not migrate with the solvent front.
(d)(iii) Which dye mixture, J, K or L, contains both dye X and dye Y? [1 mark]
Answer:
Mixture J contains both dye X and dye Y.
Explanation:
- Chromatography Result: Mixture J exhibits two distinct spots corresponding to dyes X and Y, demonstrating that it contains both dyes.
(d)(iv) Which dye mixture, J, K or L, does not contain dye Z? [1 mark]
Answer:
Mixture J does not contain dye Z.
Explanation:
- Chromatography Result: Mixture J lacks the spot corresponding to dye Z, indicating that this mixture does not include dye Z.
Question 2